Amines
Maharashtra Board-Class-12-Chemistry-Chapter-13
Solutions
Question 1. Choose the most correct option.
(i) The hybridisation of nitrogen in primary amine is ............
(a) sp
(b) sp2
(c) sp3
(d) sp3d
(c) sp3
(ii) Isobutylamine is an example of ............
(a) 2° amine
(b) 3° amine
(c) 1° amine
(d) quaternary ammonium salt.
(c) 1° amine Explanation: The general formula for isobutylamine is (CH3)2-CH-CH2-NH2. It is an ammonia derivative where the ammonia's solitary hydrogen atom is replaced with an isobutyl group. Therefore, in addition to the two N - H bonds that are present and belong to a primary amine, isobutylamine also contains a secondary carbon atom.
(iii) Which one of the following compounds has the highest boiling point ?
(a) n-Butylamine
(b) sec-Butylamine
(c) isobutylamine
(d) tert-Butylamine
(a) n-Butylamine
(iv) Which of the following has the highest basic strength ?
(a) Trimethylamine
(b) Methylamine
(c) Ammonia
(d) Dimethylamine
(d) Dimethylamine
(v) Which type of amine does produce N2 when treated with HNO2 ?
(a) Primary amine
(b) Secondary amine
(c) Tertiary amine
(d) Both primary and secondary amines
(a) Primary amine
(vi) Carbylamine test is given by
(a) Primary amine
(b) Secondary amine
(c) Tertiary amine
(d) Both secondary and tertiary amines
(a) Primary amine
(vii) Which one of the following compounds does not react with acetyl chloride ?
(a) CH3-CH2-NH2
(b) (CH3-CH2)2NH
(c) (CH3-CH2)3N
(d) C6H5-NH2
(c) (CH3-CH2)3N
(viii) Which of the following compounds will dissolve in aqueous NaOH after undergoing reaction with Hinsberg reagent ?
(a) Ethylamine
(b) Triethylamine
(c) Trimethylamine
(d) Diethylamine
(a) Ethylamine
(ix) Identify ‘B’ in the following reactions
CH3-C≡N \(\frac{Na}{C_2H_5OH}>\) A \(\frac{NaNO_2}{dil.HCL}>\) B
(a) CH3-CH2-NH2
(b) CH3-CH2-NO2
(c) CH3-CH2N2+Cl-
(d) CH3-CH2-OH
(d) CH3-CH2-OH
(x) Which of the following compounds contains azo linkage ?
(a) Hydrazine
(b) p-Hydroxyazobenzene
(c) N-Nitrosodiethylamine
(d) Ethylenediamine
(b) p-Hydroxyazobenzene
Question 2. Answer in one sentence.
(i) Write reaction of p-toluene sulfonyl chloride with diethylamine.
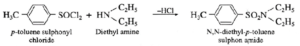
(ii) How many moles of methylbromide are required to convert ethanamine to N, N-dimethyl ethanamine ?
2 moles of methyl bromide are required to convert ethanamine to N,N-dimethyl ethanamine.
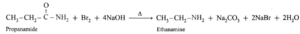
(iii) Which amide does produce ethanamine by Hofmann bromamide degradation reaction?
Propanamide (C2H5CONH2) produces ethanamine by Hofmann bromamide degradation reaction. When propanamide is treated with bromine and aqueous or alcoholic sodium hydroxide, ethanamine is obtained which has one carbon atom less.
(iv) Write the order of basicity of aliphatic alkylamine in gaseous phase.
The order of basicity of aliphatic alkyl amines in the gaseous follows the order : tertiary amine > secondary amine > primary amine > NH3.
(v) Why are primary aliphatic amines stronger bases than ammonia ?
The alkyl group in primary amines has + I effect i.e. (electron releasing). The alkyl group tends to increase the electron density on the nitrogen atom. As a result, amines can donate the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen more easily than ammonia. The amine being a base, can donate a pair of electrons to an acid. The alkyl group with + I effect will disperse the positive charge on the cation more than ammonia. Due to + I effect of alkyl group cation formed by primary amine is more stable compared to cation formed from ammonia. Also it is seen that observed increasing basic strength from ammonia to primary amine is explained on the basis of increased stabilization of conjugate acids by + I effect for the presence of alkyl (R) groups. Hence, primary or aliphatic amine is a stronger base than ammonia.
![]()

(vi) Predict the product of the following reaction. Nitrobenzene \(\underrightarrow{Sn/Conc.HCl}\)?
The product is aniline/
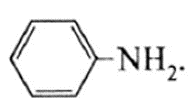
(vii) Write the IUPAC name of benzylamine.
The IUPAC name is Phenylmethanamine.
(viii) Arrange the following amines in an increasing order of boiling points.
n-propylamine, ethylmethyl amine, trimethylamine.
Amines in an increasing order of boiling points : trimethyl amine, ethyl methyl amine, n-propyl amine.
(ix) Write the balanced chemical equations for the action of dil H2SO4 on diethylamine.
2(C2H3)2NH + H2SO4 → [(C2H5)2N+H2]2SO2- Diethyl amine diethylammonium sulphate
(x) Arrange the following amines in the increasing order of their pKb values. Aniline, Cyclohexylamine, 4-Nitroaniline
Cyclohexyl amine (pKb 3.34), aniline (pKb 9.13) 4-nitroaniline (pKb 12.99).
Question 3. Answer the following
(i) Identify A and B in the following reactions.
![]()
(A) C6H5CH2CN phenyl acetonitrile (B) C6H5CH2-CH2-NH2 ß-phenyl ethyl amine
(ii) Explain the basic nature of amines with suitable example.
The basic nature of amines is due to presence of a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. Lewis theory : Amines are bases because they can share a lone pair of electrons on ‘N’ atom with an electron deficient species. Example : Trimethylamine shares its lone pair of electrons with the electron deficient boron trifluoride. Basic strength of aliphatic amines : Basic strength of amines is expressed quantitatively as Kb or pKb value. In terms of Lowry-Bronsted theory, the basic nature of amines is explained by writing the following equilibrium.
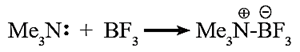
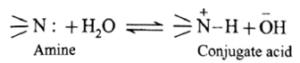
![]()
(iii) What is diazotisation ? Write diazotization reaction of aniline.
Diazotisation : The conversion of primary aromatic amine into diazonium salts is called diazotisation. Aniline reacts with nitrous acid in cold to form diazonium salt which has reasonable solubility at 273 K.

(iv) Write reaction to convert acetic acid into methylamine.
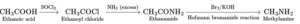
(v) Write a short note on coupling reactions.
Examples : (a) Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with alkaline solution of phenol to give p-hydroxy azo benzene (orange dye). (b) Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with aniline in mild alkaline medium to give p-aminobenzene (yellow dye).
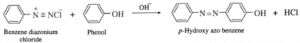
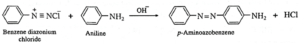
(vi) Explain Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
This method is used for the synthesis of primary amine. It involves the following three stages.
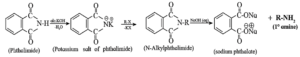
(vii) Explain carbylamine reaction with suitable examples.
Aliphatic or aromatic primary amines on heating with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide solution form carbyl amines or alkyl/aryl isocyanides with extremely unpleasant (foul) smell. This reaction is a test for primary amines. Secondary and tertiary amines do not give this test. Example :

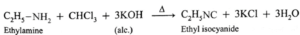
(viii) Write reaction to convert
(i) methanamine into ethanamine
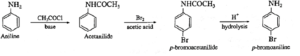
(ii) Aniline into p-bromoaniline.
(i) methanamine into ethanamine : (ii) Aniline into p-bromoaniline :
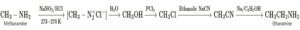
(ix) Complete the following reactions :
(a) C6H5N2+Cl- + C2H5OH → ?
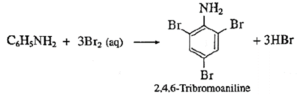
(b) C6H5NH2 + Br2(aq) → ?
(a) C6H5N2+Cl- + C2H5OH → C6H5-N=N-CH2-CH2-OH + HCl (b)
(x) Explain Ammonolysis of alkyl halides.
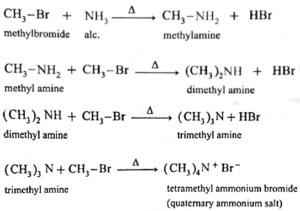
(xi) Write reaction to convert ethylamine into methylamine.

Question 4. Answer the following.
(i) Write the IUPAC names of the following amines :
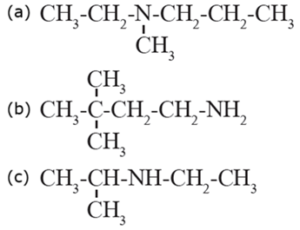
(a) N-Ethyl, N-methyl propan-1-amine (b) 3, 3-Dimethylbutan-1-amine (c) N-Ethyl propan-2-amine
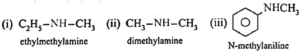
(ii) What are amines ? How are they classified ?
Amines : The alkyl or aryl derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all the three hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen are replaced by same or different alkyl or aryl groups are called amines. OR Amines are nitrogen containing organic compounds having basic character. Example : methyl amine : CH3-NH2 Classification of amines : Primary amines (1° amines) : The amines in which only one hydrogen atom of ammonia is replaced by an alkyl group or aryl group are called primary (1°) amines. Examples : Secondary amines (2° amines) : The amines in which two hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by two, same or different alkyl or aryl groups are called secondary (2°) amines. Examples : Tertiary amines (3° amines) : The amines in which all the three hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by three same or different alkyl or aryl groups are called tertiary (3°) amines. Examples : Secondary and tertiary amines are further classified as (i) simple / symmetrical amines and (ii) mixed / unsymmetrical amines. (i) Simple or symmetrical amines : When all the alkyl or aryl groups on nitrogen are same, it is a simple amine. Examples : (ii) Mixed or unsymmetrical amines : When all the alkyl or aryl groups on nitrogen are different, then the amine is a mixed amine. Examples : Amines are also divided into two major classes, namely, aliphatic and aromatic amines on the basis of nature of the groups attached to the nitrogen atom.


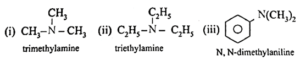
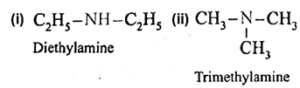
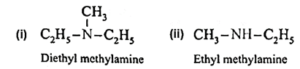
(iii) Write IUPAC names of the following amines.
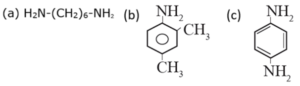
(a) Hexan-1, 6-diamine (b) 2, 4-Dimethylaniline (c) Benzene-1, 4-diamine
(iv) Write reactions to prepare ethanamine from
(a) Acetonitrile
(b) Nitroethane
(c) Propionamide
(a) Ethanamine from Acetonitrile : (b) Ethanamine from Nitroethane : (c) Ethanamine from Propionamide :
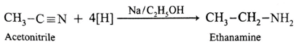
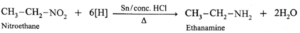

(v) What is the action of acetic anhydride on ethylamine, diethylamine and triethylamine ?
(a) Ethyl amine on reaction with acetic anhydride forms monoacetyl derivative, N-acetylethylamine. (b) Diethyl amine (a secondary amine) on reaction with acetic anhydride forms a monoacetyl derivative, N-acetyldiethyl amine (or N, N-diethyl acetamide). (c) Triethyl amine does not react with acetic anhydride as it does not have any H atom attached nitrogen atom of amine


![]()
(vii) Distinguish between ethylamine, diethylamine and triethylamine by using Hinsberg’s reagent ?
(a) Primary amine (like ethyl amine) is treated with Hinsberg’s reagent (benzene sulphonyl chloride) forms N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide which dissolve in aqueous KOH solution to form a clear solution of potassium salt and upon acidification gives insoluble N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide. (b) Secondary amine like diethyl amine is treated with benzene sulphonyl chloride forms N,N-diethyl benzene which sulphonyl amide remains insoluble in aqueous KOH and does not dissolve in acid. (b) Tertiary amine like triethyl amine does not react with benzene sulphonyl chloride and remains insoluble in KOH, however it dissolves in dil. HCl to give a clear solution due to formation of ammonium salt.
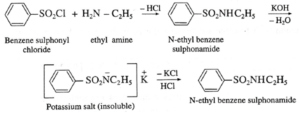
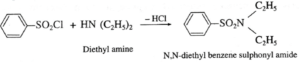

(viii) Write reactions to bring about the following conversions :
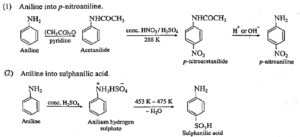
(1) Aniline into p-nitroaniline
(2) Aniline into sulphanilic acid ?
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Chemistry – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 12- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-14-Biomolecules– Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.