|
Topics to be Learn : Part-1
- Improvement in Food Production
- Plant breeding
- Tissue culture
- Single cell protein (SCP)
- Biofortification
Topics to be Learn : Part-2
Topics to be Learn : Part-3
- Microbes in human welfare
- Role of Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Energy Generation
- Role of Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Role of Microbes as Biofertilizers
|
Animal husbandry :
- Animal husbandry is an agricultural practice of breeding and raising livestock.
- Animal husbandry deals with care and breeding of livestock like buffaloes, cows, pigs, horses, cattles, sheeps, camels, goats, etc.
- It also includes poultry farming, fish farming, bee keeping, sericulture, lac culture, etc.
- Products obtained from animals : Milk, eggs, meat, wool, honey, silk, etc.
The production can be increased by -
- Effective management procedures
- New technologies in various farm systems to improve quality and productivity
- Use of industrial principles of production processing and marketing
- Management of farms includes selection of high yielding breeds, taking care of food requirements, supply of adequate nutritional sources, cleanliness of the environment and maintenance of health.
- Management of farm animals includes veterinary supervision, vaccination, high yielding cross breed development, production and preservation of products, distribution and marketing.
Animal breeding :
Aims of animal breeding :
- Aims of animal breeding is getting improved breeds with desirable qualities of product and to increase yield of animals,
- To develop breed with desirable characters such as increased production of milk, quality of product, quality of meat or maximum yield of eggs per year etc.
Breed : A group of animals related by descent and similar in most characters like general appearance, features, size, configuration, etc.
Details of various types of breeding :
Types of breeding :
Breeding can be of two main types - inbreeding and outbreeding
(1) Inbreeding : It is the mating of two closely related individuals within the same breed for 4 to 6 generations.
Merits of Inbreeding :
- Inbreeding increases homozygosity.
- Pure lines of animals can be obtained.
- Helpful in the elimination of harmful recessive genes and for the accumulation of superior genes.
Demerits of Inbreeding:
- It usually reduces the fertility and productivity. This is called inbreeding depression.
(2) Outbreeding :
- Outbreeding involves breeding of two unrelated animals.
- It is of three types, viz. outcrossing, cross-breeding and interspecific hybridization.
(i) Outcrossing :
- Outcrossing involves mating of animals of same breed, which do not have 3 common ancestors on either side of mating partners up to 4 to 6 generations.
- The progeny obtained from such mating is called an outcross.
- Outcrossing is done to overcome inbreeding depression.
(ii) Crossbreeding :
- In crossbreeding superior males of one breed are mated with superior females of another breed.
- New animal breeds of desirable characters are developed by this method.
- Example : Hisardale breed of sheep is developed in Punjab by crossing Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams.
(iii) Interspecific hybridization :
- It involves breeding of animals of two different but related species.
- It is used to produce animals with desirable characters from both the parents.
- e.g. Mule is a breed obtained from horse and donkey.
- It may not be always successful.
Artificial insemination :
- It is the technique used for controlled breeding experiments.
- Superior males of a particular commercial breed are selected.
- Semen from such superior males is collected and injected into the genital tract of female.
- This insemination is either done immediately or semen is frozen and used later on. "
- In frozen semen, sperms can remain alive for long duration. They are also convenient for transport.
Artificial insemination is preferred as it is easy and helpful to overcome several problems of normal mating.
Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer (MOET) :
- MOET technology is used to increase chances of successful production of hybrids.
- In this technique, cow is administered with Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) which induces follicular maturation and then the super ovulation is brought about.
- By such technique in each cycle, 6 to 8 eggs mature simultaneously.
- The cow is then either mated with a superior bull or she is artificially inseminated.
- The blastocysts at 8 to 32 cell stage are recovered non-surgically and transferred to surrogate mothers.
- The genetic mother who gave the egg is then again subjected to another round of super ovulation.
- This technology is used for cattle, sheep, rabbits, buffaloes, etc.
Application of MOET :
- The MOET is used to produce high milk yielding breeds of female and high quality meat yielding bulls with lean meat containing less lipids.
- It helps in increasing favourable herd size in a short period.
[collapse]
Dairy farm management :
Dairy industry : It involves production, processing, marketing and distribution of milk and various milk products. Cow dung, manure, fuel cakes and gobar gas (for cooking and lighting) are sources of additional income.
Breeds of cows :
- Indian breeds of cows : Sahiwal, Sindhi, Gir
- Exotic breeds of cows : Jersey, Brown Swiss, Holstein.
- Breeds of buffaloes in India : Jaffarabadi, Mehsana, Murrah, Nagpuri, Nili, Surati.
Cattle feed : Silage, oilcakes, minerals, vitamins and salts.
Measures to be taken to improve the quality of milk :
Measures to be taken to improve the quality of milk :
In order to improve the quality of milk, following measures should be taken at every stage of dairy farming :
- Good breeds having high yielding potential should be selected.
- The breeds selected should be suitable for the local climatic conditions.
- The breeds selected should have proper resistance to diseases.
- Cattles should be well looked after with proper care.
- The feed should be of suitable quality and quantity. Feed includes silage made from legumes, grasses, maize and jowar. Silage should be supplemented with oilcakes, minerals, vitamins and salts.
- Utmost care should be taken about cleanliness and hygiene of the cattle as well as the handlers who handle the cattle. This is especially important during milking, storage and transport of milk and its products.
- Mechanized processes should be adopted as far as possible as they reduce chance of direct contact of produce with the handlers.
- The shed must be clean and well maintained. Similarly the dairy should be spacious with adequate facilities for feeding, watering and light.
- Help of veterinary doctor should be sought from time to time for the identification of health problems, diseases and rectification.
- Transportation of milk, processing, marketing and distribution play a vital role in dairy industry.
[collapse]
Poultry farm management :
Poultry includes number of bird species such as chicken, ducks, turkey, and fowls which are domesticated for their eggs and meat.
Allied professions to poultry : Processing ofeggs and meat, marketing of poultry products, compounding and sale of poultry feed, poultry equipment, pharmaceuticals, feed additives, etc.
Requirements for poultry farm Management :
Requirements for poultry farm Management :
For the management of poultry, following aspects are to be taken care of :
- Selection of proper and disease free breed, suitable and safe farm conditions.
- Proper feeding practice and the quality of feed and water.
- Hygiene and health care of the birds.
- Management of layers is done by selecting high yielding chicken. Their farms are kept clean, dry and well ventilated. They are given proper feed at proper times. Other aspects such as debeaking, etc, are also taken care of.
- In the farm, importance is given to infrastructure such as proper and adequate lighting, placing waterer at places, looking after sanitation, culling and vaccination.
- Management of broiler similarly includes selection of breed, housing, temperature ventilation, lighting, observing the floor space and broiler feed.
[collapse]
Poultry breeds [On the basis of their origin) :
- American breeds : Plymouth Rock, New Hampshire, Rhode Island Red
- Asiatic breeds : Brahma, Cochin and Langshan
- Mediterranean breeds : Leg horn, Minorca
- English breed : Australorp
- Indian breeds : Chittagong, Aseel, Brahma and Kadaknath.
Best layer (for eggs) : Leghorn.
Best broilers (for meat) : Plymouth rock, Rhode Island Red, Aseel, Brahma and Kadaknath.
Poultry diseases :
Poultry diseases :
- Viral diseases : Ranikhet, Bronchitis, Avian influenza (bird flu), etc. Bird flu had serious impact on poultry farming and also caused infection to humans.
- Bacterial diseases : Pullorum, Cholera, Typhoid, TB, CRD (chronic respiratory disease), Enteritis, etc,
- Fungal diseases : Aspergillosis, Favus and Thrush.
- Parasitic diseases : Lice infection, round worm, caecal worm infections, etc.
- Protozoan diseases : Coccidiosis.
[collapse]
Apiculture or bee keeping :
- Apiculture or bee keeping is an artificial rearing of honey bees to obtain bee products.
Importance of apiculture :
Importance of apiculture :
- Various products such as honey, wax, pollen, bee venom, propolis (bee glue) royal jelly, etc. are obtained from this cottage industry.
- Honey is an important item as ayurvedic medicine and in food due to its nutritional value.
- Bees also help in the cross pollination of various crops. Hence in pastures, wild shrubs, fruit orchards and cultivated crops, honeybees play an important role as pollinators.
- Bee keeping in crop fields increases the productivity of both honey and the crop.
- Apiculture itself is a means for employment for rural youth. It is an age old cottage industry which can be done along with agriculture.
[collapse]
Species of honey bee :
- The four species of honey bees commonly found in India are Apis dorsata (rock bee or wild bee), Apis florea (little bee), Apis mellifera (European bee) and Apis indica (Indian bee).
- For bee keeping, Apis mellifera and Apis indica are the suitable species, hence they are known as domesticated species.
Requirements of bee keeping :
Requirements of bee keeping :
Bee keeping is practiced in the areas where sufficient wild shrubs, fruit orchards and cultivated crops are present.

- Bee keeping requires bee hive boxes which consist of comb foundation sheets.
- In addition, the bee veil, smoker, bee brush, gloves, gumshoes, uncapping knives, swarm net, queen excluder, overall hive tool, etc. are required.
- Bee keeping requires familiarity with the habits of bees, selection of suitable location, catching and hiving of swarms, management of hives during different seasons, handling and collection of honey, bee wax and other products.
- Successful bee keeping also requires periodic inspection for cleanliness of hive boxes, activity of bees and queen, condition of brood, provision of water.
[collapse]
Fishery :
Fishery is deals with the catching, processing, fish farming and marketing of fish, and other useful aquatic animals such as, prawns, lobsters, oysters, mussels and crabs.
Main divisions of fishery : Fishery can be capture fishery and culture fishery.
Three main divisions of capture fishery are: Inland fishery, estuarine fishery and marine fishery.
- Inland fishery : It is culturing and capturing of from fresh water bodies. It is carried out on about 40 to 50 lakh acres of fresh water bodies such as rivers, ponds, lakes and dams.
- Marine fishery: It includes capturing fish from sea water. India has a coastline of about 7500 km.
- Estuarine fishery: It includes capture of fish from estuaries.
- Culture fishery : Culture fishery is either of polyculture or of monoculture type. In polyculture, different species are cultured simultaneously at the same time in the same pond. In monoculture, only a single species is cultured.
Common fresh water fishes : Rohu, Catla, Mrigal, common carp, grass carp. silver carp etc.
Marine fishes : Hilsa, Bombayduck, sardines, pomphrets, mackerel, etc. are important varieties of fish.
Fish farming :
Fish farming : Fish farming is the practice of culturing the edible and commercially important fish species in the ponds, lakes or reservoirs.
For maintaining a fish farm, following aspects are taken into consideration :
- selection of the site
- excavation of the pond
- managing hatchery
- nursery
- looking after rearing ponds and
- stocking ponds besides managing the water source, supplying fertilizer and supplementary feed, etc.
[collapse]
Prevention of Fish spoilage:
Fish is a highly perishable commodity After catching the fish it immediately starts spoilage process.
In order to prevent this process, the fish preservation is done.
Methods of fish preservation :
The different methods of fish preservation are as follows :
- Chilling : This involves covering the fish with layers of ice.
- Freezing: It is a long duration preservation method. Fish are freezed at 0°C to −20°C.
- Freeze drying : The deep frozen fish at − 20 °C are dried by direct sublimation of ice to water vapour with any melting into liquid water.
- Sun drying : This inhibits the growth of microorganisms that spoil the fish.
- Smoke drying: Smoke is prepared by burning woods with less resinous matter. Bacteria are destroyed by the acid content of the smoke. Smoking also give the characteristic colour, taste and odour to fish.
- Salting : Salt removes the moisture from the fish tissues by osmosis. High salt concentration destroys autolytic enzymes and halts bacterial activity.
- Canning: Canning involves sealing the food in a container, heat ‘sterilising’ the sealed unit and cooling it to ambient temperature for subsequent storage.
[collapse]
Economic importance of fisheries :
Economic importance of fisheries :
- Fish is a nutritious food and thus is a source of many vitamins, minerals and nutrients.
- Fish oil, fish meal, fertilizers, fish guano, fish glue and Isinglass are some of the by-products made from the fish.
- These by-products are used in paints, soaps, oils and medicines.
- Some organisms like prawns and lobsters have high export value and market price.
- Fish farming and other fishery trades provide job opportunity and self-employment.
- Fish farming helps in boosting the productivity and the economy of the nation.
[collapse]
Sericulture :
- Sericulture is deals with rearing of silkworm and production of silk.
- The silkworm (Bombyx mori) is reared for obtaining best quality of silk called mulberry silk. Tussar silk and Eri silk are other varieties of silk which are inferior to the mulberry silk.
- Larvae of silkworm are fed on the mulberry leaves. Quality and quantity of silk depends on the quality of mulberry leaves.
- These larvae are reared, developed and well looked after by the skilful labour keeping a constant watch.
- Silkworm larvae may be infected by protozoans, viruses and fungi. Ants, crows, birds, and other predators are ready to attack these insects, hence the cages of these larvae must be managed to prevent predators attack.
- Silk is obtained from the cocoon of the silkworm.
- Sericulture is an age old practice and can be started with low investment and small space. It requires scientific knowledge and skill. Disabled, older and handicapped people also can practise it.
Different stages found in the life cycle of silkworm and process of cocoon formation :
Different stages found in the life cycle of silkworm and process of cocoon formation :
Stages of development in the life cycle of silkworm are egg, larva, pupa and adult.
The adult (imago) stage is the silkworm moth
- The eggs of silkworm hatch into larvae.
- The larvae develop into a caterpillar.
- Caterpillar feeds on fresh mulberry leaves.
- After its growth and moulting, the silkworm secretes a silk fibre to form cocoon.
- The silk is a continuous filament comprising fibroin protein, secreted from salivary glands of silkworm and a gum called sericin, which cements the filaments.
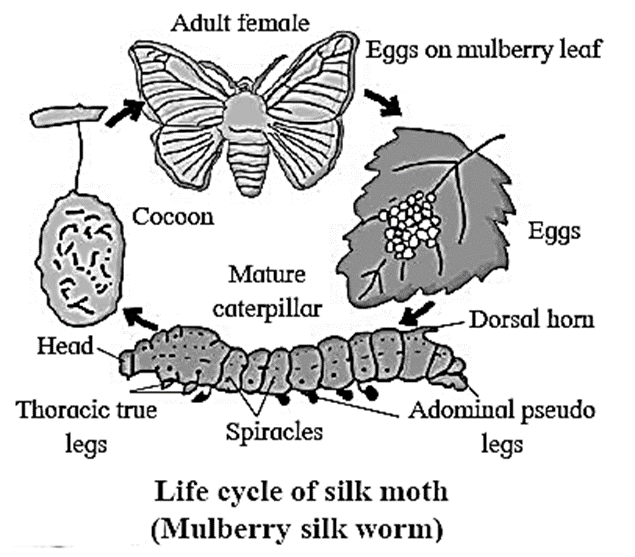
- The silk solidifies when it contacts the air.
- The silkworm spins approximately one mile of filament and completely encloses itself in a cocoon in about two or three days.
[collapse]
Lac culture :
Lac culture:
- Lac is a pink coloured resin secreted by dermal glands of female lac insect
- (Trachardia lacca) that hardens on coming in contact with air forming lac.
- Lac is a complex substance having resin, sugar, water, minerals and alkaline substances.
- Lac insect is colonial in habit and it feeds on succulent twigs like ber, peepal, palas, kusum, babool.
- These plants are artificially inoculated in order to get better and regular supply of good quality and quantity of lac.
- Natural lac is always contaminated and pure form of lac obtained by washing and filtering is called as shellac.
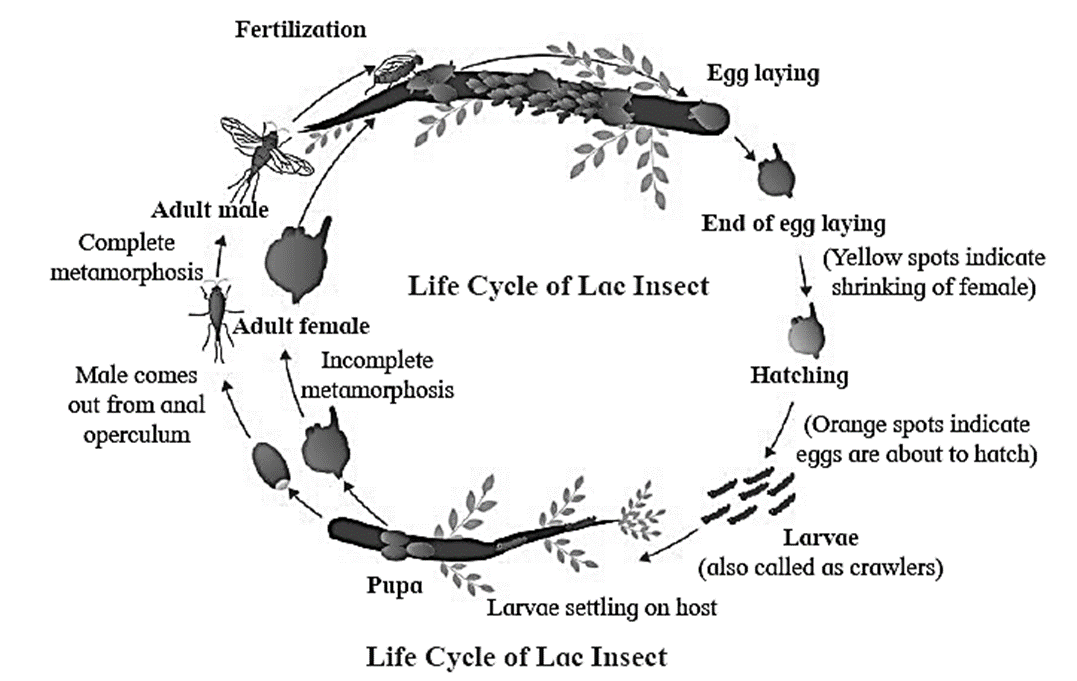
Lac is used for the following purposes :
- For making bangles.
- For making different types of toys.
- It is used in wood works.
- Polish is made from lac.
- Inks can be prepared from lac.
- Lac is largely used for silvering mirrors.
Lac insect is a native of India and its share is 85 % of total lac produced in the world.
[collapse]



We reply to valid query.