Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones
NCERT-Class-8-Science (Curiosity)-Chapter-6
Solutions (Exercise + Intext)
NCERT Probe & Ponder Questions :
Question 1. Why are winds stronger on some days than on others?
- Wind is air moving from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas.
- When the difference in pressure (called the pressure gradient) is large, the air moves faster — so the wind is strong.
- When the pressure difference is small, the air moves slowly — so the wind is gentle.
- Other factors like temperature differences, land and sea heating, and mountains or valleys can also affect how strong the wind becomes.
Question 2. Why are water tanks usually placed at a height?
- When the tank is high, the water inside it has more potential energy.
- Gravity pulls the water downward, creating water pressure in the pipes.
- This pressure helps the water reach taps, bathrooms, and kitchens on lower floors without using a pump.
Therefore, water tanks are placed high so that gravity can push water with enough pressure to flow through pipes and reach all parts of a building.
Question 3. Can air pressure really crush us?
Yes — air pressure is actually strong enough to crush us, but it doesn’t, because:
- The air around us presses on our bodies with a force of about 1 kilogram per square centimeter (or about 10 tons on your whole body!).
- However, our body pushes back with the same pressure from the inside — especially the air in our lungs and fluids in our body.
- Because these pressures are balanced, we don’t feel crushed.
It means, air pressure could crush us if there were no pressure inside our bodies to balance it — but since the forces are equal, we stay perfectly safe!
Question 4. What causes storms and cyclones? If the Earth stopped rotating, would cyclones still form?
What causes storms and cyclones:
- Warm ocean water heats the air above it.
- The warm, moist air rises, creating a low-pressure area near the surface.
- Cooler air from surrounding areas rushes in to replace it.
- As the warm air rises, it cools and condenses, forming clouds and heavy rain.
- The Earth’s rotation causes the moving air to spin, turning the storm into a cyclone (called the Coriolis effect).
So, cyclones are powered by warm ocean water, moist rising air, and Earth’s rotation. If the Earth stopped rotating, storms might still occur, but cyclones would not.
Intext Questions :
Question 1. Why fallen leaves rise in the air or trees bend when a strong wind blows? (Page 81)
The force exerted by the wind creates wind pressure which causes fallen leaves to rise in the air and bending or swinging of trees when a strong wind blows.
Question 2. Can the shape or the size of the straps really make a difference provided both the bags are equally heavy? (Page 81)
- When we carry a bag, we feel its weight because gravity pulls it downward on our shoulders.
- If the bag has narrow straps, its weight acts on a small area, creating more pressure on our shoulders.
- But if the bag has broad straps, the same weight spreads over a larger area, reducing the pressure.
- That’s why we feel more comfortable carrying a bag with broad straps.
Question 3. (a) Why overhead tanks are kept at a height?
(b) Suppose you are living on the second floor of a three storeyed building and an overhead tank is placed on the top floor. Will you or your friend on the first floor receive more powerful stream of tap water? Give reasons. (Page 84)
(a) Overhead tanks are placed at a height to increase the water pressure. The higher the tank, the taller the water column, and the greater the pressure at the taps below. This ensures a strong and steady flow of water to all floors.
(b) Who gets more powerful water stream—second floor or first floor?
My friend on the first floor will receive a more powerful stream of tap water than me on the second floor.
Reason:
- Water pressure increases with depth from the tank.
- The first floor is farther below the overhead tank than the second floor.
- So, the water column is taller, and pressure is higher at the first floor.
Question 4. Why water spurts out like a fountain from leaking joints or holes in water pipes? (Page 85)
- Water tanks are usually placed high above the ground, so the water in the connected pipes forms a long column. This creates high pressure inside the pipes.
- Water pushes in all directions — on the bottom, sides, and walls of the pipe.
- When it finds a narrow opening such as a hole or a leak, the water rushes out forcefully, spurting like a fountain.
Question 5. What happens when an inflated balloon is kept without closing its mouth? (Page 86)
- If an inflated balloon is kept without closing its mouth, the air inside the balloon escapes rapidly, causing the balloon to deflate quickly and lose its shape and volume.
- This happens because the air inside the balloon is at a higher pressure than the surrounding atmosphere, and when the mouth is left open, the high-pressure air moves out to the lower-pressure environment, leading to rapid deflation
Question 6. Does the difference in air pressure have anything to do with the formation of winds? (Page 88)
Air moves from a high-pressure region to a low-pressure region. Moving air is called wind. Thus, it is the difference in air pressure that results in formation of wind.
Keep The Curiosity Alive :
Question 1. Choose the correct statement.
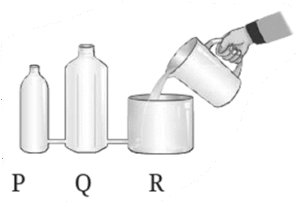
(i) Look at below Fig. carefully. Vessel R is filled with water. When pouring of water is stopped, the level of water will be ____________________.
(a) the highest in vessel P
(b) the highest in vessel Q
(c) the highest in vessel R
(d) equal in all three vessels
(d) equal in all three vessels
(ii) A rubber sucker (M) is pressed on a flat smooth surface and an identical sucker (N) is pressed on a rough surface:
(a) Both M and N will stick to their surfaces.
(b) Both M and N will not stick to their surfaces.
(c) M will stick but N will not stick.
(d) M will not stick but N will stick.
(c) M will stick but N will not stick.
(iii) A water tank is placed on the roof of a building at a height ‘H’. To get water with more pressure on the ground floor, one has to
(a) increase the height ‘H’ at which the tank is placed.
(b) decrease the height ‘H’ at which the tank is placed.
(c) replace the tank with another tank of the same height that can hold more water.
(d) replace the tank with another tank of the same height that can hold less water.
(a) increase the height ‘H’ at which the tank is placed.
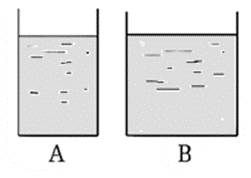
(iv) Two vessels, A and B contain water up to the same level as shown in below Fig. PA and PB is the pressure at the bottom of the vessels. FA and FB is the force exerted by the water at the bottom of the vessels A and B.
(a) PA = PB, FA = FB
(b) PA = PB, FA < FB
(c) PA < PB, FA = FB
(d) PA > PB, FA > FB
(b) PA = PB, FA <FB
Question 2. State whether the following statements are True [T] or False [F].
(i) Air flows from a region of higher pressure to a region of lower pressure. [ ]
(ii) Liquids exert pressure only at the bottom of a container. [ ]
(iii) Weather is stormy at the eye of a cyclone. [ ]
(iv) During a thunderstorm, it is safer to be in a car. [ ]
(i) [True]
(ii) [False] : liquids exert pressure in all directions, including on the walls of the container.
(iii) [False] : it is calm at the eye of a cyclone.
(iv) [True]
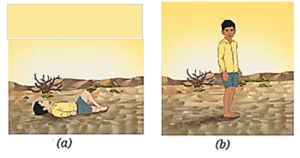
Question 3. Fig. (a) shows a boy lying horizontally, and Fig. (b) shows the boy standing vertically on a loose sand bed. In which case does the boy sink more in sand? Give reasons.
The boy in Figure (b) will sink more.
- The weight of the boy is the same but in Fig. (a) the force (of the weight) is acting on a large area. The pressure in this case is lesser.
- In Fig. (b) the same force (of the weight) is acting on a small area. The pressure therefore, is more. The boy will sink more in sand in this case.
Question 4. An elephant stands on four feet. If the area covered by one foot is 0.25 m2, calculate the pressure exerted by the elephant on the ground if its weight is 20000 N.
Given:
- Weight of the elephant (Force) = 20,000 N
- Area of one foot = 25 m²
- The elephant stands on 4 feet
Step 1: Find total area in contact with the ground
Total area = 4 x 0.25 = 1.00 m²
Step 2: Use the pressure formula
Pressure = \(\frac{Force}{Area}\) = \(\frac{20000N}{1.00m^2}\) = 20000 N/m²
The pressure exerted by the elephant on the ground is 20,000 N/m² (or 20 kPa).
Question 5. There are two boats, A and B. Boat A has a base area of 7 m2, and 5 persons are seated in it. Boat B has a base area of 3.5 m2, and 3 persons are seating in it. If each person has a weight of 700 N, find out which boat will experience more pressure on its base and by how much?
Given:
- Weight of each person = 700 N
- Boat A: Base area = 7 m², Number of persons = 5
- Boat B: Base area = 3.5 m², Number of persons = 3
Step 1: Find total weight on each boat
- Boat A: Total weight = 5 x 700 = 3500 N
Boat B: Total weight = 3 x 700 = 2100 N
Step 2: Calculate pressure on each boat’s base
Pressure = \(\frac{Force}{Area}\)
Boat A: PA = \(\frac{Force}{Area}\) = \(\frac{3500}{7}\) = 500 N/m²
Boat B: PB = \(\frac{Force}{Area}\) = \(\frac{2100}{3.5}\) = 600 N/m²
Step 3: Compare the pressures
PB - PA = 600 - 500 = 100 N/m²
Boat B experiences more pressure on its base. It experiences 100 N/m² more pressure than Boat A.
Question 6. Would lightning occur if air and clouds were good conductors of electricity? Give reasons for your answer.
No — lightning would not occur if air and clouds were good conductors of electricity.
Reason :
- Lightning happens because electric charges build up in clouds and on the ground.
- Air is normally a poor conductor (an insulator), so charges cannot move easily.
- When the difference in charge becomes very large, the air suddenly breaks down and allows electricity to jump across — that’s the flash of lightning.
If air and clouds were good conductors, the charges would flow smoothly and continuously, without building up.
So, no sudden discharge — and therefore, no lightning.
Question 7. What will happen to the two identical balloons A and B as shown in Fig. when water is filled into the bottle up to a certain height. Will both the balloons bulge? If yes, will they bulge equally? Explain your answer.
- When water is filled into the bottle up to a certain height (sufficiently above the level of the entry points of water from the bottle) both the balloons will bulge.
- The entry points of water from the bottle to the balloons are at the same height.
- The balloons being elastic exert some force on the water. Assuming that the balloons are equally elastic, both the balloons will bulge equally.
Question 8. Explain how a storm becomes a cyclone.
- Warm ocean water heats the air above it.
- The warm, moist air rises, creating a low-pressure area near the surface.
- Cooler air from nearby areas moves in to fill the gap, but it also gets heated and rises.
- This continuous cycle of rising warm air and inflowing cool air makes the system stronger — forming a storm.
- Because of the Earth’s rotation (Coriolis effect), the moving air starts to spin around the low-pressure center.
- As more warm air rises and more moisture condenses, the storm grows bigger and more powerful.
When this spinning storm over the ocean becomes very strong and organized, it turns into a cyclone.
Question 9. Fig. shows trees along the sea coast in a summer afternoon. Identify which side is land — A or B. Explain your answer.
- During daytime in a summer afternoon, there is a sea breeze that blows from sea to land. This happens because the land gets heated faster and the air above land rises resulting in low-pressure region over land.
- Cooler air over sea moves from high pressure region towards the land.
- The bending of trees due to wind, as shown in the figure suggest that wind is blowing in the direction from B to A. This suggests 'A' side is land.
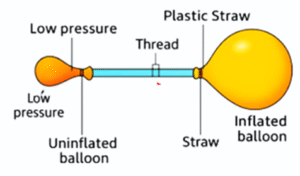
Question 10. Describe an activity to show that air flows from a region of high pressure to a region of low pressure.
Activity to show that air flows from a region of high pressure to a region of low pressure.
Materials required: Two similar balloons made of thin rubber, a drinking straw and some thread.
Procedure:
- Insert one end of the straw into one balloon and secure it with the thread.
- Inflate the second balloon and insert the free end of the straw into the neck of the inflated balloon and secure it with the thread. (Ensure that the air from the inflated balloon does not leak.
Observations: Some air moves from the inflated balloon to the uninflated balloon and the sizes of both the balloons change. After sometime both the balloons attain almost the same size and the flow of air stops.
Conclusion: The inflated balloon has higher pressure inside it and the uninflated
balloon has low pressure inside. When the two balloons are connected through a straw, air moves from high-pressure area (inside the inflated balloon) to the low-pressure area (inside the uninflated balloon).
Question 11. What is a thunderstorm? Explain the process of its formation.
A thunderstorm is a weather condition that produces thunder, lightning, heavy rain, and strong winds. It happens when warm, moist air rises rapidly into the atmosphere.
Process of Formation:
- Heating of the Earth’s surface: The Sun heats the land, and the warm air near the ground becomes lighter.
- Rising of warm, moist air: This warm, moist air rises upward into cooler regions of the atmosphere.
- Cooling and condensation: As the air rises, it cools and the water vapor condenses to form cumulonimbus clouds (large, tall thunderclouds).
- Formation of lightning and thunder: Inside these clouds, strong air movements cause electric charges to build up. When the difference in charge becomes large, lightning occurs, followed by thunder.
- Rain and wind: The condensed water droplets fall as rain, and the fast-moving air causes gusty winds.
Question 12. Explain the process that causes lightning.
- Charge Separation: Inside a storm cloud, strong winds make ice particles move up and water droplets fall down. When they rub against each other, they produce electric charges. The lighter ice particles become positively charged and move to the top of the cloud, while the heavier water droplets collect negative charges and stay near the bottom.
- Induction: The negatively charged bottom of the cloud causes the ground and objects below it (like trees and buildings) to become positively charged.
- Electrical Discharge: When the difference between these charges becomes too large, the air can no longer stop them from meeting. A sudden flow of electricity occurs, creating a bright flash called lightning.
- This can happen inside a cloud, between clouds, or between a cloud and the ground.
Thunder: Lightning heats the air around it very quickly, making the air expand and create a loud sound called thunder.
Question 13. Explain why holes are made in banners and hoardings.
Holes are made in banners and hoardings to prevent them from being blown away by strong winds.
- When wind blows fast, it creates a difference in air pressure — high pressure on the front side and low pressure on the back side of the banner.
- If there are no holes, this pressure difference becomes large and can tear or blow away the banner.
- The holes allow air to pass through, reducing the pressure difference on both sides.
- This helps the banner or hoarding stay steady and safe, even in high-speed winds.
Key Features of Kitabcd Exam Master :
|
Click on below links to get PDF from store
PDF : Class 8 -Curiosity-Chapter-6-Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones– Notes
PDF : Class 8 -Curiosity-Chapter-6-Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones– Exam Master
PDF Set :
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Notes Set (13-PDF)-Rs.58
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Exam Master Set (13-PDF)-Rs.74
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Notes + Exam Master Set (26-PDF)-Rs.116
Main Page : NCERT-Class-8-Science (Curiosity) – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-5- Exploring Forces – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-7- Particulate Nature of Matter – Online Solutions


We reply to valid query.