-Study of Animal Type-Cockroach
Maharashtra Board-Class-11-Science-Biology-Chapter-11
Solution
Question 1.
Choose correct option
(A) Chemical nature of chitin is .............
(a) protein.
(b) carbohydrate.
(c) lipid.
(d) glycoprotein.
(b) carbohydrate.
(B) Cockroach has ................ type of mouthparts.
(a) sponging
(b) chewing and biting
(c) piercing and Sucking
(d) lapping
(b) chewing and biting
(C) Spiracle is a part of ................ system of cockroach.
(a) circulatory
(b) respiration
(c) reproductive
(d) nervous
(b) respiration
(D) ................... is a part of digestive system.
(a) Trachea
(b) Hypopharynx
(c) Haemocyte
(d) Seminal vesicle
(b) Hypopharynx
(E) ..................... is also called as brain of cockroach.
(a) Supra-oesophageal ganglion
(b) Sub-oesophageal ganglion
(c) Hypo-cerebral ganglion
(d) Thoracic ganglion
(a) Supra-oesophageal ganglion
Question 2.
Answer the following questions
(A) Describe the digestive system of cockroach.
Digestive System of Cockroach : Digestive system of cockroach consists of mouthparts, alimentary canal and salivary glands. Mouth parts : Pre-oral cavity present in front of the mouth receives food. It is bounded by chewing and biting type of mouth parts. These are movable, segmented appendages that help in ingestion of food. The mouthparts of cockroach comprises of: Labrum: It forms the upper lip. It is a single flap-like movable part which covers the mouth from upper side. It forms an anterior wall of pre-oral cavity. Mandibles: These are two dark, hard, chitinous structures with serrated median margins. They are true jaws present on either side, behind the labrum. Maxillae: These are the accesssory jaws. They are also called as first pair of maxillae. These are situated on the either side of mouth behind the mandibles. Each maxilla consists of sclerites like cardo, stipes, galea, lacinia and maxillary palps. Labium: It forms the lower lip. Labium is also known as second maxilla which covers the pre-oral cavity from the ventral side. It is firmly attached to the posterior part of head. It has three jointed labial palps which are sensory in function. Hypopharynx : Hypopharynx / tongue / lingua is a somewhat cylindrical single structure, located in front of the labium and between first maxillae. A salivary duct opens at the base of Hypopharynx. Hypopharynx bears comb-like plates called super-lingua on either side. Alimentary canal: It is long (6 - 7cm) tube of different diameters and two openings Cockroach does not have the buccal cavity thus, the alimentary canal begins from pre-oral cavity The alimentary canal is divisible into three parts: foregut, midgut and hindgut. (i) Foregut or stomodaeum : It consists of pharynx, oesophagus, crop and gizzard. (ii) Midgut or mesenteron: It consists of stomach and hepatic caeca. (iii) Hindgut or proctodaeum : It consists of ileum, colon and rectum. Salivary glands:
(B) Give an account on tracheal system of cockroach?
Respiratory System or Tracheal System : Cockroaches have an internal respiratory system of air tubes called the tracheal system, which brings air into the body and makes contact with every pan. It enables direct gas exchange between air and tissues without the use of blood. These air tubes of internal respiratory system begin at the opening on body surface called spiracles. Tracheoles : These are fine intracellular tubes that penetrate deep into tissues. They are thin and not lined by chitin. They end blindly in the cells. Each tracheole at the blind end is filled with a watery fluid through which exchange of gases takes place. The content of the fluid keeps changing. At high muscular activity, part of fluid part is drawn into the tissues to enable more and rapid oxygen intake. 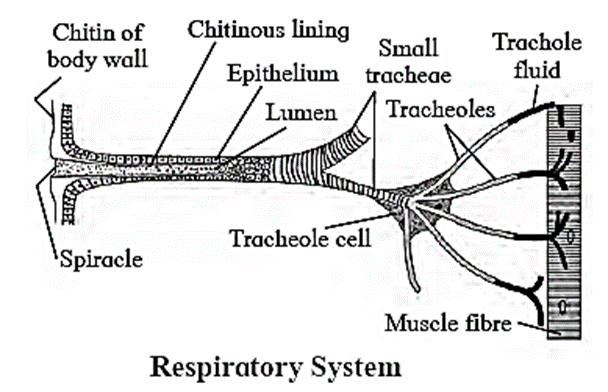
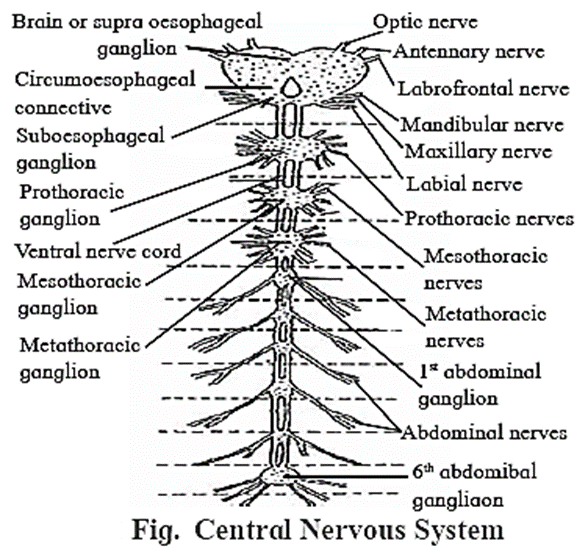
(C) Describe nervous system of cockroach.
Nervous System : Nervous system of cockroach is ventral, solid and ganglionated. It consists of central nervous system (CNS), peripheral nervous system (PNS) and autonomous nervous system (ANS). Central nervous system (CNS): Central nervous system consists of (1) nerve ring and (2) ventral nerve cord. (1) Nerve ring consists of: (i) Supra-oesophageal ganglia or cerebral ganglia : A pair of supra-oesophageal ganglia is collectively known as the brain. Brain is present in head, above the oesophagus and between antennal bases. Each supra-oesophageal ganglion is formed by the fusion of three small ganglia - protocerebrum, deutocerebmm and tritocerebrum. (ii) Circum-oesophageal connectives: Supra-oesophageal ganglia are connected to sub-oesophageal ganglion by a pair of lateral nerves called as circum-oesophageal connectives. Connectives arise from supra-oesophagial ganglia. (iii) Sub-oesophageal ganglia: It is a bilobed and present below the 0esophagus, in head. It is also formed by the fusion of three pairs of ganglia. (2) Ventral nerve cord : Peripheral nervous system (PNS): Autonomic nervous system (ANS): It consists of four ganglia and a retro cerebral complex. The ganglia are as follows:
(D) With help of neat labelled diagram, describe female reproductive system of cockroach.
Female reproductive system : In females, the 7th sternum is boat shaped and together with 8th and 9th sternum forms a brood or genital pouch whose anterior pan contains gonopore, spennathecal pores and collateral glands. 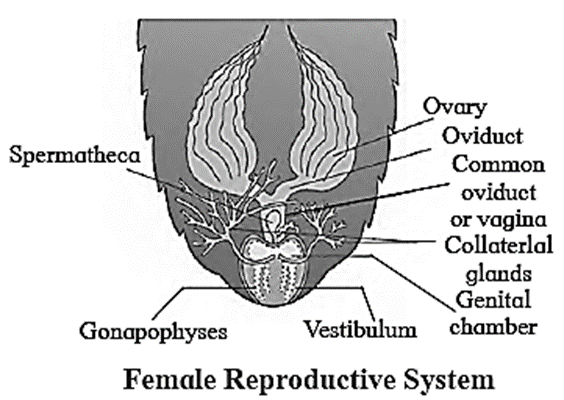
(E) With help of neat labelled diagram, describe the digestive system of cockroach.
Digestive System of Cockroach : Digestive system of cockroach consists of mouthparts, alimentary canal and salivary glands. Mouth parts : Pre-oral cavity present in front of the mouth receives food. It is bounded by chewing and biting type of mouth parts. These are movable, segmented appendages that help in ingestion of food. Alimentary canal: It is long (6 - 7cm) tube of different diameters and two openings Cockroach does not have the buccal cavity thus, the alimentary canal begins from pre-oral cavity. The alimentary canal is divisible into three parts: foregut, midgut and hindgut. Salivary glands: [Also refer Q.2(A)] 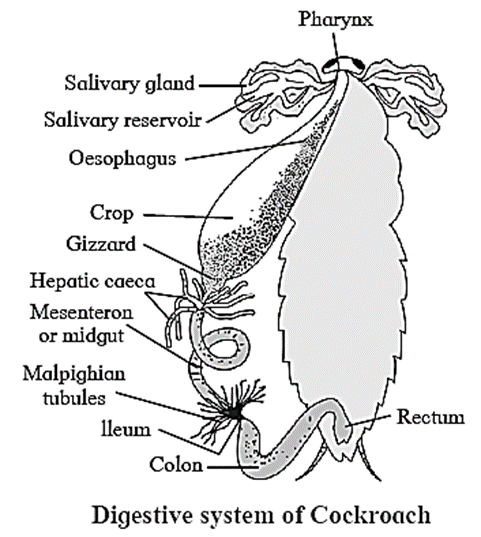
(F) A student observed that the cockroaches are killed for dissection by simply putting them in soap water. He inquired whether soap is so poisonous. Teacher said it is due to its peculiar respiratory system. How?
When cockroaches are immersed in soap solution, the solution enters their bodies through small respiratory openings known as spiracles. As a result, cockroaches may be unable to breathe and may suffocate.
(G) Describe the circulatory system of cockroach.
Circulatory System or Blood Vascular System : Cockroach has open circulatory system. It consists of colourless blood (haemolymph), a dorsal blood vessel (heart and dorsal aorta) and haemocoel. Haemolymph: Haemolymph is colourless as it is without any pigment. It consists of plasma and seven types of blood cells/haemocytes. Plasma consists of water with some dissolved organic and inorganic solutes. It is rich in nutrients and nitrogenous wastes like uric acid. Haemocoel: The body cavity of cockroach (haemocoel) can be divided into three sinuses due to two diaphragms i.e. dorsal and ventral diaphragm. These diaphragms are thin, fibromuscular septa (sing.septum). It remains attached to terga along lateral sides at intermittent points. (i) Dorsal diaphragm : It has 12 pairs (10 abdominal and 2 thoracic) of fan-like alary muscles. Alary muscles are triangular with pointed end attached to terga at lateral side and broad end lies between the heart and dorsal diaphragm. (ii) Ventral diaphragm: It is flat and present just above the ventral nerve cord. Laterally, it is attached to stema at intermittent points. (iii) Sinuses: The coelom of cockroach is divided into three sinuses — pericardial sinus, perivisceral sinus and perineural sinus. Dorsal blood vessel : This is present in pericardial sinus, just below the tergum. It is divisible into posterior heart and anterior aorta (dorsal aorta/cephalic vessel). _ . Anterior aorta : Heart is continued by a short, thin-walled vessel called dorsal aorta. It lies in head region and opens in haemocoel.

Question 3.
Answer the following questions
(A) How will you identify male or female cockroach?
Male cockroach
Female cockroach
Abdomen is relatively long and narrow
Abdomen is shod and broad
7th tergum covers 8th tergum
7th tergum covers 8th and 9th terga
Antennae are longer in size
Antennae are shorter in size
Anal styles are present
Anal styles are absent
Brood pouch is absent
Brood pouch is present
All 9 stema visible
Only 7 sterna visible
(B) Write a note on : Gizzard of cockroach.
Gizzard: Gizzard or proventriculus is a small spherical organ. It is provided internally with a circlet of six chitinous teeth and backwardly directed bristles. The foregut ends with gizzard. Function: The chitinous teeth present in gizzard are responsible for crushing the food and the bristles help to filter the food.
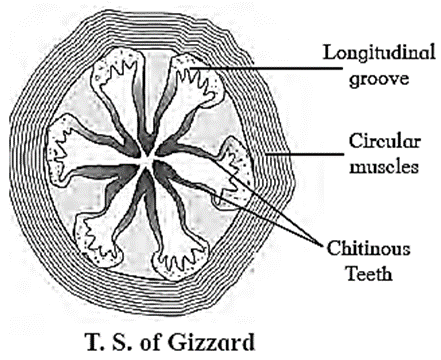
(C) Give the systematic position of cockroach.
Systematic Position :
Classification
Reason
Kingdom : Animalia
Cell wall absent, heterotrophic nutrition.)
Phylym : Arthropoda
Jointed appendages are present, segmented body, chitinous exoskeleton.
Class : Insecta
Two pairs of wings and three pairs of walking legs are present.
Genus : Periplaneta
Nocturnal, straight wings.
Species : americana
Origin is in Continent of America
(D) What would have happened if cockroach did not had gizzard?
(E) What is the functional difference between eyes of cockroach and human being?
(F) What is the functional difference between respiratory systems of cockroach and human being?
Question 4.
Explain the following in short
(A) What are anal cerci?
Anal cerci are a pair of appendages at the end of the abdomen that arise from the 10th segment of the body of cockroach.
(B) What is the ganglion?
Ganglion is a group of nerve cell bodies.
(C) What is the role of hypopharynx?
Hypopharynx : Hypopharynx / tongue / lingua is a somewhat cylindrical single structure, located in front of the labium and between first maxillae. A salivary duct opens at the base of Hypopharynx. Hypopharynx bears comb-like plates called super-lingua on either side. Hypopharynx is useful in the process of feeding and mixing saliva with food.
(D) What is mesenteron?
Midgut or mesenteron: It consists of stomach and hepatic caeca.
(E) Location of turgum.
(F) What is ootheca?
Ootheca :
(G) How many chambers are present in heart of cockroach?
13 chambers are present in heart of a cockroach, out of which 10 chambers are in abdominal region and three are in thoracic region.
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 11th-Biology – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-10- Animal Tissues – Online Solution
Next Chapter : Chapter-12-Photosynthesis – Online Solution
We reply to valid query.