Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
Maharashtra Board-Class-12-Chemistry-Chapter-12
Solutions
Question 1. Choose the most correct option.
(i) In the following resonating structures A and B, the number of unshared electrons in valence shell present on oxygen respectively are
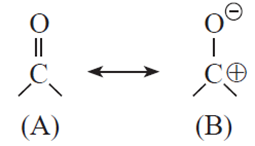
(a) 2, 4
(b) 2, 6
(c) 4, 6
(d) 6, 4
(c) 4, 6
Explanation:
- In structure (A), the oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons, which means there are 4 unshared electrons.
- In structure (B), the oxygen atom has three lone pairs of electrons, totalling 6 unshared electrons.
(ii) In the Wolf -Kishner reduction, alkyl aryl ketones are reduced to alkyl benzenes. During this change, ketones are first converted into
(a) acids
(b) alcohols
(c) hydrazones
(d) alkenes
(c) hydrazones
(iii) Aldol condensation is
(a) electrophilic substitution reaction
(b) nucleophilic substitution reaction
(c) elimination reaction
(d) addition - elimination reaction
(d) addition - elimination reaction
(iv) Which one of the following has lowest acidity ?


(v) Diborane reduces
(a) ester group
(b) nitro group
(c) halo group
(d) acid group
(d) acid group
(vi) Benzaldehyde does NOT show positive test with
(a) Schiff reagent
(b) Tollens' ragent
(c) Sodium bisulphite solution
(d) Fehling solution
(d) Fehling solution
Question 2. Answer the following in one sentence
(i) What are aromatic ketones?
The compounds in which a C=O group is attached to either two aryl groups or one aryl and one alkyl group are called aromatic ketones.
Example :

(ii) Is phenyl acetic acid an aromatic carboxylic acid ?
No. Phenyl acetic acid is not an aromatic carboxylic acid.
(iii) Write reaction showing conversion of ethanenitrile into ethanol.

(iv) Predict the product of the following reaction:
![]()
![]()
(v) Name the product obtained by reacting toluene with carbon monoxide and hydrogen chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride.

(vi) Write reaction showing conversion of Benzonitrile into benzoic acid.

(vii) Name the product obtained by the oxidation of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene with acidified potassium permanganate.

(viii) What is formalin ?
The aqueous solution of formaldehyde (40%) is known as formalin.
(ix) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their boiling points : Formaldehyde, ethane, methyl alcohol.
Ethane, formaldehyde, methyl alcohol.
(x) Acetic acid is prepared from methyl magnesium bromide and dry ice in presence of dry ether. Name the compound which serves not only reagent but also as cooling agent in the reaction.
The cooling agent used in the above reaction is dry ice (O = C = O).
Question 3. Answer in brief.
(i) Observe the following equation of reaction of Tollens' reagent with aldehyde. How do we know that a redox reaction has taken place. Explain.
![]()
Tollen's reagent oxidises acetaldehyde to acetic acid (carboxylate ion) and Ag+ in Tollen's reagent complex are reduced to silver. In this reaction, oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously hence, it is a redox reaction.
(ii) Formic acid is stronger than acetic acid. Explain.
- In acetic acid, methyl group is an electron donating group. The acetate ion formed gets destabilized due to electron releasing effect of methyl group (+ I effect) which is higher than that of H-atom in the corresponding formic acid.
- As a result, acetic acid dissociates to a lesser extent. Thus decreasing the acidity of acetic acid.
CH3-COOH + H2O ⇌ CH3-COO- + H3O+
- Formic acid having lower pKa value than acetic acid. Hence, formic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
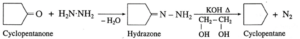
(iii) What is the action of hydrazine on cyclopentanone in presence of KOH in ethylene glycol ?
(iv) Write reaction showing conversion of Acetaldehyde into acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal.

(v) Aldehydes are more reactive toward nucleophilic addition reactions than ketones. Explain.
Reactivity of aldehydes and ketones is due to the polarity of carbonyl group which results in electrophilicity of carbon. In general, aldehydes are more reactive than ketones toward nucleophilic attack. This can be well explained in terms of both the electronic effects and steric effect.
(i) Influence of electronic effects:
- Alkyl groups have an electron-donating inductive effect (+I). A ketone has two electron-donating alkyl groups bonded to carbonyl carbon which are responsible for decreasing its positive polarity and electrophilicity.
- In contrast, aldehydes have only one electron-donating group bonded to the carbonyl carbon. This makes aldehydes more electrophilic than ketones.

(ii) Steric effects:
- Two bulky alkyl groups in ketone come in the way of the incoming nucleophile. This is called steric hindrance to nucleophilic attack.
- On the other hand, nucleophile can easily attack the carbonyl carbon in aldehyde because it has one alkyl group and is less crowded or sterically less hindered. Hence, aldehydes are more easily attacked by nucleophiles.
(vi) Write reaction showing the action of the following reagent on propanenitrile –
(a) Dilute NaOH
(b) Dilute HCl ?
(a) Action of dilute NaOH :

(b) Action of dilute HCL :
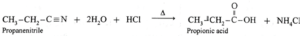
(vi) Arrange the following carboxylic acids with increasing order of their acidic strength and justify your answer.

The increasing order of acidity will be (1) < (3) < (2).
Acidity depends on mainly two factors :
(i) ease of proton release
(ii) stability of conjugate base formed.
In example (3) the ether O exerts a -I effect and is closer to -COOH group than in (2) (I effect diminishes). Also the conjugate base formed will be stabilized by the same -I effect by delocalization of charge.
Question 4. Answer the following
(i) Write a note on –
(a) Cannizzaro reaction
Cannizzaro reaction :
- Aldehydes which do not have a-hydrogen atom, on heating with concentrated alkali (50% aqueous or ethanolic solution of NaOH or KOH) undergo self oxidation and reduction reaction or redox reaction. This self redox reaction or disproportionation reaction is called Cannizzaro reaction.
- In this reaction one molecule of the aldehyde is oxidised to carboxylic acid while the second molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to alcohol (carboxylic acid formed, reacts with alkali, NaOH and forms a salt R—COONa).
- When formaldehyde (methanal) is heated with 50% NaOH solution, methanol (reduction product) and sodium formate (oxidation product) are formed.

Similarly, benzaldehyde gives Cannizzaro reaction.

- Ketones and aldehydes like acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, etc. having α-H atom do not give Cannizzaro reaction.
(b) Stephen reaction.
Nitriles are reduced to imine hydrochloride by stannous chloride in presence of hydrochloric acid which on acid hydrolysis give corresponding aldehydes. This reaction is called Stephen reaction.

Examples :

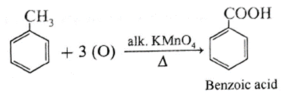
(ii) What is the action of the following reagents on toluene ?
(a) Alkaline KMnO4 , dil. HCl and heat
(b) CrO2Cl2 in CS2

(c) Acetyl chloride in presence of anhydrous AlCl3.

(iii) Write the IUPAC names of the following structures :
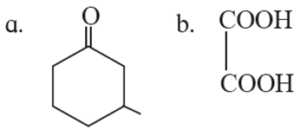
(a) IUPAC name : 3-Methylcyclohexanone
(b) IUPAC name : Ethanedioic acid
(iv) Write reaction showing conversion of p- bromoisopropyl benzene into p-Isopropyl benzoic acid ( 3 steps).
Step 1: Converting - Br group to - CN
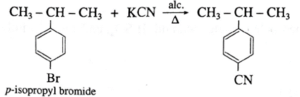
Step 2: Converting - CN group to - CONH2

Step 3: Converting - CONH2 group to - COOH

(v) Write reaction showing aldol condensation of cyclohexanone.

Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Chemistry – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 11- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-13-Amines- Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.