Hydrocarbons
Maharashtra State Board-Class-11-Science-Chemistry-Chapter -15
Solutions
Question 1. Choose correct options
(A) Which of the following compound has highest boiling point ?
(a) n-pentane
(b) iso-butane
(c) butane
(d) neopentane
(a) n-pentane
(B) Acidic hydrogen is present in :
(a) acetylene
(b) ethane
(c) ethylene
(d) dimethyl acetylene
(a) acetylene
(C) Identify 'A' in the following reaction:

(a) KMnO4/H+
(b) alkaline KMnO4
(c) dil. H2SO4/1% HgSO4
(d) NaOH/H2O2
(a) KMnO4/H+
(D) Major product of chlorination of ethyl benzene is :
(a) m-chlorethyl benzene
(b) p - chloroethyl benzene
(c) chlorobenzene
(d) o - chloroethylbenzene
(b) p - chloroethyl benzene
(E) 1 - chloropropane on treatment with alc. KOH produces :
(a) propane
(b) propene
(c) propyne
(d) propyl alcohol
(b) propene
Question 2. Name the following :
(A) The type of hydrocarbon that is used as lubricant.
The hydrocarbon that are used as lubricant are branched paraffins, cyclic alkanes and aromatic hydrocarbon.
(B) Alkene used in the manufacture of polythene bags.
Alkene used in the manufacture of polythene bags. - Ethene
(C) The hydrocarbon said to possess carcinogenic property.
Aromatic polycyclic compounds and benzene possess carcinogenic property.
(D) What are the main natural sources of alkane?
Natural sources of alkane :
(E) Arrange the three isomers of alkane with molecular formula C5H12 in increasing order of boiling points and write their IUPAC names.
The three isomers of C5H12 in the increasing order of boiling points and their IUPAC names : (1) IUPAC name : 2, 2-Dimethylpropane (New Pentane), Boiling point : 10 ℃ (2) IUPAC name : 2-Methyl butane (Isopentane), Boiling point : 27.8 ℃ (3) IUPAC name : Pentane (n-Pentane), Boiling point : 36.1 ℃
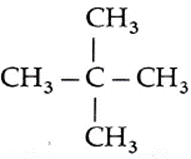
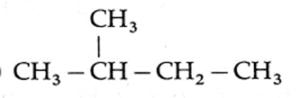
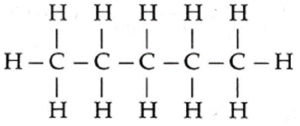
(F) Write IUPAC names of the products obtained by the reaction of cold concentrated sulphuric acid followed by water with the following compounds.
(a) propene (b) but-l-ene
The IUPAC names of the products. (a) Propan-2-ol (b) Butan-2-ol
(G) Write the balanced chemical reaction for preparation of ethane from
(a) Ethyl bromide
(b) Ethyl magnesium iodide
(a) Preparation of ethane from ethyl bromide: CH3-CH2-Br + 2H \(\underrightarrow{Zn/HCl}\) CH3-CH3 + HBr (b) From Ethyl magnesium bromide : CH3-CH2-Mg-Br + H-O-H \(\underrightarrow{dil. HCl}\) CH3-CH3 + MgBr(OH)
(H) How many monochlorination products are possible for
(a) 2-methylpropane ?
(b) 2-methylbutane ?
Draw their structures and write their IUPAC names.
(a) Two products are possible for chlorination of 2-methyl propane. (b) Two products are possible for chlorination of 2-methylbutane.



(I) Write all the possible products for pyrolysis of butane.
Pyrolysis of n-butane forms the following alkenes
C4H10 Butane
CH3-CH2-CH=CH2
But-1-ene
CH3-CH=CH-CH3
But-2-ene
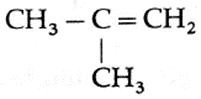
2-Methyl prop-1-ene
CH3-CH=CH2
Propene
CH2 = CH2
ethene
(J) Which of the following will exhibit geometrical isomerism ?
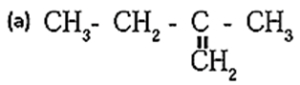
(b) (CH3)2C=CH2
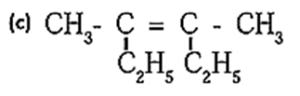
Option (a): This structure does not have a double bond that fulfills the conditions for geometrical isomerism. Therefore, this compound does not exhibit geometrical isomerism. Option (b) : The carbon atom on the left has two identical methyl groups (CH3). Since both groups are the same, geometrical isomerism is not possible here. Option (c) : The double bond in this compound has two different groups on both carbons of the double bond (CH3 and C2H5). This satisfies the condition for geometrical isomerism. Hence, this compound will exhibit geometrical isomerism. Correct Answer: (c)
(K) What is the action of following on ethyl iodide ?
(a) alc, KOH
(b) Zn, HCl
(a) The action of alc. KOH on ethyl iodide: CH3-CH2-I + alc. KOH \(\underrightarrow{Δ}\) CH2=CH2 + KI + H2O (b) Action of Zn, HCl : CH3-CH2-I + H2 \(\underrightarrow{Zn/HCl}\) CH3-CH3 + HI
(L) An alkene ‘A’ an ozonolysis gives 2 moles of ethanal. Write the structure and IUPAC name of ‘A’.
The structure and IUPAC name of A is

(M) Acetone and acetaldehyde are the ozonolysis products of an alkene. Write the structural formula of an alkene and give IUPAC name of it.
The structural formula of an alkene is
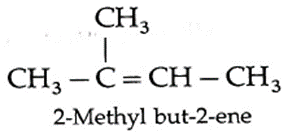
(N) Write the reaction to convert
(a) propene to nypropylalcohol.
(b) propene to isoproyl alcohol.
(a) Propene to n-propyl alcohol : CH3-CH= CH2 + HBr \(\underrightarrow{Benzoyl\,perodoxide}\) H3C-CH2-CH2-Br (n-propyl bromide) (b) Propene to isopropyl alcohol :

(O) What is the action of following on but-2-ene ?
(a) dil alkaline KMnO4
(b) acidic KMnO4
(a) Action of dil alkaline KMnO4 (b) Action of acidic KMnO4
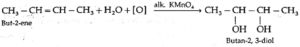

(P) Complete the following reaction sequence :
HC ≡ CH \(\underrightarrow{LiNH_2}\) A \(\underrightarrow{CH_3CH_2Cl}\) B \(\underrightarrow{HBr}\) C
Comment on the acidic nature of B.
In But-1-yne (B), the sp hybrid carbon atom on terminal alkynes is more electronegative than sp2 carbon atom in alkene. Due to high electronegative character of carbon in terminal alkyne, proton can be easily given away to very strong base. Hence But-1-yne is acidic in nature.

(Q) Write the balanced chemical reactions to get benzene from
(a) Sodium benzoate.
(b) Phenol.
(a) From Sodium benzoate. (b) From Phenol.
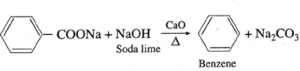
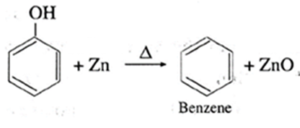
(R) Predict the possible products of the following reaction.
(a) chlorination of nitrobenzene,
(b) sulfonation of chlorobenzene,
(c) bromination of phenol,
(d) nitration of toluene.
(a) Chlorination of nitrobenzene : (b) Sulfonation of chlorobenzene : (c) Bromination of phenol : (d) Nitration of toluene :



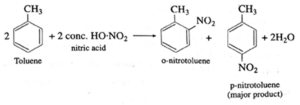
Question 3. Identify the main product of the Reaction
(a) CH3-CH2-CH3 \(\underrightarrow{O_2/Δ}\)
CH3-CH2-CH3 \(\underrightarrow{O_2/Δ}\) 3CO2 + 4H2O + Heat
(b)

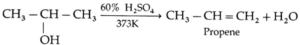
(c) HC ≡ C-CH3 \(\underrightarrow{(H_2)/(Pd-C/quinoline)}\)
HC ≡ C-CH3 \(\underrightarrow{(H_2)/(Pd-C/quinoline)}\) CH3-CH=CH2 (Propene)
(d) H-C ≡ CH3 + H2O \(\underrightarrow{(40%H_2SO_4)/(1%HgSO_4)}\)
Alkynes react with water in the presence of 40% sulphuric acid and 1% mercuric sulphate to form aldehydes or ketones i.e. carbonyl compounds. [Note : The reactant H-C ≡ CH3 given in this reaction is modified to H-C ≡ C-CH3]

Question 4. Read the following reaction and answer the questions given below.

(a) Write IUPAC name of the product.
(b) State the rule that governs formation of this product.
(a) IUPAC name : 1-Bromopropane (b) The rule that governs formation of 1-Bromopropane is Anti-Markovnikov addition or peroxide effect or Kharasch-Mayo effect. The addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkene in the presence of organic peroxide (R -O-O-R) takes place in the opposite orientation to that of Markovnikov's rule.
Question 5. Identify A, B, C in the following reaction sequence :
![]()

Question 6. Identify giving reason whether the following compounds are aromatic or not.

Question 7. Name two reagents used for acylation of benzene.
(i) Acetic anhydride (CH3CO)2O (ii) Acetyl chloride CH3COCl
Question 8. Read the following reaction and answer the questions given below.

(A) Write the name of the reaction.
(B) Identify the electrophile in it.
(C) How is this electrophile generated?
(A) The name of the reaction is Friedel-Craft's alkylation. (B) Electrophile : +CH3 (C) The generation of electrophile : CH3-Cl + AlCl3 → +CH3 + AlCl4 Methyl carbocation
PDF : Class-11-Chemistry-Chapter-15-Hydrocarbons-Text Book
PDF : Class-11-Chemistry-Chapter-15-Hydrocarbons- Notes
PDF : Class-11-Chemistry-Chapter-15-Hydrocarbons-Solution
All 16 Chapters Notes -11-Chemistry-(16 PDF) Rs.132
All 16 Chapters-Solutions-11-Chemistry- (16 PDF) Rs.128
All 16 Chapters-Notes+Solutions-11-Chemistry- (32 PDF) Rs.228
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 11th-Chemistry – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-14-Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-16-Chemistry in Everyday Life – Online Solutions