Ecosystems and Energy Flow
Maharashtra Board-Class-12th-Biology-Chapter-14
Solutions
Question 1. Multiple choice questions
(1) Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
(a) Producers
(b) Primary consumers
(c) Secondary consumers
(d) Decomposers
(a) Producers
(2) The second trophic level in a lake is ________________
(a) Phytoplankton
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Benthos
(d) Fishes
(b) Zooplankton
(3) Secondary consumers are __________
(a) Herbivores
(b) Producers
(c) Carnivores
(d) Autotrophs
(c) Carnivores
(4) What is the % of photosynthetically active radiation in the incident solar radiation?
(a) 100%
(b) 50 %
(c) 1-5%
(d) 2-10%
(b) 50 %
(6) Give the term used to express a community in its final stage of succession?
(a) End community
(b) Final community
(c) Climax community
(d) Dark community
(c) Climax community
(7) After landslide which of the following type of succession occurs?
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Climax
(a) Primary
(8) Which of the following is most often a limiting factor of the primary productivity in any ecosystem.
(a) Carbon
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Phosphorus
(d) Sulphur
(c) Phosphorus
Question 2. Very short answer question.
(1) Give an example of ecosystem which shows inverted pyramid of numbers.
Number of insects dependent on a single tree, is an example of ecosystem having inverted pyramid of numbers.
(2) Give an example of ecosystem which shows inverted pyramid of biomass.
Oceanic ecosystem has inverted pyramid of biomass.
(3) Which mineral acts as limiting factor for productivity in an aquatic ecosystem.
Phosphorus acts as limiting factor for productivity in an aquatic ecosystem.
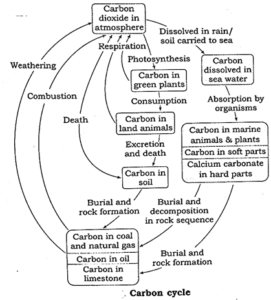
(4) Name the reservoir and sink of carbon in carbon cycle.
Atmosphere is the reservoir of carbon cycle, while fossil fuels embedded in ocean and oceanic waters are the sink of carbon in carbon cycle.
Question 3. Short answer questions.
(1) Distinguish between upright and inverted pyramid of biomass
Upright pyramid of biomass
Inverted pyramid of biomass
In upright pyramid, the number and biomass of the organisms which are at first trophic level of producers is high.
The inverted pyramid shows that the number and biomass of organisms at the first trophic levels of producers are the lowest.
Biomass decreases at each level.
The biomass foes on increasing at each trophic level.
Base always contains large number of producers.
The base of pyramid is always in small numbers of producers.
Pyramid is always upright.
Pyramid is always inverted.
(2) Distinguish between Food chain and Food web.
1. Grazing food chain 2. Detritus food chain
Food chain
Food web
The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms that feeds on a single type of organism.
Food web is interconnections between many small food chains.
Energy flows through a single pathway from lower to higher trophic levels.
In food web, the energy flow is interconnected through numerous food chains in the ecosystem.
Higher trophic level members feed on only one type of organism.
It allows one organism to feed on multiple types of organisms.
Energy flow can be easily calculated in the food chain.
Energy flow is difficult to calculate in a food web.
Increased instability occurs due to the number of separate and confined food chains.
The complexity of food chains increases stability and prevents disturbance from the removal of one group of organisms.
The food chain consists of 4-6 trophic levels of different species, and competition occurs between members of the same trophic level.
The food web contains numerous trophic levels and diverse species populations, with competition observed in members of the same and different trophic levels.
Food chains are of two types :
In food web there are no types
Question 4. Long answer questions.
(1) Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Ecological Pyramids : Ecological Pyramids are the representation of relationships between different components of ecosystem at successive trophic levels. Pyramid of numbers : Pyramid of biomass :
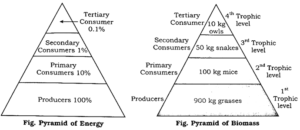
(2) What is primary productivity? Give brief description of factors that affect primary productivity.
Primary Productivity: Primary productivity refers to the rate of biomass generation in an ecosystem, measured in grams per square metre per day (g/m2/day), expressed in units of mass per unit surface per unit time. Factors affecting primary productivity: Gross primary productivity (GPP) depends on the following factors :
(3) Define decomposition and describe the processes and products of decomposition.
(4) Write important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem.
(5) Describe carbon cycle and add a note on the impact of human activities on carbon cycle.
Carbon cycle :
Notes, Solutions, Text Book-PDF
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-14-Ecosystems and Energy Flow-Text Book
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-14-Ecosystems and Energy Flow- Notes
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-14-Ecosystems and Energy Flow- Solution
PDF SET :
All Chapters Notes-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-130
All Chapters Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-128
All Chapters Notes+Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(30-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-240
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Biology – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-13-Organisms and Population– Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-15-Ecosystems and Energy Flow –Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.