Reproduction in Lower & Higher Animals
Maharashtra Board-Class-12th-Biology-Chapter-2
Notes-Part-2
Topics to be Learn : Part-2
|
Fertilization / Syngamy
Fertilization : Process of fusion of the haploid male and female gametes into diploid zygote is called fertilization.
Fertilization is internal and in the ampulla of the fallopian tube the gametes meet.
The sequence of events of fertilization :

Significance of fertilization :
Embryonic development :
- After syngamy the zygote that is formed undergoes divisions to form embryo. These mitotic divisions are called cleavages.
- When the zygote passes through the fallopian tube, the cleavages start.
- Till morula stage, zona pellucida layer is retained as it prevents the implantation of the blastocyst at an abnormal site.
Cleavage :
- Cleavages are rapid mitotic divisions of zygote to form a hollow spherical multieellular blastula. Cleavage converts the zygote first into a mass of cells called morula.
- Cleavage occurs during its passage through the fallopian tube to the uterus.
- In human beings, cleavage is holoblastic, equal and indeterminate.
- Cleavage divisions are rapid with short interphase.
- There is no time for cells to grow in size. Thus, cells become progressively smaller. The resulting daughter cells are called blastomeres.
- Cleavage shows faster synthesis of DNA.
Cleavage
Direction
Time
Results
First
Vertical along animal pole — vegetal pole
32 hours after fertilization
Two blastomeres
Second
Vertical at the right angles to the first one
60 hrs after fertilization
Four blastomeres
Third
Horizontal / latitudinal division and at right angles to the first two cleavages
32 hrs after fertilization
Eight celled stage
Successive Division
Reaches uterus about 4 — 6 days after fertilization.
Morula— 16 celled having outer layer of smaller clearer cells and an inner mass of larger cells
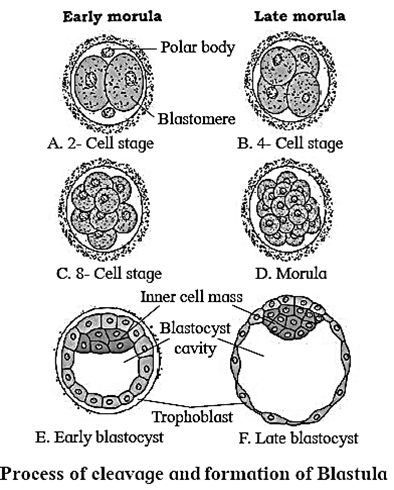
Blastulation :
- During blastulation hollow and multicellular blastocyst is formed from 16-32 celled stage of morula.
- Blastocyst now reaches uterus and starts absorbing glycogen rich uterine milk.
- The outer layer of cells forms trophoblast layer Whereas inner large cells form inner cell mass or embryoblast.
- Size of blastocyst doubles from 0.15 mm to 0.30 mm.
- Due to the absorption of glycogen rich uterine milk, the trophoblast cells become flat and a cavity called blastocyst cavity is formed.
- Cells of rauber : These are the cells of trophoblast which are in contact with the embryonal knob.
- Blastocyst becomes fully developed by the end of the 7th day.
Implantation :
- Implantation is the process of embedding the blastocyst in the uterine endometrium for further gestation.
- On 7th to 10th day after fertilization, implantation takes place. Embryo is completely buried inside the endometrium.
- Trophoblast divides into two layers, viz. cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast. With processes of synctiotrophoblast the blastocyst is buried in the endometrium layer of uterus.
Gastrulation :
Formation of gastrula from the blastocyst is called gastrulation. It starts at about 8 days after fertilization.
Two important events during gastrulation are :
- [a] Differentiation of blastomeres : Three germinal layers are formed by rearrangement of blastomeres.
- [b] Morphogenetic movements : Movements of cells to reach their destined area of differentiation is called morphogenetic movements.
Gastrulation and implantation of blastocyst takes place simultaneously.
Gastrulation involves the following sequential changes :
Organogenesis : Process of forming organs after the process of gastrulation is called organogenesis.
Fate of germinal layers : At the end of gastrulation, embryo develops into three germinal layers viz., ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. Different tissues and organs are formed from germinal layers. This process is called histogenensis.
Fate of ectoderm : Following tissues, structures and organs develop from the ectoderm : Fate of mesoderm : The mesoderm forms the following derivatives : Fate of endoderm : The following organs develop from the endoderm :
Pregnancy / Gestation :
Gestation or pregnancy is the condition of developing foetus in the uterus. It may be one or two asin twins.
In human beings, gestation period is about 280 days. It is divided into three trimesters of three months each.
First Trimester : (From fertilization to 12th week) During first trimester there are radical changes in the body of mother as well as in the embryo. Second Trimester : (From 13th to 26th week) Third Trimester : (From 27th week till the parturition]
Placenta : Placenta is a flattened, discoidal organ attached to the wall of the uterus and to the baby’s umbilical cord.
- It facilitates the supply of oxygen and nutrients and also for removal of carbon dioxide and excretory products produced by the foetus.
- Placenta is the only organ, which is formed of tissues from two different individuals the mother and the foetus.
- Foetal placenta is the choronic villi while maternal placenta is the highly vascularized uterine wall. So human placenta is called haemochorial.
- The placenta also acts as an endocrine tissue and produces hormones like hCG. progesterone, estrogen and relaxin.

Note :
|
Parturition : Parturition is the birth process which is accompanied with labour pains.
- It is a neuro-endocrine mechanism which involves rise in estrogen : progesterone ratio and increase in oxytocin receptors in myometrium of uterine wall.
- The fully developed foetus gives signals for the uterine contractions by secreting Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from pituitary and corticosteroids from adrenal gland.
- This triggers release of oxytocin from mother’s pituitary gland, which acts on uterine muscles of mother and causes vigorous uterine contractions.
- This leads to expulsion of the baby from the uterus.
- Parturition involves three stages, viz. dilation stage, expulsion stage and after birth or placental stage.
Steps of parturition :
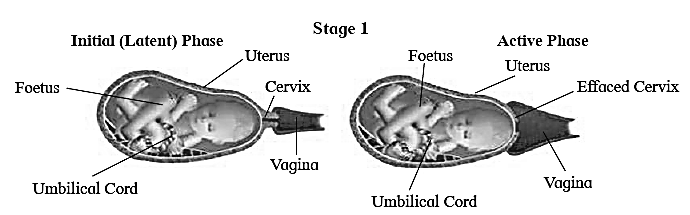
Dilation stage :
- Dilation stage means dilating the birth canal or passage through which baby is pushed out.
- In the beginning uterine contractions start from top and baby is moved to cervix. Due to compression of blood vessels and movements of flexible joints in pelvic girdle, mother experiences labour pains.
- Oxytocin is secreted later in more amount causing severe uterine contractions. This pushes baby in a head down position and closer to cervix.
- Cervix and vagina both are dilated. This stage lasts for about 12 hours.
- At the end, amniotic sac ruptures and amniotic fluid is passed out.
Expulsion stage :
- During second stage of about 20 to 60 minutes, the uterine and abdominal contractions become stronger.
- Foetus moves out with head down position through cervix and vagina.
- The umbilical cord which connects the baby to placenta is tied and cut off close to the baby’s navel.

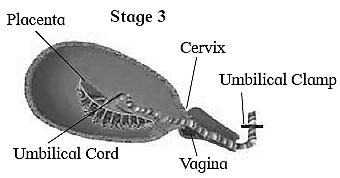
After birth or placental stage :
- In the last stage of 10 to 45 minutes, once the baby is out then the placenta is also separated from uterine wall and is expelled out as “after birth". This is accompanied by severe contractions of the uterus.
Lactation : After parturition the new born is given nourishment through milk. The process of secretion of milk is called lactation.
- In which mammary glands of mother become functional.
- The first milk is called colostrum which is rich in proteins, lactose and mother’s antibodies e.g. IgA.
- Lactation is also neuroendocrine process, in which almost all endocrine glands of mother are involved.
Distinguish between Asexual reproduction and Sexual reproduction : 2-Meiosis does not take place in asexual reproduction. Only mitosis takes place. 3-Gamete formation, fertilization and zygote formation does not take place. 4-Progeny and parent are identical genetically 5-Large number of progeny is developed by asexual reproduction. E.g. Spore formation, gemmule formation, budding, regeneration are the types of a sexual reproduction. 2-Sexual reproduction involves meiosis and mitosis. 3-Gamete formation, fertilization and zygote formation are important processes in sexual reproduction. 4-Progeny and parents are genetically dissimilar. 5-Limited number of progeny is developed by sexual reproduction. E.g. Sexual reproduction is only by a single method.
Asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
1-Asexual reproduction requires single parent.
1-Sexual reproduction needs two different parents.
Reproductive health : Total wellbeing of a person's emotional, behavioural, physical and social aspects involving reproduction is called reproductive health.
- In India, Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) programmes are undertaken to improve reproductive health.
- India was amongst the first few countries in the world to initiate action plans and programmes at a national level to improve reproductive health.
- One of the objectives of this programme is to control the population growth of India.
Goals of RCH Programmes: The goals of RCH can be achieved by the following ways:
Birth control : For controlling the family size, birth control measures are taken which are called contraceptive measures.
Contraceptive methods are of two main types, i.e. temporary and permanent.
Temporary methods :
Permanent methods surgical operations : In men surgical operation is called vasectomy and in women it is called tubectomy. These are surgical methods, also called sterilization. In vasectomy a small part of the vas deferens is tied and cut where as in tubectomy, a small part of the fallopian tube is tied and cut. This blocks, gamete transport and prevent pregnancy.

Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) : An intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy before full term is called Medical termination of Pregnancy.
- MTP is induced abortion.
- MTP can indirectly control population.
- MTP is legalized in India since 1971.
- MTP is performed if unwanted pregnancy has to be discontinued or if there are defects in the growing foetus.
- MTP to abort healthy female embryo is illegal.
- MTP can be safely done only during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Amniocentesis :
- Process in which amniotic fluid containing foetal cells is collected using a hollow needle inserted into the uterus under ultrasound guidance.
- This is done for studying the chromosomes to check any possible abnormality in the developing foetus.
- Sex determination by amniocentesis is legally banned in India.
| PC-PNDT Act : The Pre-conception and Pre-natal Diagnostic Techniques (Prohibition of Sex Selection) Act or PC-PNDT Act 2003.
Its mandates as follows :
The main purpose of enacting the Act is to ban the use of sex selection techniques after conception and prevent the misuse of pre-natal technique for sex selective abortions. This Act is enacted to stop female foeticides and thereby reduce the declining sex ratio in India. Hence this mandate is essential to prevent foetal sex determination and sex selective abortion. I |
Sexually Transmited Diseases (STDs) : Disease or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are collectively called Sexually Transmited Diseases (STDs) or Venereal Diseases (VDs) or Reproductive Tract Infections (RTI).
The major venereal diseases are syphilis and gonorrhoea.
A. Syphilis : Syphilis is a sexually transmitted veneral disease caused by a Spirochaete bacterium Treponema pallidum. The site of infection is the mucous membrane in genital, rectal and oral region. Modes of transmission : Symptoms of syphilis : Preventive measures : Treatment : Prompt treatment with Antibiotic-Penicillin
B. Gonorrhoea : Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted veneral disease caused by Diplococcus bacterium, Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Modes of transmission : Symptoms in Males : Partial blockage of urethra and reproductive ducts, pus from penis, pain and burning sensation during urination, arthritis, etc. Symptoms in female : Pelvic inflammation of urinary tract, sterility, arthritis. The children born to affected mother suffer from gonococcal ophthalmia. In girl-child, there is occurrence of gonococcal vulvovaginitis before puberty. Preventive measures : Treatment : Treated with Cefixime which is antibiotic.
Infertility : Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive naturally after (one year of) regular unprotected intercourse.
Today infertile couples have many options to have a child such as fertility drugs, test tube babies, artificial insemination, IUI, surrogate motherhood, etc.
The couple could be assisted to have child / children through certain special techniques commonly known as Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART).
| Note: Tobacco, marijuana and other drugs smoking may cause infertility in both men and women.
Nicotine blocks the production of sperm and decreases the size of testicles. Alcoholism by men interferes with the synthesis of testosterone and has an impact on sperm count. Use of cocaine or marijuana may temporarily reduce the number and quality of sperm. |
Click on below link to get PDF from store
PDF : Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-2-Reproduction in Lower & Higher Animals-Text Book
PDF : Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-2-Reproduction in Lower & Higher Animals– Notes
PDF : Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-2-Reproduction in Lower & Higher Animals– Solutions
PDF SET :
All Chapters Notes-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-130
All Chapters Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-128
All Chapters Notes+Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(30-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-240
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Biology – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-1-Reproduction in Lower & Higher plants – Online Notes
Next Chapter : Chapter-3-Inheritance and Variations – Online Notes
We reply to valid query.