Halogen Derivatives
Maharashtra Board-Class-12-Chemistry-Chapter-10
Solutions
Question 1. Choose the most correct option.
(i) The correct order of increasing reactivity of C-X bond towards nucleophile in the following compounds is
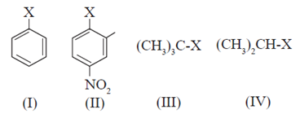
(a) I < II < III < IV
(b) II < I < III < IV
(c) III < IV < II < I
(d) IV < III < I < II
(d) IV < III < I < II Explanation: Alkyl halides are more reactive than aryl halides. This is because of the partial double bond character between the benzene ring and the halogen. Further, in alkyl halides, the greater the stability of carbocation formed, the more would be the reactivity. Thus, the tertiary halide is more reactive. Nitro group which is electron-withdrawing increases the reactivity of aryl halide.
(ii) CH3-CH=CH2 \(\underrightarrow{Hi/Peroxide}\)
The major product of the above reaction is,

(b) CH3-CH2-CH2I
(iii) Which of the following is likely to undergo racemization during alkaline hydrolysis ?
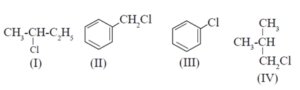
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) II and IV
(d) Only IV
(a) Only I
(iv) The best method for preparation of alkyl fluorides is
(a) Finkelstein reaction
(b) Swartz reaction
(c) Free radical fluorination
(d) Sandmeyer's reaction
(b) Swartz reaction
(v) Identify the chiral molecule from the following.
(a) 1-Bromobutane
(b) 1,1- Dibromobutane
(c) 2,3- Dibromobutane
(d) 2-Bromobutane
(d) 2-Bromobutane
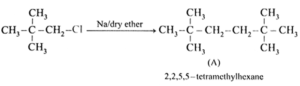
(vi) An alkyl chloride on Wurtz reaction gives 2,2,5,5-tetramethylhexane. The same alkyl chloride on reduction with zinc-copper couple in alcohol give hydrocarbon with molecular formula C5H12. What is the structure of alkyl chloride


(vii) Butanenitrile may be prepared by heating
(a) propanol with KCN
(b) butanol with KCN
(c) n-butyl chloride with KCN
(d) n-propyl chloride with KCN
(d) n-propyl chloride with KCN
(viii) Choose the compound from the following that will react fastest by SN1 mechanism.
(a) 1-iodobutane
(b) 1-iodopropane
(c) 2-iodo-2 methylbutane
(d) 2-iodo-3-methylbutane
(c) 2-iodo-2 methylbutane
(ix)

The product 'B' in the above reaction sequence is,

![]()
(x) Which of the following is used as source of dichlorocarbene
(a) tetrachloromethane
(b) chloroform
(c) iodoform
(d) DDT
(b) chloroform
Question 2. Do as directed.
(i) Write IUPAC name of the following compounds
(a) 4-Bromo-3, 4 dimethyl but-2-ene (b) 2-Chloro-3-methyl pentane (c) 1-Chloro-4-ethyl cyclohexane (d) 1,4-Dichloro-2-methyl benzene
(ii) Write structure and IUPAC name of the major product in each of the following reaction.


(iii) Identify chiral molecule/s from the following.

(iv) Which one compound from the following pairs would undergo SN2 faster from the?
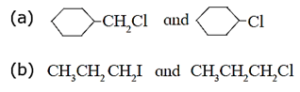
(a) Since (b) Since iodine is a better leaving group than chloride, 1-iodopropane (CH3CH2CH2I) undergoes SN2 reaction faster than 1-chloropropane (CH3CH2CH2Cl).
![]() is a primary halide it undergoes SN2 reaction faster than
is a primary halide it undergoes SN2 reaction faster than ![]()
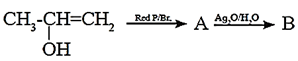
(v) Complete the following reactions giving major product.
![]()
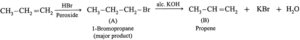
(b)
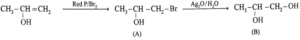
(c)
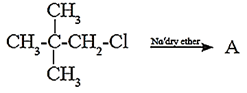
(d)

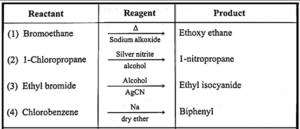
(vi) Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversions.
(a) Bromoethane to ethoxyethane
(b) 1-Chloropropane to 1 nitropropane
(c) Ethyl bromide to ethyl isocyanide
(d) Chlorobenzene to biphenyl
(vii) Arrange the following in the increase order of boiling points
(a) 1-Bromopropane (b) 2- Bromopropane (c) 1- Bromobutane (d) 1-Bromo-2-methylpropane
2-Bromopropane < 1-Bromopropane < 1-Bromo-2-methylpropane < 1-Bromo butane.
(viii) Match the pairs.
| Column I | Column II |
| i. vinyl halide | |
| b. CH2=CH-CH2X | ii. alkyl halide |
| c. CH2=CH-X | iii. allyl halide |
| iv. benzyl halide | |
| v. aryl halide |
Column I
Column II
![]()
i. vinyl halide
b. CH2=CH-CH2X
iii. allyl halide
c. CH2=CH-X
i. vinyl halide
Question 3. Give reasons
(i) Haloarenes are less reactive than halo alkanes.
Therefore, haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes.
(ii) Alkyl halides though polar are immiscible with water.
Hence, alkyl halides though moderately polar are immiscible with water.
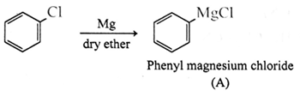
(iii) Reactions involving Grignard reagent must be carried out under anhydrous condition.
(iv) Alkyl halides are generally not prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes.
Question 4. Distinguish between - SN1 and SN2 mechanism of substitution reaction?
Factor
SN1
SN2
Number of steps
Two steps
One step
Molecularity/Order
Unimolecular/1st order
Bimolecular/2nd order
Reaction rate
Depends upon concentration of one reacting species
Depends upon concentration of two reacting species
Attack of a nucleophile
Back side attack and front side attack on a substrate with equal probability
Only back side attack on a substrate
Transition state
Two steps, two transition states
One step, one transition state
Type of substrate
Mainly tertiary (3°) substrate
Mainly primary (1°) substrate
Stereochemistry
50% inversion and 50% retention of configuration
100% inversion of configuration
Enantiomer
Forms racemic mixture
Forms opposite enantiomer
Solvent
Polar solvent favourable
Nonpolar solvent favourable
Energy of activation
Two values of energies of activation
One value of energy activation
Intermediate
Carbocation intermediates
No intermediate
Nucleophile
Weak nucleophile favourable
Strong nucleophile favourable
Order of reactivity in alkyl halides
Tertiary > Secondary > Primary
Primary > Secondary > Tertiary
Question 5. Explain - Optical isomerism in 2-chlorobutane.
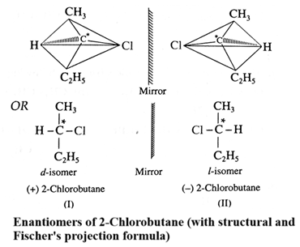
Question 6. Convert the following.
(i) Propene to propan-1-ol
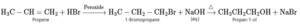
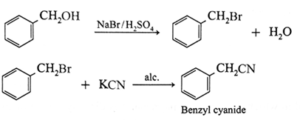
(ii) Benzyl alcohol to benzyl cyanide
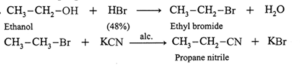
(iii) Ethanol to propane nitrile
(iv) But-1-ene to n-butyl iodide
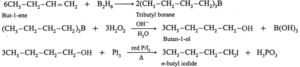
(v) 2-Chloropropane to propan-1-ol
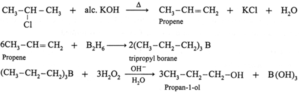
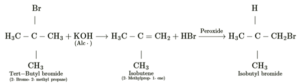
(vi) tert-Butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide
(vii) Aniline to chlorobenzene

(viii) Propene to 1-nitropropane
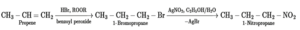
Question 7. Answer the following
(i) HCl is added to a hydrocarbon 'A' (C4H8) to give a compound 'B' which on hydrolysis with aqueous alkali forms tertiary alcohol 'C' (C4H10O). Identify 'A', 'B' and 'C'.

(ii) Complete the following reaction sequences by writing the structural formulae of the organic compounds 'A', 'B' and 'C' .
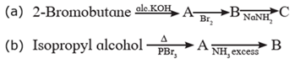
(a) (b)
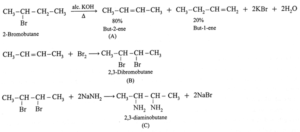
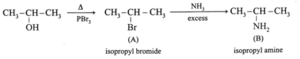
(iii) Observe the following and answer the questions given below.
![]()
(a) Name the type of halogen derivative
(b) Comment on the bond length of C-X bond in it
(c) Can react by SN1 mechanism?
Justify your answer.
(1) Vinyl halide (2) C-X bond length shorter in vinyl halide than alkyl halide. Vinyl halide has partial double bond character due to resonance. In vinyl halide, carbon is sp2-hybridized. The bond is shorter and stronger and the molecule is more stable. (3) Yes, It reacts by SN1 mechanism. SN1 mechanism involves formation of carbocation intermediate. The vinylic carbocation intermediate formed is resonance stabilized, hence SN1 mechanism is favoured.
PDF : Chapter-10-Halogen Derivatives-Text Book
PDF : Chapter-10-Halogen Derivatives- Notes
PDF : Chapter-10-Halogen Derivatives- Solution
All 16 Chapters Notes -Class-12-Chemistry (16-PDF)
All 16 Chapters Solutions -Class-12-Chemistry (16-PDF)
All 16 Chapters Notes+Solutions -Class-12-Chemistry (32-PDF)
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Chemistry – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 9- Coordination Compounds – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-11-Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers– Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.