Linear Equations in Two Variables
Class-10-Mathematics-1-Chapter-1-Maharashtra Board
Solutions (Practice Set 1.1, 1.2)
Practice Set 1.1
Question 1.
Complete the following activity to solve the simultaneous equations :
5x + 3y = 9 …..(1)
2x - 3y = 12 (2)
Let’s add equations (1) and (2) \(\begin{array}{rrrrrrr} ∴ x = 3 Place x = 3 in equation …..(1). 5´× [3] + 3y = 9 3y = 9 –[15] ∴ 3y = [-6] \(∴ y =\frac{-6}{3}\) ∴ y = [-2] ∴ Solution is (x, y) = ([3],[-2])
& 5x & + & 3y & = & 9 &\text{…..(1)}\\
+ & & & & & & \\
& 2x & - & [3y] & = & 12 &\text{…..(2)} \\ \hline
& 7x & & & = & 21 & \\
\end{array}\)
Question 2.
Solve the following simultaneous equations :
(1) 3a + 5b = 26; a + 5b = 22.
3a + 5b = 26 …..(1) a + 5b = 22 ……(2) Subtracting equation (2) from equation (1), \(\begin{array}{rrrrrrr} ∴ a = 2 (Dividing both the sides by 2) Substituting a = 2 in equation (2), 2 + 5b = 22 5b = 22 - 2 5b = 20 \b=20/5 ∴ b = 4 Answer (a, b) = (2, 4).
& 3a & + & 5b & = & 26 &\text{…..(1)}\\
- & & & & & & \\
&a & + & 5b & = & 22 &\text{…..(2)} \\
-& & -& & &-& \\ \hline
& 2a & & & = & 4 & \\
\end{array}\)
(2) x + 7y = 10; 3x—2y = 7.
x + 7y = 10 …..(1) 3x - 2y = 7 …..(2) Multiplying equation (1) by 3, 3x + 21y =30 …..(3) Subtracting equation (2) from equation (3), \(\begin{array}{rrrrrrr} ∴ y = 1 ….. (Dividing both the sides by 23) Substituting y = 1 in equation (1) x + 7×(1) = 10 x + 7 = 10 ∴ x = 10 -7 ∴ x = 3 Answer is (x, y) = (3, 1).
& 3x & + & 21y & = & 30 &\text{…..(2)}\\
- & & & & & & \\
&3x& - & 2y & = & 7 &\text{…..(3)} \\
-& & +& & &-& \\ \hline
& & & 23y & = & 23 & \\
\end{array}\)
(3) 2x — 3y = 9; 2x + y = 13.
2x — 3y = 9 …..(1) 2x + y = 13 ……(2) Subtracting equation (1) from equation (2), \(\begin{array}{rrrrrrr} ∴ y = 1 … (Dividing both the sides by 4) Substituting y = 1 in equation (2), 2x + 1 = 13 2x = 13-1; ∴ 2x = 12 ∴ x = 6 Answer is (x, y) = (6, 1).
& 2x & + & y & = & 13 &\text{…..(2)}\\
- & & & & & & \\
&2x& - & 3y & = & 9 &\text{…..(1)} \\
-& & +& & &-& \\ \hline
& & & 4y & = & 4 & \\
\end{array}\)
(4) 5m - 3n = 19; m - 6n = - 7.
5m - 3n = 19 ……(1) m—6n = - 7 ………(2) ∴ m= - 7 + 6n …….(3) Substituting this value of m in equation (1), 5(- 7 + 6n) - 3n = 19 ∴ - 35 + 30n - 3n = 19 27n = 19 + 35 27n = 54 n = 2 ……..(Dividing both the sides by 27) Substituting n = 2 in equation (3), m = - 7 + 6(2) ∴ m = - 7 + 12; ∴ m = 5 Answer is (m, n) = (5, 2).
(5) 5x + 2y = −3; x + 5y = 4.
5x + 2y = − 3 ……(1) x + 5y = 4 …….(2) x = 4 − 5y ……..(3) Substituting this value of x in equation (1), 5(4 − 5y) + 2y = −3 20 −25y + 2y = −3 − 23y = −3 −20 − 23y = − 23 y = 1 ……[Dividing both the sides by (-23)] Substituting y = 1 in equation (3), x = 4 − 5(1) x = 4 −5 ; ∴ x = −1 Answer is (x, y) = ( - 1, 1).
(6) \(\frac{1}{3}x+y=\frac{10}{3}\); \(2x+\frac{1}{4}y=\frac{11}{4}\)
\(\frac{1}{3}x+y=\frac{10}{3}\) ……. (1) \(2x+\frac{1}{4}y=\frac{11}{4}\) ……. (2) Multiplying equation (1) by 3, x + 3y =10 …….(3) Multiplying equation (2) by 4, 8x + y = 11 …….(4) Multiplying equation (4) by 3, 24x + 3y = 33 …….(5) Subtracting equation (3) from equation (5), \(\begin{array}{rrrrrrr} x = 1 …..(Dividing both the sides by 23) Substituting x = 1 in equation (3), 1 + 3y = 10; 3y = 10 − 1; ∴ 3y = 9 ∴ y = 3 Answer is (x, y) = (1, 3).
& 24x & + & 3y & = & 33 &\text{…..(5)}\\
- & & & & & & \\
&x& + & 3y & = & 10 &\text{…..(3)} \\
-& & -& & &-& \\ \hline
& 23x & & & = & 23 & \\
\end{array}\)
(7) 99x + 101y = 499; 101x + 99y = 501.
99x + 101y = 499 ……(1) 101x + 99y = 501 ……(2) Adding equations (1) and (2), \(\begin{array}{rrrrrrr} x + y = 5 …. (3) ….. (Dividing both the sides by 200) Subtracting equation (1) from equation (2), \(\begin{array}{rrrrrrr} x − y = 1 …..(4) ……. (Dividing both the sides by 2) Adding equations (3) and (4), \(\begin{array}{rrrrrrr} ∴ x = 3 Substituting x = 3 in equation (3), 3 + y = 5 ∴ y = 5 −3 ∴ y = 2 Answer is. (x, y) = (3, 2)
& 99x & + & 101y & = & 499 &\text{…..(1)}\\
+ & & & & & & \\
&101x& + & 99y & = & 501 &\text{…..(2)} \\
& & & & && \\ \hline
& 200x &+ &200y & = & 1000 & \\
\end{array}\)
& 101x & + & 99y & = & 501 &\text{…..(2)}\\
- & & & & & & \\
&99x& + & 101y & = & 499 &\text{…..(1)} \\
-& & -& & &-& \\ \hline
& 2x & - &2y & = & 2 & \\
\end{array}\)
& x & + & y & = & 5 &\text{…..(3)}\\
+ & & & & & & \\
&x& - & y & = & 1 &\text{…..(4)} \\
& & & & & & \\ \hline
& 2x & & & = & 6 & \\
\end{array}\)
(8) 49x - 57y = 172; 57x — 49y = 252.
49x − 57y = 172 …..(1) 57x − 49y = 252 ….(2) Adding equations (1) and (2), \(\begin{array}{rrrrrrr} x − y = 4 …… (3) ……(Dividing both the sides by 106) Subtracting equation (1) from equation (2), \(\begin{array}{rrrrrrr} x + y = 10 ….(4) …….(Dividing both the sides by 8) Adding equations (3) and (4), x − y = 4 ……..(3) x + y = 10 …...(4) 2x = 14 …….(Dividing both the sides by 2) ∴ x = 7. Substituting x = 7 in equation (4), 7 + y = 10 y = 10 −7 ; ∴ y = 3 Answer is (x, y) = (7, 3)
& 49x & - & 57y & = & 172 &\text{…..(1)}\\
+ & & & & & & \\
&57x& - & 49y & = & 252 &\text{…..(2)} \\
& & & & & & \\ \hline
& 106x &- &106y & = & 424 & \\
\end{array}\)
& 57x & - & 49y & = & 252 &\text{…..(2)}\\
- & & & & & & \\
&49x& - & 57y & = & 172 &\text{…..(1)} \\
& -& -& & & -& \\ \hline
& 8x &+ &8y & = & 80& \\
\end{array}\)
Practice Set 1.2
Question 1.
Complete the following table to draw graph of the equations -
(I) x + y = 3 (II) x − y = 4
i) x + y = 3
| x | 3 | ||
| y | 5 | 3 | |
| (x, y) | (3,0) | ( ) | (0,3) |
ii) x - y = 4
| x | −1 | 0 | |
| y | 0 | −4 | |
| (x, y) | ( ) | ( ) | (0,−4) |
(i) x + y = 3 ∴ y = 0 x + 5 = 3 ∴ x = − 2 ….(Given) ∴ x = 0 (ii) x − y = 4 x − 0 = 4 ∴ x = 4 − 1 − y = 4 ∴ y = − 5
x
3
−2
0
y
0
5
3
(x, y)
(3,0)
(−2,5)
(0,3)
(x, y) = (3, 0) and x = 3 ….(Given)
Substituting y = 5
(x, y) = (0, 3) and y = 3
x
4
−1
0
y
0
−5
−4
(x, y)
(4,0)
(−1,−5)
(0,−4)
Substituting y = 0
Substituting x = −1
Question 2.
Solve the following simultaneous equations graphically
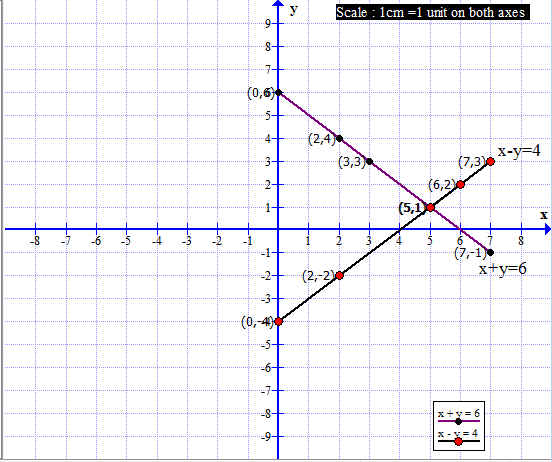
(1) x + y = 6 ; x − y = 4
x + y = 6 ; ∴ y = 6 − x x − y = 4; ∴ y = 4− x The coordinates of the point of intersection are (5, 1). Ans- The solution of the given simultaneous equations is x = 5, y = 1.
x
0
2
3
7
y
6
4
3
−1
(x, y)
(0,6)
(2,4 )
(3,3)
(7,−1)
x
0
2
6
7
y
−4
−2
2
3
(x, y)
(0,−4)
(2,−2 )
(6,2)
(7,3)
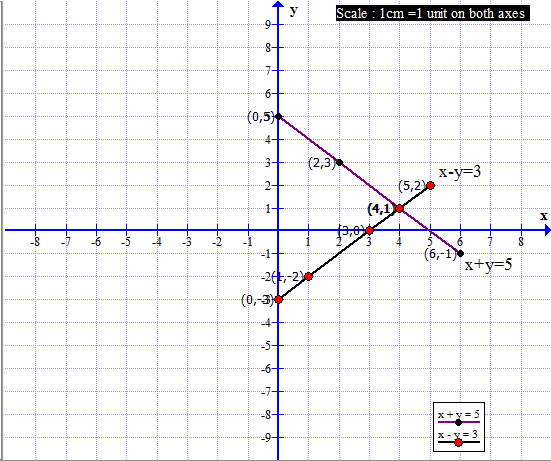
(2) x + y = 5 ; x − y = 3
x + y = 5; ∴ y = 5 −x x - y = 3 ; ∴ y = x − 3 The coordinates of the point of intersection are (4, 1). Ans- The solution of the given simultaneous equations is x = 4, y = 1.
x
0
2
4
6
y
5
3
1
−1
(x, y)
(0,5)
(2,3 )
(4,1)
(6,−1)
x
0
1
3
5
y
−3
−2
0
2
(x, y)
(0,−3)
(1,−2 )
(3,0)
(5,2)
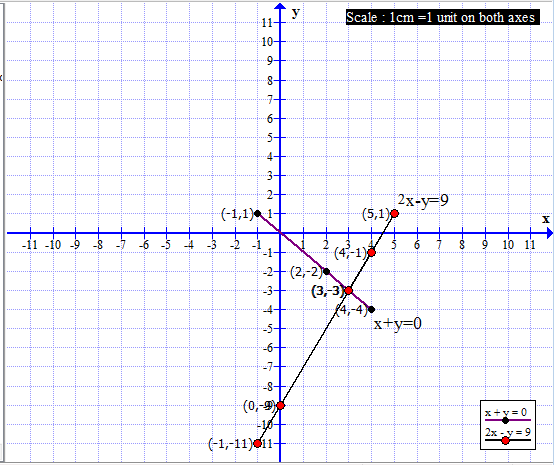
(3) x + y = 0 ; 2x − y = 9
x + y = 0 ∴ y = −x 2x − y = 9 ∴ y = 2x − 9 The coordinates of the point of intersection are (3, −3). Ans- The solution of the given simultaneous equations is x = 3, y = −3.
x
−1
0
2
4
y
1
0
−2
−4
(x, y)
(−1,1)
(0,0 )
(2,−2)
(4,−4)
x
−1
0
4
5
y
−11
−9
−1
1
(x, y)
(−1,−11)
(0,−9 )
(4,1)
(5,1)
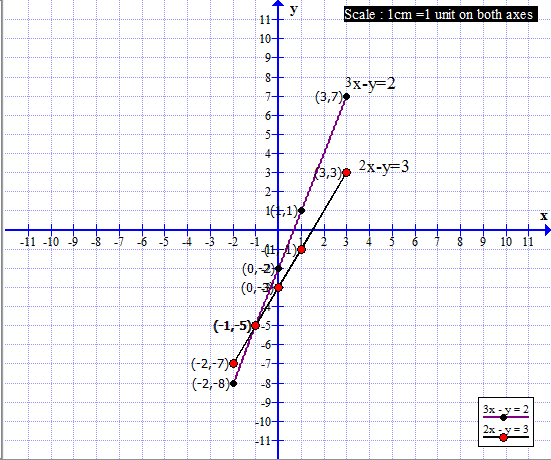
(4) 3x − y = 2 ; 2x − y = 3
3x − y = 2 ; ∴ y = 3x − 2 2x − y = 3 ; ∴y = 2x −3 The coordinates of the point of intersection are (−1, −5). Ans- The solution of the given simultaneous equations is x = −1, y = −5.
x
−2
0
1
3
y
−8
−2
1
7
(x, y)
(−2,−8)
(0,−2 )
(1,1)
(3,7)
x
−2
0
1
3
y
−7
−3
−1
3
(x, y)
(−2,−7)
(0,−3 )
(1,−1)
(3,3)
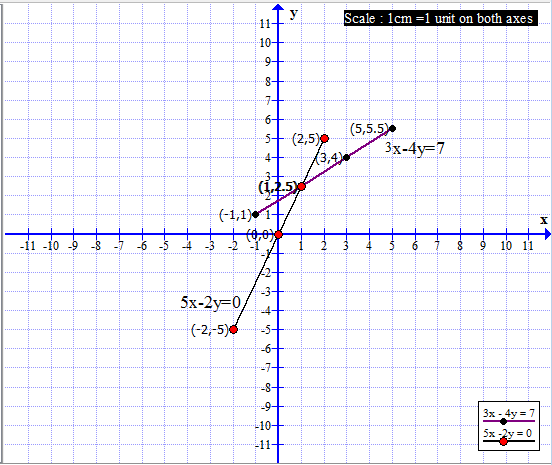
(5) 3x − 4y = −7 ; 5x − 2y = 0
3x − 4y = −7 ∴ y = \(\frac{3x+7}{4}\) 5x − 2y = 0 ∴ y = \(\frac{5x}{2}\) The coordinates of the point of intersection are (1, 2.5). Ans- The solution of the given simultaneous equations is x = 1, y = 2.5.
x
−1
1
3
5
y
1
2.5
4
5.5
(x, y)
(−1,1)
(1,2.5 )
(3,4)
(5,5.5)
x
−2
0
1
2
y
−5
0
2.5
5
(x, y)
(−2,−5)
(0,0 )
(1,2.5)
(2,5)
(6) 2x − 3y = 4 ; 3y − x = 4
2x −3y = 4 ∴ y = \(\frac{2x-4}{3}\) 3y − x = 4 ∴ y = \(\frac{4+x}{3}\) The coordinates of the point of intersection are (8, 4). Ans- The solution of the given simultaneous equations is x = 8, y = 4.
x
−1
2
5
8
y
−2
0
2
4
(x, y)
(−1,−2)
(2,0 )
(5,2)
(8,4)
x
−4
−1
2
5
y
−0
1
2
3
(x, y)
(−4,0)
(−1,1 )
(2,2)
(5,3)
Chapter-1-Linear Equations in Two Variables
-Kitabcd Academy Offer-
Buy Notes(Rs.7)+ Practice Set Solution(Rs.7) PDF of this chapter
Price : Rs.14 / Rs.12
Click on below button to buy PDF : Notes + Practice Set Solutions (2 PDF)-Rs.12
-Kitabcd Academy Offer-
Buy Notes(Rs.7)+ Practice Set Solution (Rs.7) + Problem Set Solution (Rs.5) PDF of this chapter
Price : Rs.19 / Rs.15
Click on below button to buy PDF : Notes + Practice Set Solutions + Problem Set Solutions (3 PDF)-Rs.15
Click on below links to get PDF from store
PDF : Class 10th-Mathematics-Chapter-1-Linear Equations in Two Variables-Notes
PDF : Class 10th-Mathematics-Chapter-1-Linear Equations in Two Variables-Practice Set Solution
PDF : Class 10th-Mathematics-Chapter-1-Linear Equations in Two Variables-Problem Set Solution
All Chapters Notes-Class-10-Mathematics-1 and 2- (13 PDF)-Rs.77
All Chapters Solutions-Class-10-Mathematics-1 and 2- (13 PDF)-Rs.74
All Chapters Notes + Practice Set Solutions-Class-10-Mathematics-1 and 2- (26 PDF)-Rs.131
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 10th-Mathematics – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Next Chapter : Chapter-2-Quadratic equation – Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.