The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solution
NCERT-Class-8-Science (Curiosity)-Chapter-9
Solutions (Exercise + Intext)
Probe and ponder/Intext Questions :
Question 1. What do you think is happening in the picture above?
It appears that a group of people are gathered at the seashore to collect salt from the sand.
This scene represents a freedom movement protest, where people are breaking the salt law by making salt themselves.
Question 2. What happens when you add too much sugar to your tea and it stops dissolving? How can you solve this problem?
When you add too much sugar to your tea, it stops dissolving because the tea becomes a saturated solution. This means the tea cannot dissolve any more sugar at that temperature, so the extra sugar settles at the bottom.
To solve this problem:
- Heat the tea: Warm tea can dissolve more sugar.
- Add more tea or water: This increases the amount of solvent, so more sugar can dissolve.
So, increasing temperature or the amount of liquid helps the extra sugar dissolve.
Question 3. Why do sugar and salt dissolve in water but not in oil? Why is water considered a good solvent?
This happened because of different properties of water and oil.
- Water is a polar solvent. Its molecules have partial positive (H⁺) and partial negative (O⁻) charges.
- Oil is non-polar. It has no charges to attract or stabilize ions/polar molecules.
- Polar substances dissolve in polar solvents, non-polar substances dissolve in non-polar solvents.
- Since sugar and salt are polar/ionic, they don’t dissolve in non-polar oil, but dissolved in polar solvent water
Water is considered a good solvent :
- Water can dissolve many substances such as salts, sugars, acids, and bases.
- Its polar nature helps it dissolve both solid and some liquid substances.
- Because it dissolves many materials, water is called a universal (good) solvent.
Question 4. Why are water bottles usually tall and cylindrical in shape instead of spherical?
Water bottles are usually tall and cylindrical instead of spherical for several practical reasons:
- Easy to hold and grip
- Stability : Cylindrical bottles can stand upright easily. A spherical bottle would roll and fall.
- Easy to store and pack : Cylindrical bottles fit well in bags, cupboards, refrigerators, and bottle holders. Spherical bottles waste space.
- Easy to pour and drink from : The tall shape allows better control while pouring or drinking.
So, water bottles are cylindrical because they are convenient, stable, space-saving, and practical for daily use.
Question 5. We know air is a mixture. Would a mixture of gases also be considered a solution? (Page 135)
- Yes, just as water can act as a solvent in liquid solutions, gases can also form solution.
- Air is a gaseous solution. Since nitrogen is present in the largest amount in the air, it is considered as the solvent, while oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide, and other gases are considered as solutes.
Question 6. What will happen if we keep on adding more salt in a given amount of water? (Page 136)
- If we keep adding more salt to a fixed amount of water, the salt will dissolve only up to a certain limit. After this point, the solution becomes saturated and no more salt can dissolve. Any extra salt added will remain undissolved and settle at the bottom of the container.
- No more solute can be dissolved into the saturated solution at that specific temperature.
Question 7. Do gases also dissolve in water? (Page 139)
Yes, gases also dissolve in water. For example, oxygen and carbon dioxide dissolve in water, which helps aquatic plants and animals survive. However, gases dissolve in much smaller amounts than solids, and their solubility depends on temperature and pressure.
Question 8. I observed that in some non-uniform mixtures, such as sawdust in water, the sawdust floats, whereas in the mixture of sand and water, the sand sinks. I wonder why that happens? (Page 139)
- This happens mainly because of the difference in density of the substances.
- Sawdust is less dense than water, so it floats on the surface.
- Sand is denser than water, so it sinks to the bottom.
- The size and shape of particles also affect how quickly they sink or float.
Question 9. Some packets of ghee or oil are labelled with a volume of 1 litre but a weight of only say 910 grams? What does this tell us about the density of the oil, and is it less or more than that of water? (Page 141)
- If 1 litre of oil weighs only about 910 grams, it means the density of oil is 0.91 g/mL.
- Since 1 litre of water weighs 1000 grams (density = 1 g/mL), the density of oil is less than that of water. This is why oil floats on water.
Question 10. Why are measuring cylinders always designed narrow and tall instead of wider and short like a beaker? (Page 144)
Measuring cylinders are narrow and tall so that small changes in volume cause a noticeable change in liquid level. This makes the reading more accurate and easier to measure. In wider containers like beakers, the same volume change causes only a small rise in level, leading to more reading errors.
Question 11. How the level of a coloured liquid is measured? (Page 145)
In case of coloured liquids the mark on the measuring cylinder should coincide with the top of the meniscus!
Keep The Curiosity Alive :
Question 1. State whether the statements given below are True [T] or False [F]. Correct the false statement(s).
(i) Oxygen gas is more soluble in hot water rather than in cold water.
False: Oxygen is more soluble in cold water.
(ii) A mixture of sand and water is a solution.
False: Mixture of sand and water is not a solution. Sand does not dissolve in water but settles down.
(iii) The amount of space occupied by any object is called its mass.
False: The amount of space occupied by any object is called its volume.
(iv) An unsaturated solution has more solute dissolved than a saturated solution.
False: A saturated solution has more solute dissolved than an unsaturated solution.
(v) The mixture of different gases in the atmosphere is also a solution.
True.
Question 2. Fill in the blanks.
(i) The volume of a solid can be measured by the method of displacement, where the solid is __________ in water and the ____________ in water level is measured.
placed; rise
(ii) The maximum amount of _______________ dissolved in _______________ at a particular temperature is called solubility at that temperature.
solute, solvent
(iii) Generally, the density ____________ with increase in temperature.
Decrease
(iv) The solution in which glucose has completely dissolved in water, and no more glucose can dissolve at a given temperature, is called a __________ solution of glucose.
Saturated
Question 3. You pour oil into a glass containing some water. The oil floats on top. What does this tell you?
(i) Oil is denser than water
(ii) Water is denser than oil
(iii) Oil and water have the same density
(iv) Oil dissolves in water
(ii) Water is denser than oil
Question 4. A stone sculpture weighs 225 g and has a volume of 90 cm3. Calculate its density and predict whether it will float or sink in water.
Density = \(\frac{mass}{volume} = \frac{225}{90}\) = 2.5 g/cm³
The stone sculpture has a density of 2.5 g/cm³. Since this exceeds water's density of 1 g/cm³, it will sink.
Question 5. Which one of the following is the most appropriate statement, and why are the other statements not appropriate?
(i) A saturated solution can still dissolve more solute at a given temperature.
(ii) An unsaturated solution has dissolved the maximum amount of solute possible at a given temperature.
(iii) No more solute can be dissolved into the saturated solution at that temperature.
(iv) A saturated solution forms only at high temperatures.
(a) The most appropriate statement is (iii): “No more solute can be dissolved into the saturated solution at that temperature.”
- A saturated solution means it has dissolved the maximum amount of solute possible at a given temperature.
- Any extra solute added will remain undissolved because the solvent cannot accommodate more.
(b) Why the others are not appropriate
(i) Incorrect: A saturated solution cannot dissolve more solute at the same temperature; that’s the definition of saturation.
(ii) Incorrect: This describes a saturated solution, not an unsaturated one. An unsaturated solution can still dissolve more solute.
(iv) Incorrect: Saturated solutions can form at any temperature, not only at high temperatures. The saturation point depends on solubility at that specific temperature.
Question 6. You have a bottle with a volume of 2 litres. You pour 500 mL of water into it. How much more water can the bottle hold?
The bottle’s total capacity is 2 litres = 2000 mL.
I have already poured in 500 mL.
So, remaining capacity = 2000 mL − 500 mL = 1500 mL
The bottle can hold 1500 mL (or 1.5 litres) more water.
Question 7. An object has a mass of 400 g and a volume of 40 cm³. What is its density?
Density = \(\frac{mass}{volume} = \frac{400}{40}\) = 10 g/cm³
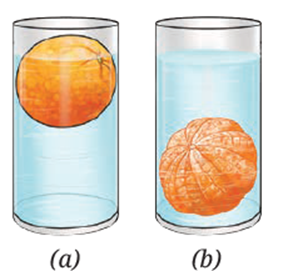
Question 8. Analyse Fig. (a) and (b) Why does the unpeeled orange float, while the peeled one sinks? Explain.
An unpeeled orange floats, while a peeled orange sinks, because of density and trapped air.
Unpeeled orange:
- The peel is thick and porous, with tiny air pockets inside it.
- These air pockets increase the orange’s volume without adding much mass.
- This makes the average density of the orange less than water, so it floats.
Peeled orange:
- When the peel is removed, the air pockets are gone.
- The remaining fruit is denser than water.
- Its average density becomes greater than water, so it sinks.
Question 9. Object A has a mass of 200 g and a volume of 40 cm³. Object B has a mass of 240 g and a volume of 60 cm³. Which object is denser?
Density of object A = \(\frac{mass}{volume} = \frac{200}{40}\) = 5 g/cm³
Density of object B = \(\frac{mass}{volume} = \frac{240}{60}\) = 4 g/cm³
Object A is denser, having more density than object B.
Question 10. Reema has a piece of modeling clay that weighs 120 g. She first moulds it into a compact cube that has a volume of 60 cm3. Later, she flattens it into a thin sheet. Predict what will happen to its density.
When Reema flattens the clay into a thin sheet, its mass remains 120 g and its volume remains 60 cm³ (only the shape changes).
Therefore, the density stays the same (2 g/cm³). Changing the shape does not affect density, since density depends only on mass and volume, not on form.
Question 11. A block of iron has a mass of 600 g and a density of 7.9 g/cm³. What is its volume?
We know, Density = \(\frac{mass}{volume}\)
Therefore, Volume = \(\frac{mass}{density} = \frac{600}{7.9}\) = 75.94 cm³
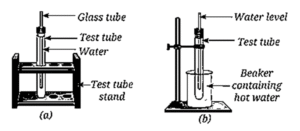
Question 12. You are provided with an experimental setup as shown in Fig. (a) and (b). On keeping the test tube (Fig. b) in a beaker containing hot water (~70 °C), the water level in the glass tube rises. How does it affect the density?
The density of the water decreases.
- When the water is heated by the beaker containing hot water (70 °C), the particles of the water tend to move away and spread.
- This spreading results in an increase in the water's volume (as indicated by the rising water level in the glass tube).
- Since density is defined as Mass/Volume, and the mass does not change while the volume increases, the density of the substance decreases upon heating.
Key Features of Kitabcd Exam Master :
|
Click on below links to get PDF from store
PDF : Class 8 -Curiosity-Chapter-9-The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solution– Notes
PDF : Class 8 -Curiosity-Chapter-9-The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solution– Exam Master
PDF Set :
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Notes Set (13-PDF)-Rs.58
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Exam Master Set (13-PDF)-Rs.74
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Notes + Exam Master Set (26-PDF)-Rs.116
Main Page : NCERT-Class-8-Science (Curiosity) – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-8-Nature of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures– Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-10- Light: Mirrors and Lenses – Online Notes
We reply to valid query.