Question 1.
Choose correct option
(A) Which one of the following organisms would spend maximum energy in production of nitrogenous waste?
(a) Polar bear
(b) Flamingo
(c) Frog
(d) Shark
(B) In human beings, uric acid is formed due to metabolism of __________.
(a) amino acids
(b) fatty acids
(c) creatinine
(d) nucleic acids
(C) Visceral layer : Podocytes :: PCT : _______
(a) Cilliated cells
(b) Squamous cells
(c) Columnar cells
(d) Cells with brush border
Answer :
(d) Cells with brush border
(D) Deproteinised plasma is found in __________.
(a) Bowman's capsule
(b) Descending limb
(c) Glomerular capillaries
(d) Ascending limb
Answer :
(c) Glomerular capillaries
(E) Specific gravity of urine would _______ if level of ADH increases.
(a) remain unaffected
(b) increases
(c) decreases
(d) stabilise
(F) What is micturition?
(a) Urination
(b) Urine formation
(c) Uremia
(d) Urolithiasis
(G) Which one of the following organisms excrete waste through nephridia?
(a) Cockroach
(b) Earthworm
(c) Crab
(d) Liver Fluke
(H) Person suffering from kidney stone is advised not to have tomatoes as it has _______.
(a) seeds
(b) lycopene
(c) oxalic acid
(d) sour taste
(I) Tubular secretion does not take place in ________.
(a) DCT
(b) PCT
(c) collecting duct
(d) Henle's loop
(J) The minor calyx ____________.
(a) collects urine
(b) connects pelvis to ureter
(c) is present in the cortex
(d) receives column of Bertini
(K) Which one of the followings is not a part of human kidney?
(a) Malpighian body
(b) Malpighian tubule
(c) Glomerulus
(d) Loop of Henle
(L) The yellow colour of the urine is due to presence of ___________
(a) uric acid
(b) cholesterol
(c) urochrome
(d) urea
(M) Hypotonic filtrate is formed in _______
(a) PCT
(b) DCT
(c) LoH
(d) CT
(N) In reptiles, uric acid is stored in _____
(a) cloaca
(b) fat bodies
(c) liver
(d) anus
(O) The part of nephron which absorbs glucose and amino acid is______
(a) collecting tubule
(b) proximal tubule
(c) Henle's loop
(d) DCT
(P) Bowman's capsule is located in kidney in the ________
(a) cortex
(b) medulla
(c) pelvis
(d) pyramids
(Q) The snakes living in desert are mainly__________
(a) aminotelic
(b) ureotelic
(c) ammonotelic
(d) uricotelic
(R) Urea is a product of breakdown of ___________
(a) fatty acids
(b) amino acids
(c) glucose
(d) fats
(S) Volume of the urine is regulated by__________
(a) aldosterone
(b) ADH
(c) both a and b
(d) none
Question 2.
Answer the following questions
(A) Doctors say Mr. Shaikh is suffering from urolithiasis. How it could be explained in simple words?
Answer :
Urolithiasis is the process of formation of stones in the kidney, bladder and/or urethra. Hence, in simple words, it can be said that Mr. Shaikh has been diagnosed with kidney stones.
(B) Anitaji needs to micturate several times and feels very thirsty. This is an indication of change in permeability of certain part of nephron. Which is this part?
Answer :
- A sign of diabetes insipidus is the need to micturate multiple times and feeling extremely thirsty (imbalance of fluids in the body).
- ADH inhibits diuresis, and when ADH is absent, a considerable amount of dilute urine is excreted.
- ADH promotes reabsorption of water from the final section of the DCT and the whole collecting duct by enhancing cell permeability.
- When the permeability of these cells changes, it causes an increase in urine volume (frequent micturition) and a rise in blood osmolarity. Thirst is increased by an imbalance in the volume and osmolarity of bodily fluids.
(C) Effective filtration pressure was calculated to be 20 mm Hg; where glomerular hydrostatic pressure was 70 mm of Hg. Which other pressure is affecting the filtration process? How much is it?
Answer :
The other pressure affecting the filtration process is osmotic pressure of blood and capsular pressure.
Commonly effective filtration pressure (EFP) is represented as :
EFP = Hydrostatic pressure in glomerulus — (Osmotic pressure of blood + Filtrate Hydrostatic pressure)
If EFP = 20 mmHg and Hydrostatic pressure of glomerulus = 70 mmHg
Then (Osmotic pressure of blood + Filtrate Hydrostatic pressure) = 70 – 20 = 50 mmHg
(D) Name any one guanotelic organism.
Answer :
Animals such as spiders, scorpions and penguins are guanotelic organisms as they excrete guanine.
(E) Why are kidneys called 'retroperitoneal'?
Answer :
Kidneys are located in abdomen. Kidneys are not surrounded by peritoneum instead they are located posterior to it. Thus, kidneys are called retroperitoneal.
(F) State role of liver in urea production.
Answer :
- Ammonia is converted into urea in the liver of ureotelic animals.
- This conversion takes place by the help of the ornithine / urea cycle.
- 3 ATP molecules are used to produce one molecule of urea using the omithine/ urea cycle.
Hence, since the liver contains carrier molecules and enzymes necessary for urea cycle, it plays a major role in urea production.
(G) Why do we get bad breath after eating garlic or raw onion?
Answer :
- Raw onion and garlic contain volatile sulphur-containing compounds.
- Sulphur-containing compounds have a distinctive odour which remain in the mouth after consumption of onion and garlic.
- Also, volatile compounds (like certain sulphur containing compounds) in foodstuff are generally excreted through the lungs and may result in bad breath.
Question 3.
Answer the following questions
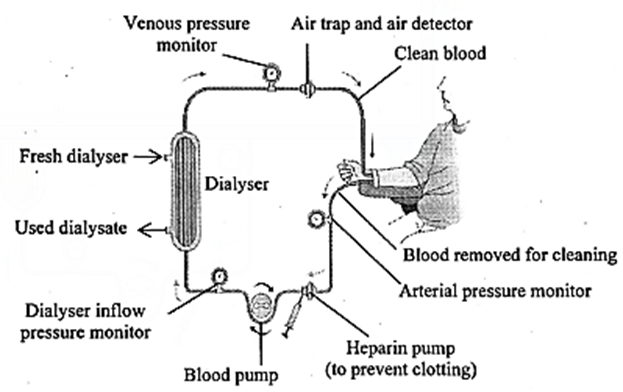
(A) John has two options as treatment for his renal problem : Dialysis or kidney transplants. Which option should he choose? Why?
Answer :
- If John has two options of dialysis and kidney transplant, readily available he must opt for kidney transplant.
- A kidney transplant, if successful, can improve the quality of life of a patient and reduce the risk of death.
- The patient would not have to endure frequent dialysis procedures. Repeated visits for dialysis takes time and may not allow the patient to perform normal activities or go to office regularly.
- Dialysis is regarded as a holding measure until kidney transplant can be performed or a supportive measure in those for whom a transplant would be inappropriate. Hence, if John has an option of kidney transplant, he must opt for it.
(B) Amphibian tadpole can afford to be ammonotelic. Justify.
Answer :
- Ammonia is very toxic and requires large quantity of water for its elimination.
- Tadpole (larval stage of life cycle of amphibian) is aquatic.
- The water lost during excretion can be made up through the surrounding water
Hence, amphibian tadpole can afford to be ammonotelic.
(C) Birds are uricotelic in nature. Give reason.
Answer :
- The 'inosinic acid pathway' in birds' livers is capable of converting ammonia to uric acid.
- Because uric acid is the least harmful, it can be stored in the body for a long time.
- It requires a negligible amount of water to be eliminated.
- This style of excretion can also aid reduce body weight (for flight), and uricotelism is followed by animals that need to conserve more water.
- Birds are thus uricotelic in nature in order to preserve water as an adaptation for flight.
Question 4.
Write the explanation in your word
(A) Nitya has been admitted to hospital after heavy blood loss. Till proper treatment could be given; how did Nitya's body must have tackled the situation?
Answer :
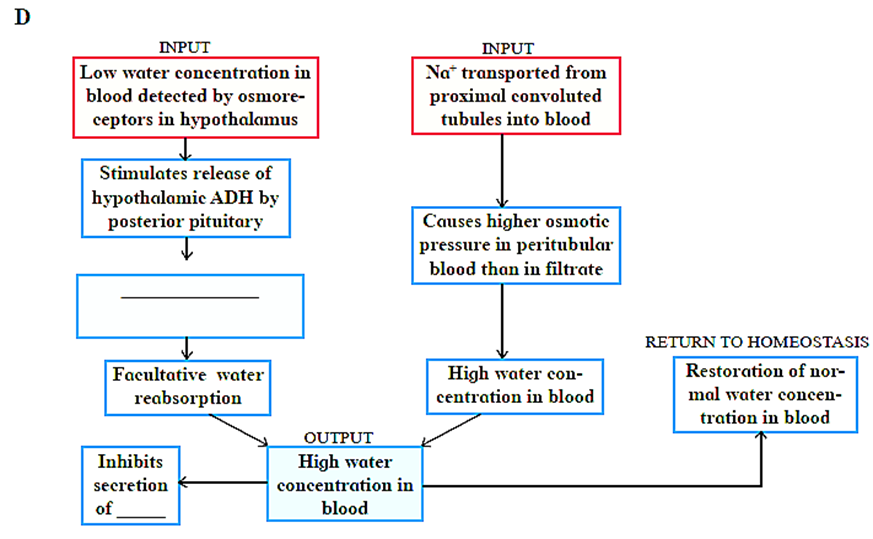
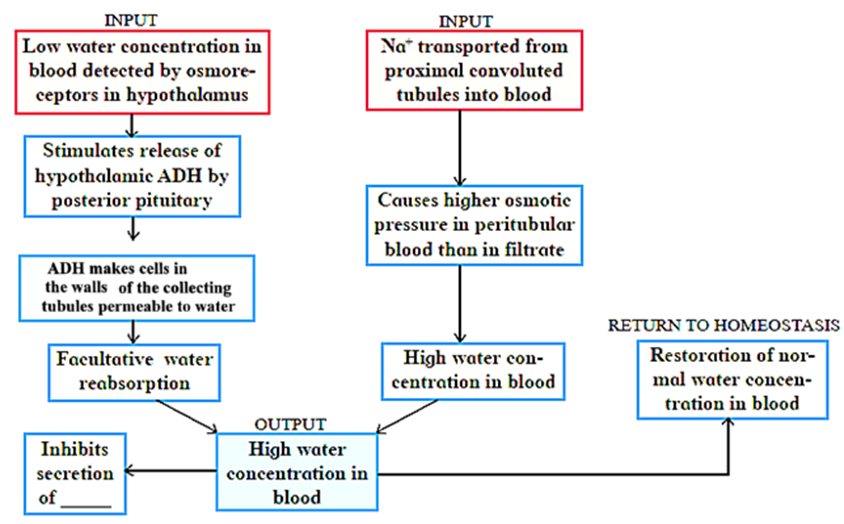
Incase of haemorrhage or severe dehydration, the osmoreceptors stimulate Antidiuretie hormone (ADH) secretion.
ADH is important in regulating water balance through the kidneys. For derailed mechanism of reabsorption by ADH:
Regulating water reabsorption through ADH:
- Hypothalamus in the midbrain has special receptors called osmoreceptors which can detect change in osmolarity (measure of total number of dissolved particles per liter of solution) of blood.
- If osmolarity of blood increases due to water loss from the body (after eating namkeen or due to sweating), osmoreceptors trigger release of Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary).
- ADH stimulates reabsorption of water from last part of DCT and entire collecting duct by increasing the permeability of cells.
- This leads to reduction in urine volume and decrease in osmolarity of blood.
- Once the osmolarity of blood comes to nonnal, activity of osmoreceptor cells decreases leading to decrease in ADH secretion. This is called negative feedback.
- In case of hemorrhage or severe dehydration too, osmoreceptors stimulate ADH secretion. ADH is important in regulating water balance through kidneys.
- In absence of ADH, diuresis (dilution of urine) takes place and person tends to excrete large amount of dilute urine. This condition called as diabetes insipidus.
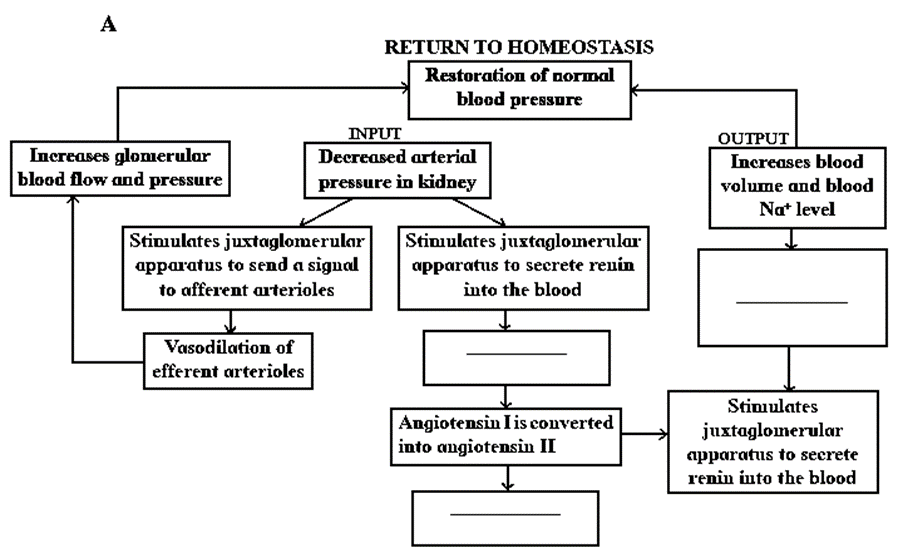
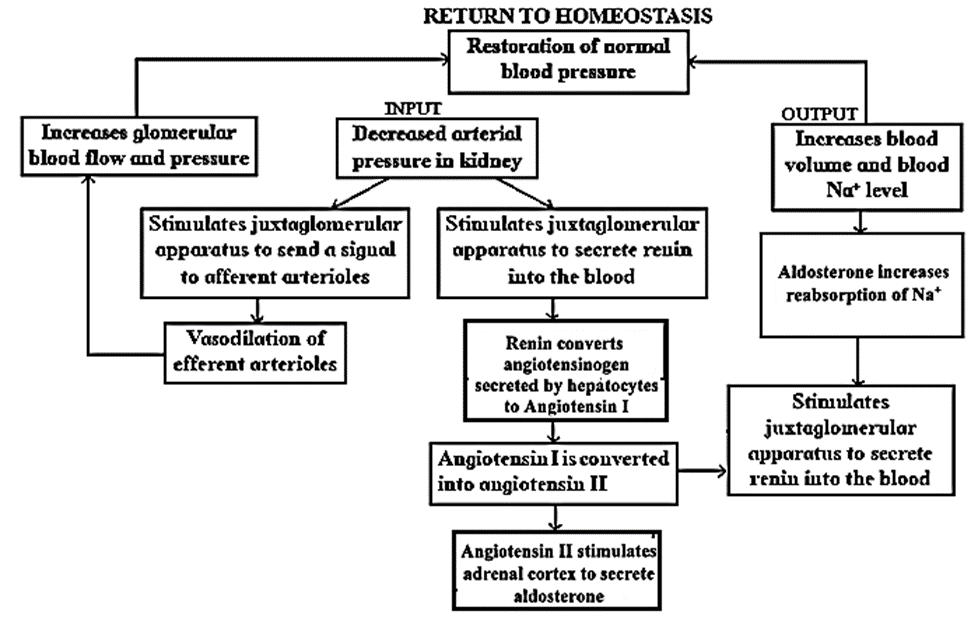
Another regulatory mechanism that must have been activated is RAAS.
Electrolyte reahsorption through RAAS:
- Another regulatory mechanism is RAAS (Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System) by Juxta Glomemlar Apparatus (JGA).
- Whenever blood supply (due to change in blood pressure or blood volume) to afferent arteriole decreases (e.g. low BP/dehydration), JGA cells release Renin. Renin converts angiotensinogen secreted by hepatocytes in liver to Angiotensin I. ‘Angiotcnsin converting enzyme’ further modifies Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II, the active form of hormone. It stimulates adrenal cortex to release another hormone called aldosterone that stimulates DCT and collecting ducts to reabsorb more Na+ and water, thereby increasing blood volume and pressure.
Question 5.
Complete the diagram / chart with correct labels / information. Write the conceptual details regarding it
Answer :
Nephrons :
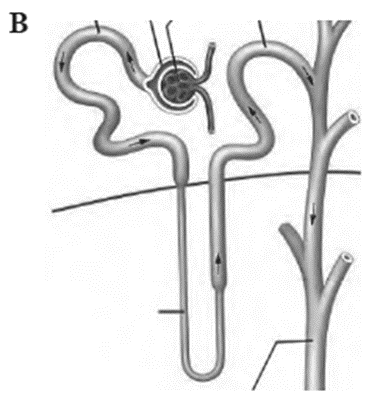
- Nephrons are structural and functional units of kidney.
- Each nephron consists of a 4-6 cm long, thin-walled tube called the renal tubule and a bunch of capillaries known as the glomerulus.
- The wall of the renal tubule is made up of a single layer of epithelial cells.
- Its proximal end is wide, blind, cup-like and is called as Bowman’s capsule, whereas the distal end is open.
- The nephron is divisible into Bowman’s capsule, neck proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), Loop of Henle (LoH), distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting tubule (CT).
- The glomerulus is present in the cup-like cavity of B0wman’s capsule and both are collectively known as renal corpuscle or Malpighian bodv.
Answer :

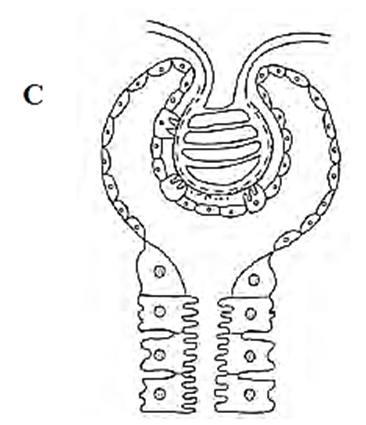
(i) Malpighian body: Each Malpighian body is about 200um in diameter and consists of a Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus.
Glomerulus:
- Glomerulus is a bunch of fine blood capillaries located in the cavity of Bowman’s capsule.
- A small terminal branch of the renal artery, called as afferent arteriole enters the cup cavity
- (Bowman capsule) and undergoes extensive fine branching to form network of several capillaries.
- This bunch is called as glomerulus.
- The capillary wall is fenestrated (perforated).
- All capillaries reunite and form an efferent arteriole that leaves the cup cavity.
- The diameter of the afferent arteriole is greater than the efferent arteriole. This creates a high hydrostatic pressure essential for ultrafiltration, in the glomerulus.
Bowman’s capsule:
- It is a cup-like structure having double walls composed of squamous epithelium.
- The outer wall is called as parietal wall and the inner wall is called as visceral wall.
- The parietal wall is thin consisting of simple squamous epithelium.
- There is a space called as capsular space / urinary space in between two walls.
- Visceral wall consists of special type of squamous cells called podocytes having a foot-like pedicel.
- These podocytes are in close contact with the walls of capillaries of glomerulus.
- There are small slits called as filtration slits in between adjacent podocytes.
Question 6.
Prove that mammalian urine contains urea.
Answer :
- Urea is a nitrogenous waste formed by breakdown of protein (deamination of amino acids).
- During this process, amino groups are removed from the amino acids present in the proteins and converted to highly toxic ammonia. The ammonia is finally converted to area through ornithine cycle. Thus, the urea formed is passed to kidneys and excreted out of the body through urine.
- Reabsorption of urea (proximal tubule, collecting ducts) and active secretion of urea (Henle loop) leads to a urea circulation (urea recycling) between the lumen of the nephron and renal medulla, which is an important element of the renal urine concentration.
- About 54 g of urea are filtered per day in the glomerular capsule, of which approximately 30 g is excreted in the urine and 24 g is reabsorbed into blood (assuming GFR is 180 litres/day).
- Urinalysis can help detect the amount of urea in urine (Urine urea nitrogen test, urease test, etc.).







We reply to valid query.