Electromagnetic Waves and Communication System
Maharashtra Board-Class-11-Science-Physics-Chapter-13
Solutions
Question 1. Choose the correct option.
(i) The EM wave emitted by the Sun and responsible for heating the Earth’s atmosphere due to green house effect is
(A) Infra-red radiation
(B) X ray
(C) Microwave
(D) Visible light
(A) Infra-red radiation
(ii) Earth’s atmosphere is richest in
(A) UV
(B) IR
(C) X-ray
(D) Microwaves
(B) IR
(iii) How does the frequency of a beam of ultraviolet light change when it travels from air into glass?
(A) No change
(B) increases
(C) decreases
(D) remains same
(D) remains same
(iv) The direction of EM wave is given by
(A) \(\vec{E}\) × \(\vec{B}\)
(B) \(\vec{E}\)·\(\vec{B}\)
(C) along \(\vec{B}\)
(D) along \(\vec{E}\)
(A) \(\vec{E}\) × \(\vec{B}\)
(v) The maximum distance upto which TV transmission from a TV tower of height h can be received is proportional to
(A) h1/2
(B) h
(C) h3/2
(D) h2
(A) h1/2
(vi) The waves used by artificial satellites for communication purposes are..
(A) Microwave
(B) AM radio waves
(C) FM radio waves
(D) X-rays
(A) Microwave
(vii) If a TV telecast is to cover a radius of 640 km, what should be the height of transmitting antenna?
(A) 32000 m
(B) 53000 m
(C) 42000 m
(D) 55000 m
(A) 32000 m
Question 2. Answer briefly.
(i) State two characteristics of an EM wave.
(ii) Why are microwaves used in radar?
Microwaves can penetrate haze, light rain and snow, clouds and smoke. Hence, microwaves are used in radar for locating distant ships and aircrafts.
(iii) What are EM waves?
An electromagnetic wave is a wave of oscillating electric and magnetic fields emitted by an accelerated electric charge, propagating in space at the speed of light. The fields oscillate in phase at right angles to each other and the direction of propagation, with the maximum and minimum values occurring simultaneously.
(iv) How are EM waves produced?
According to Maxwell's electromagnetic theory, an accelerated charge radiates electromagnetic waves. For example,

(v) Can we produce a pure electric or magnetic wave in space? Why?
No. Reason : In vacuum, an electric field cannot directly induce another electric field so a "pure" electric field wave cannot exist and same can be said for a "pure" magnetic wave.
(vi) Does an ordinary electric lamp emit EM waves?
Yes. An incandescent lamp emits both visible and infrared radiations.
(vii) Why do light waves travel in vacuum whereas sound wave cannot?
Light waves do not need a medium for propagation whereas sound waves are mechanical progressive waves that require a material medium for propagation. Hence, sound cannot travel in vacuum while light can.
(viii) What are ultraviolet rays? Give two uses.
UV radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted in atomic transitions of orbital electrons. It is produced when the substance is at very high temperature. Uses of ultraviolet radiation :
(ix) What are radio waves? Give its two uses.
Uses :
(x) Name the most harmful radiation entering the Earth's atmosphere from the outer space.
High energy ultraviolet radiation. It can accelerate aging of skin and cause skin cancer.
(xi) Give reasons for the following:
(i) Long distance radio broadcast uses short wave bands.
(ii) Satellites are used for long distance TV transmission.
(i) Long wave, medium frequency radio broadcasts use ground or surface wave propagation, but their range is limited due to energy losses from absorption by Earth and diffraction around obstacles. Therefore, long distance radio broadcasts use short wave high frequency bands and sky wave or ionospheric propagation. (ii) TV transmission uses the VHF (30 MHz to 300 MHz) and UHF (300 MHz to 3 GHz) ranges of the FM band. Ground wave propagation due to energy losses is very high, making long-distance communication impossible. Short wave communication is also not possible due to the frequencies being higher than critical frequencies for ionospheric reflection. Therefore, communication satellites are necessary for long-distance TV transmission.
(xii) Name the three basic units of any communication system.
There are three basic (essential) elements of every communication system : (1) transmitter (2) communication channel (3) receiver. From the transducers at the transmitting end to those at the receiving end, noise can distort original information. The challenge is to keep the noise to the minimum.
(xiii) What is a carrier wave?
The high-frequency waves on which the signals to be transmitted are superimposed are called carrier waves.
(xiv) Why high frequency carrier waves are used for transmission of audio signals?
Transmitting signal frequencies directly presents several challenges. Hence to address these issues, high radio frequency (RF) carrier waves are used to modulate audio signals before transmission. This ensures efficient transmission of audio signals over a given channel.
(xv) What is modulation?
(xvi) What is meant by amplitude modulation?
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a method where the amplitude of a radio frequency carrier wave is adjusted proportionally to the amplitude of a baseband signal at a frequency equal to the modulating baseband signal. The frequency of the modulated wave is the same as that of the carrier wave.
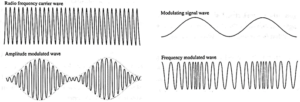
(xvii) What is meant by noise?
Noise, as a term used in a communication system, is unwanted, randomly fluctuating electric energy that tends to distort a signal at any point during communication.
(xviii) What is meant by bandwidth?
Bandwidth :- The bandwidth of an electronic circuit is the range of frequencies over which it operates efficiently. It is measured in hertz. Communication systems have specific bandwidths for efficient operation, affecting various electronic circuits and channels. Point-to-point communication lines have bandwidths ranging from 2 MHz to 100 GHz, while the International Telecommunication Union allocates and monitors different frequency bands for various communication types, including broadcasts, TV transmission, cellular communication, and satellite communication.
(xix) What is demodulation?
The process of recovering the modulating baseband signal from a modulated wave is called demodulation.
(xx) What type of modulation is required for television broadcast?
Frequency modulation.
(xxi) How does the effective power radiated by an antenna vary with wavelength?
The maximum power radiated from a straight antenna of length L is proportional to \((\frac{L}{λ})^2\) where λ is the wavelength of the radiated radio wave. Therefore, the maximum power that can be radiated from an antenna of given length increases as λ decreases or frequency increases. The higher the power radiated, the greater is the transmission range. Hence, it is desirable that the radio waves should have short wavelength i.e., high frequency.
(xxii) Why should broadcasting programs use different frequencies?
A receiver in a communication system selectively picks up a desired modulated wave from a communication channel, detects the baseband signal, and feeds it after amplification to an appropriate electrical transducer for conversion into a nonelectrical signal, such as sound, light, etc. for the user of information. Different broadcasting stations are allotted different, well separated, carrier frequencies for distinct reception.
(xxiii) Explain the necessity of a carrier wave in communication.
High frequency carrier waves are used to modulate information signals to overcome transmission difficulties.
(xxiv) Why does amplitude modulation give noisy reception?
An amplitude modulated wave is susceptible to noise which distorts the transmitted signal at any point during communication. A receiver cannot distinguish between the amplitude variations representing a noise and those of a modulated carrier. Hence, amplitude modulation gives noisy reception.
(xxv) Explain why is modulation needed.
Question 2. Solve the numerical problem.
(i) Calculate the frequency in MHz of a radio wave of wavelength 250 m. Remember that the speed of all EM waves in vacuum is 3.0 × 108 m/s.
Given : λ0 = 250 m, co = 3.0 x 108 m/s The frequency of the radio wave, ν = \(\frac{c_0}{λ_0}\) = \(\frac{3.0×10^8}{250}\) = 1.2 × 106 Hz = 1.2 MHz
(ii) Calculate the wavelength in nm of an X-ray wave of frequency 2.0 × 1018 Hz.
Given : ν = 2.0 × 1018 Hz, co = 3.0 x 108 m/s The wavelength of the X-ray wave, λ0 = \(\frac{c_0}{ν}\) = \(\frac{3.0×10^8}{2.0×10^{18}}\) = 1.5 × 10−10 m = 0.15 × 10−9 m = 0.15 nm
(iii) The speed of light is 3 × 108 m/s. Calculate the frequency of red light of wavelength of 6.5 × 10-7 m.
Given : λ0 = 6.5 × 10-7 m, co = 3.0 x 108 m/s The frequency of the red light, ν = \(\frac{c_0}{λ_0}\) = \(\frac{3.0×10^8}{6.5×10^{-7}}\) = 4.615 × 1014 Hz
(iv) Calculate the wavelength of a microwave of frequency 8.0 GHz.
Given : ν = 80 GHz = 8.0 × 109 Hz, co = 3.0 x 108 m/s The wavelength of the microwave, λ0 = \(\frac{c_0}{ν}\) = \(\frac{3.0×10^8}{8.0×10^9}\) = 3.75 × 10−2 m = 3.75 cm
(v) In a EM wave the electric field oscillates sinusoidally at a frequency of 2 × 1010 Hz. What is the wavelength of the wave?
Given : ν = 2.0 × 1010 Hz, co = 3.0 x 108 m/s The wavelength of the microwave, λ0 = \(\frac{c_0}{ν}\) = \(\frac{3.0×10^8}{2.0×10^{10}}\) = 1.5 × 10−2 m
(vi) The amplitude of the magnetic field part of a harmonic EM wave in vacuum is B0 = 5 × 10-7 T. What is the amplitude of the electric field part of the wave?
Given : B0 = 5 × 10-7 T, co = 3.0 x 108 m/s The wavelength of the microwave, c0 = \(\frac{E_0}{B_0}\), ∴ E0 = coB0 = (3.0 x 108)( 5 × 10-7) = 150 N/C = 150 V/m 150 V/m is the amplitude of the electric field part of the wave.
(vii) A TV tower has a height of 200 m. How much population is covered by TV transmission if the average population density around the tower is 1000/km2? (Radius of the Earth = 6.4 × 106 m)
Given : h = 200 m, R = 6.4 x 106 m, average population density = 1000/km2 = 10-3/m2 Range, d = \(\sqrt{2Rh}\) = (\sqrt{2×6.4×10^6×200}\) = 5.06 × 104 m ∴ Area covered = πd2 = 3.142 x (5.06 x 104)2 = 80.44 × 108 m2 ∴ The population covered by TV transmission = 10-3 x 80.44 × 108 = 8.044 × 106
(viii) Height of a TV tower is 600 m at a given place. Calculate its coverage range if the radius of the Earth is 6400 km. What should be the height to get the double coverage area?
Given : h = 600 m, R = 6.4 x 106 m, (i) The coverage range of the TV tower, d = \(\sqrt{2Rh}\) = \(\sqrt{2×6.4×10^6×600}\) = 8.764 × 104 m = 87.64 km (ii) Coverage area, A = πd2 ∴ A1 = πd12 and A2 = πd22 ∴ \(\frac{A_2}{A_1}\) = \(\frac{d_2^2}{d_1^2}\) = \(\frac{2Rh_2}{2Rh_1}\) = \(\frac{h_2}{h_1}\) For \(\frac{A_2}{A_1}\) = 2, h2 = 2h1 = 2 x 600 = 1200 m This is the required height of a TV tower.
(ix) A transmitting antenna at the top of a tower has a height 32 m and that of the receiving antenna is 50 m. What is the maximum distance between them for satisfactory communication in line of sight mode ? Given radius of Earth is 6.4 × 106 m.
Given : h1 = 32 m, h2 = 50 m, R = 6.4 x 106 m dmax = \(\sqrt{2Rh_1}\) + \(\sqrt{2Rh_2}\) = \(\sqrt{2×6.4×10^6×32}\) + \(\sqrt{2×6.4×10^6×50}\) = \(\sqrt{409.6}\) × 103 + \(\sqrt{640}\) × 103 = 20.24 × 103 m + 25.3 × 103 m = 45.54 × 103 m = 45.54 km This is the required maximum distance.
PDF : Class 11th-Physics-Chapter-13-Electromagnetic Waves and Communication System-Text Book
PDF : Class 11th-Physics-Chapter-13-Electromagnetic Waves and Communication System- Notes
PDF : Class 11th-Physics-Chapter-13-Electromagnetic Waves and Communication System-Solution
All Chapters Notes-Class-11-Science-Physics-(14 PDF)
All Chapters Solutions-Class-11-Science-Physics-(14 PDF)
All Chapters Notes + Solutions-Class-11-Science-Physics-(28 PDF)
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 11th-Physics – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 12: Magnetism – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter 14: Semiconductors – Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.