Elements of Group 13, 14 and 15
Maharashtra State Board-Class-11-Science-Chemistry-Chapter -9
Solutions
Question 1. Choose correct option.
(A) Which of the following is not an allotrope of carbon ?
(a) bucky ball
(b) diamond
(c) graphite
(d) emerald
(d) emerald
(B) is inorganic graphite
(a) borax
(b) diborane
(c) boron nitride
(d) colemanite
(c) boron nitride
(C) Haber’s process is used for preparation of
(a) HNO3
(b) NH3
(c) NH2CONH2
(d) NH4OH
(b) NH3
(D) Thallium shows different oxidation state because
(a) of inert pair effect
(b) it is inner transition element
(c) it is metal
(d) of its high electronegativity
(a) of inert pair effect
(E) Which of the following shows most prominent inert pair effect ?
(a) C
(b) Si
(c) Ge
(d) Pb
(d) Pb
Question 2. Identify the group 14 element that best fits each of the following description.
(A) Non metallic element
Carbon
(B) Form the most acidic oxide
Carbon
(C) They prefer +2 oxidation state.
Pb and Sn
(D) Forms strong π bonds.
Carbon.
Question 3. Give reasons.
(A) Ga3+ salts are better reducing agent while Tl3+ salts are better oxidising agent.
(B) PbCl4 is less stable than PbCl2
Question 4. Give the formula of a compound in which carbon exhibit an oxidation state of
(A) +4
(B) +2
(C) −4
(A) +4 : CO2 (B) +2 : CO (C) −4 : CH4
Question 5. Explain the trend of the following in group 13 elements :
(A) atomic radii
(B) ionization enthalpy
(C) electron affinity
Question 6. Answer the following
(A) What is hybridization of Al in AlCl3?
Aluminium in AlCl3 undergoes sp2 hybridisation.
(B) Name a molecule having banana bond.
Diborane (B2H6)
Question 7. Draw the structure of the following
(A) Orthophosphoric acid
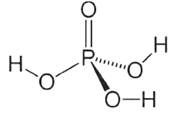
(B) Resonance structure of nitric acid
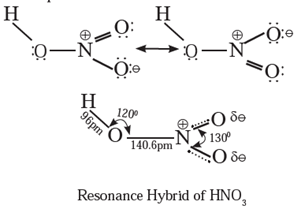
Question 8. Find out the difference between
(A) Diamond and Graphite.
Diamond
Graphite
Diamond is very hard.
Graphite is soft and slippery
Diamond has three dimensional network of sp3−hybridised carbon atoms joined by extended covalent bonds which are difficult to break.
Graphite has two dimensional sheet like structure, like layers of hexagonal rings from sp2−hybridised carbon atoms. These layers are held by weak van der Waals forces, which can be broken easily.
Used as an abrasive.
Used as lubricant.
Diamond is a non−conductor of electricity.
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
Diamond does not have any mobile, delocalised electrons in its structure since all electrons are involved in covalent bonding.
Graphite has delocalised electrons which are mobile all over the sheet like structure of graphite. These electrons conduct electricity.
(B) White phosphorus and Red phosphorus
White phosphorus
Red phosphorus
It has discrete tetrahedral P4 molecules.
It has chains of P4 tetrahedra linked by covalent bonds.
It glows in dark.
It does not glow in dark.
It is less stable and more reactive.
It is stable and less reactive.
It is poisonous.
It is nonpoisonous.
Question 9. What are silicones ? Where are they used ?
Silicones are organo silicon polymers containing repeated R2SiO units, where R is an alkyl group or an aryl group held by They have empirical formula R2SiO. Since, it is similar to that of ketones (R2CO), these compounds are names as silicones. Uses of silicones :
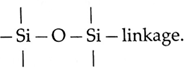
Question 10. Explain the trend in oxidation state of elements from nitrogen to bismuth.
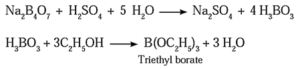
Question 11. Give the test that is used to detect borate radical is qualitative analysis.
When borax is heated with ethyl alcohol and concentrated H2SO4 volatile vapours of triethylborate are formed which burn with green flame. This flame test is used to detect borate radical (BO3−3) in the qualitative analysis.
Question 12. Explain structure and bonding of diborane.
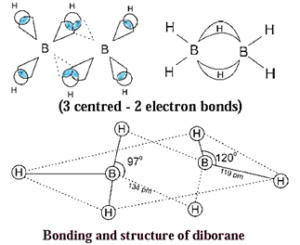
Question 13. A compound is prepared from the mineral colemanite by boiling it with a solution of sodium carbonate. It is white crystalline solid and used for inorganic qualitative analysis.
(a) Name the compound produced.
(b) Write the reaction that explains its formation.
(a) The compound obtained is borax. (b) Borax is prepared from its mineral by boiling it with a solution of sodium carbonate. On crystallisation it forms Na2B4O7.10H2O. (It is a white solid).
![]()
Question 14. Ammonia is a good complexing agent. Explain.
The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom facilitates the complexation of ammonia with transition metal ions. Thus, ammonia is a good complexing agent as it forms a complex by donating its lone pair of electrons. This reaction is used for the detection of metal ions such as Cu2+ and Ag+.
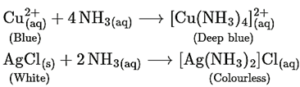
Question 15. State true or false. Correct the false statement.
(A) The acidic nature of oxides of group 13 increases down the graph.
False. The acidic nature of oxides of group 13 decreases down the group. The last two elements form amphoteric oxides SnO2 and PbO2.
(B) The tendency for cantenation is much higher for C than for Si.
True.
Question 16. Match the pairs from column A and B.
| A | B |
| BCl3 | Angular molecule |
| SiO2 | Linear covalent molecule |
| CO2 | Tetrahedral molecule |
| Planar trigonal molecule |
A
B
BCl3
Planar trigonal molecule
SiO2
Tetrahedral molecule
CO2
Linear covalent molecule
Question 17. Give the reactions supporting basic nature of ammonia.
Basic nature of ammonia is due to the formation of OH− ions. NH3(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ NH4+(aq) + OH−(aq) The following reactions show the basic nature of ammonia. (1) Ammonia reacts with acids to form salts. NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl 2NH3 + H2SO4 → (NH4)2 SO4. (2) Aqueous solution of ammonia precipitates hydroxides of metals from their salt solutions. ZnSO4(aq) + 2NH4OH(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s) + (NH4)2 SO4(aq) FeCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(aq) → Fe(OH)3(s) + 3NH4Cl(aq)
Question 18. Shravani was performing inorganic qualitative analysis of a salt. To an aqueous solution of that salt, she added silver nitrate. When a white precipitate was formed. On adding ammonium hydroxide to this, she obtained a clear solution. Comment on her observations and write the chemical reactions involved.
The aqueous salt solution which Shravani used contains Cl− anions. These Cl− ions give white precipitate with silver nitrate solution. Cl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → AgCl(s) + NO3(aq) Further, on adding ammonium hydroxide to the white precipitate, a clear solution is obtained as white precipitate of AgCl dissolves in ammonium hydroxide forming a complex. AgCl(s) + 2NH4OH → [Ag(NH3)2] Cl(aq) + 2H2O
PDF : Class-11-Chemistry-Chapter-9-Elements of Group 13, 14 and 15- Notes
PDF : Class-11-Chemistry-Chapter-9-Elements of Group 13, 14 and 15-Solution
All 16 Chapters Notes -11-Chemistry-(16 PDF) Rs.132
All 16 Chapters-Solutions-11-Chemistry- (16 PDF) Rs.128
All 16 Chapters-Notes+Solutions-11-Chemistry- (32 PDF) Rs.228
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 11th-Chemistry – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-8-Elements of Group 1 and 2 – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-10-States of Matter – Online Solutions