Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects
NCERT-Class-8-Science (Curiosity)-Chapter-4
Solutions (Exercise + Intext)
NCERT Probe & Ponder Questions (Page ) :
Question 1. If we don’t have an electric lamp while making an electric circuit with an electric cell, is there any other way through which we can find out if current is flowing in the circuit?
Yes! Even without an electric lamp, there are several ways to check if electric current is flowing in a circuit. Here are some simple and practical methods:
(i) Magnetic Effect of Current
- Place a small magnetic compass near a straight wire in the circuit.
- If the compass needle deflects when the circuit is switched on, current is flowing. Because a current-carrying wire creates a magnetic field around it.
(ii) Heating Effect of Current
- Use a thin wire like nichrome in the circuit.
- After switching on for a few seconds, carefully touch the wire (or observe if it feels warm).
- If it’s warm, current is flowing—some electrical energy is turning into heat.
(iii) Use a Buzzer or Small Motor
- Connect a buzzer or DC motor instead of a lamp.
- If it makes sound or rotates, current is definitely flowing.
(iv) Use a Galvanometer or Multimeter
- A galvanometer shows needle movement when current flows.
- A multimeter (set to current or voltage mode) gives a digital reading.
Question 2. Is it possible to make temporary magnets? How can these be made?
Yes, we can make temporary magnets. These magnets work only for a short time and lose their magnetism after the cause is removed.
How to Make Temporary Magnets :
(i) Using a Permanent Magnet:
- Rub a strong magnet on an iron nail in one direction.
- After rubbing it several times, the nail becomes a magnet for a short time.
- It can attract small objects like pins or paper clips.
(ii) Using Electric Current (Electromagnet):
- Wrap copper wire around an iron nail.
- Connect the wire to a battery.
- When current flows, the nail becomes a magnet.
- When the battery is disconnected, the magnetism disappears.
Question 3. We can generate heat by burning fossil fuels and wood; but how is heat generated in various electrical appliances?
Electrical appliances like heaters, irons, and kettles produce heat using a process called the heating effect of electric current.
- When electric current flows through a wire (especially one with high resistance), it faces opposition.
- This resistance causes the wire to heat up.
- The electrical energy is converted into heat energy.
Example:
- Appliances use a special wire called nichrome.
- Nichrome has high resistance, so it gets hot quickly when current flows through it.
- This heat is used for cooking, ironing, or heating water.
Question 4. How do we know if a cell or a battery is dead? Can all cells and batteries be recharged?
A dead battery or cell means it can no longer supply electricity. You can tell it’s dead when:
- The device doesn’t turn on or stops working.
- The battery discharges quickly or doesn’t hold charge.
- The battery doesn’t charge properly or takes too long.
- In some cases, the battery may look swollen or leak.
You can also use a battery tester or multimeter to check if it still has voltage. If the reading is very low or zero, the battery is likely dead.
Can All Batteries Be Recharged?
No, not all batteries can be recharged.
Rechargeable Batteries:
- Can be used many times by charging again.
- Examples: Lithium-ion batteries (used in phones, laptops), nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd), and lead-acid batteries (used in cars, inverters).
Non-Rechargeable Batteries:
- Can be used only once.
- Examples: Alkaline batteries (used in remote controls, wall clocks), dry cells.
Once non-rechargeable batteries are used up, they must be disposed of properly.
Intext Questions :
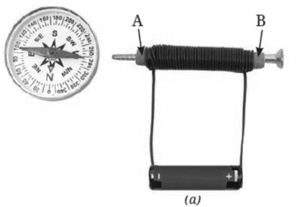
Question 1. Can we use electric current to make a magnet? (Page 49)
Yes, magnetic effect of the electric current is used to make a magnet.
- When electric current flows through a wire, it creates a magnetic field around the wire.
- If you coil the wire into loops (called a solenoid) and pass current through it, the magnetic field becomes stronger.
- Now, if you place an iron nail or any ferromagnetic material inside the coil, it becomes magnetized.
- This setup acts like a temporary magnet—only active when current flows.
Question 2. Does electromagnet also have two poles like a bar magnet? (Page 50)
Yes, electromagnets also have two poles—just like a bar magnet.
- When electric current flows through a wire coiled around an iron nail, the nail becomes an electromagnet.
- One end of the nail becomes the North pole, and the other becomes the South pole.
- These poles appear only when current is flowing.
How to Test the Poles -
- Bring the North pole of a compass needle near one end of the nail.
- If the needle repels, that end is also a North pole.
- If the needle attracts, that end is a South pole.
- Magnets follow the rule: Like poles repel, unlike poles attract.
- This shows that the electromagnet has two poles, just like a permanent magnet.
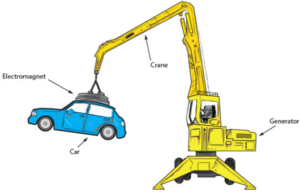
Question 3. Are electromagnets also used in real life, for lifting objects? (Page 52)
Electromagnets are very useful for lifting and moving heavy metal items like iron and steel.
How It Works :
- A large electromagnet is attached to a crane.
- The crane operator moves the magnet over a pile of metal.
- When the electric current is switched ON, the magnet becomes active and attracts magnetic items.
- The crane then moves the magnet to another location.
- When the current is switched OFF, the magnetic field disappears, and the metal items fall off.
Why It’s Useful :
- Helps in sorting and moving heavy metal quickly.
- Used in scrap yards, factories, and recycling plants.
Question 4. While doing the activity for electromagnet, did you also notice that the wire ends got warm? Why would that (Page 52)
- The wire ends get warm when current flows through the wires for some time. This happens due to the heating effect of electric current.
- Depending on the nature of the metals used as conductors, the conductors offer some resistance to the flow of the current.
- In the process, a part of the electric energy is converted into heat energy that warms the ends of the wires.
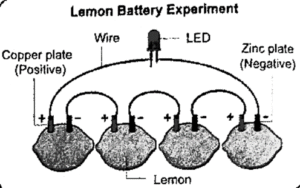
Question 5. Can we also make our own Voltaic cell using easily available materials? (Page 56)
Yes, we can make our own Voltaic cell using simple materials found at home!
Voltaic Cell – Simple Method
We can use fruits or vegetables like lemons or potatoes as the electrolyte, and two different metals as electrodes.
Materials Needed:
- 1 lemon or potato
- 1 copper strip or wire
- 1 iron nail or zinc strip
- Connecting wires
- Small LED or buzzer
Steps:
- Insert the copper strip and iron nail into the lemon (not touching each other).
- Connect wires to both metals.
- Attach the wires to a small LED or buzzer.
- If the LED glows or the buzzer sounds, your Voltaic cell is working!
We can also try this with multiple lemons or potatoes connected in series to increase the voltage.
Keep The Curiosity Alive (Pages 58-61) :
Question 1. Fill in the blanks
(i) The solution used in a Voltaic cell is called ________.
The solution used in a Voltaic cell is called Electrolyte
(ii) A current carrying coil behaves like a __________
A current carrying coil behaves like a magnet.
Question 2. Choose the correct option:
(i) Dry cells are less portable compared to Voltaic cells. (True/False)
False : (Voltaic cells are less portable due to liquid electrolyte.)
(ii) A coil becomes an electromagnet only when electric current flows through it. (True/False)
True.
(iii) An electromagnet, using a single cell, attracts more iron paper clips than the same electromagnet with a battery of 2 cells. (True/False)
False : (stronger current of battery of 2 cells make the coil a stronger magnet.)
Question 3. An electric current flows through a nichrome wire for a short time.
(i) The wire becomes warm.
(ii) A magnetic compass placed below the wire is deflected.
Choose the correct option:
(a) Only (t) is correct
(b) Only (ii) is correct
(c) Both (i) and (it) are correct
(d) Both (i) and (it) are not correct
(c) Both (i) and (i) are correct
Question 4. Match the items in Column A with those in Column B.
| Column A | Column B | ||
| (i) | Voltaic cell | (a) | Best suited for electric heater |
| (ii) | Electric iron | (b) | Works on magnetic effect of electric current |
| (iii) | Nichrome wire | (c) | Works on heating effect of electric current |
| (iv) | Electromagnet | (d) | Generates electricity by chemical reactions |
(i) - (d), (ii) - (c), (iii) - (a), (iv) - (b)
Question 5. Nichrome wire is commonly used in electrical heating devices because it
(i) is a good conductor of electricity.
(ii) generates more heat for a given current.
(iii) is cheaper than copper.
(iv) is an insulator of electricity.
(ii) generates more heat for a given current.
Question 6. Electric heating devices (like an electric heater or a stove) are often considered more convenient than traditional heating methods (like burning firewood or charcoal). Give reason(s) to support this statement considering societal impact.
Electric heating devices like heaters, stoves, and irons are considered more convenient than burning firewood or charcoal for several important reasons:
(i) Cleaner and Healthier :
- Burning wood or charcoal produces smoke and harmful gases. These can cause breathing problems and air pollution, especially indoors.
- Electric devices do not produce smoke, making them safer for health.
(ii) Environment-Friendly :
- Firewood and charcoal come from cutting trees, which leads to deforestation.
- Electric heating reduces the need to burn natural resources and helps in protecting forests.
(iii) Time-Saving and Easy to Use :
- Electric devices heat up quickly and are easy to control.
- No need to collect wood or light fires—just switch on and use.
(iv) Safer for Homes :
- Open fires can cause accidents like burns or house fires.
- Electric heaters are safer when used properly with good wiring and plugs.
(v) Supports Modern Living :
- In cities and towns, electricity is easily available.
- Electric heating fits well with urban lifestyles and helps in efficient cooking and heating.
Considering Societal Impact :
Using electric heating devices helps:
- Improve public health
- Reduce pollution
- Save natural resources
- Promote clean energy
- Support a modern and safe lifestyle
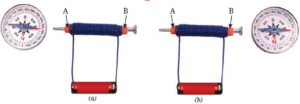
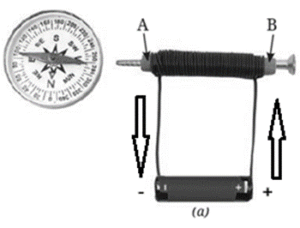
Question 7. Look at the Fig. If the compass placed near the coil deflects:
(i) Draw an arrow on the diagram to show the path of the electric current.
(ii) Explain why the compass needle moves when current flows.
(iii) Predict what would happen to the deflection if you reverse the battery terminals.
(i) The current flows from the positive terminal of the cell to end marked B of the coil, then through the coil to end marked A and then to the negative terminal of the cell as shown by the arrows in the Fig.
(ii) The compass needle moves as the coil becomes a magnet on passing the current through it and the compass needle in its magnetic field moves.
(iii) When we reverse the battery terminals, the poles of the coil electromagnet change. Therefore, the deflection in the compass needle also changes accordingly. The pole of the compass needle that was earlier attracted to the coil, will move away from it and the other pole of the compass needle will get attracted towards the coil.
Question 8. Suppose Sumana forgets to move the switch of her lifting electromagnet model to OFF position (in introduction story). After some time, the iron nail no longer picks up the iron paper clips, but the wire wrapped around the iron nail is still warm. Why did the lifting electromagnet stop lifting the clips? Give possible reasons.
- A coil works like a magnet only when electric current passes through it. Once the current stops, the coil is no longer a magnet.
The magnetic effect is present only as long as the current flows. - The heating effect of current changes some electrical energy into heat, which makes the wire hot. When the current stops, heating also stops. But the wire, which has become hot, takes some time to cool down to normal temperature.
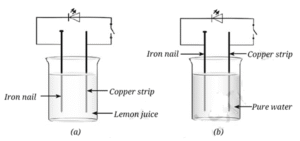
Question 9. In Fig. in which case the LED will glow when the switch is closed?
- The LED will glow when the switch is closed in case of (a). Here the electrolyte is the lemon juice. Copper and iron plates properly placed in a weak acid or salt solution and connected in a circuit, produce electricity.
- In case of (b) the liquid used is pure water that does not become an electrolyte.
Question 10. Neha keeps the coil exactly the same as in Activity 4.4 but slides the iron nail out, leaving only the coiled wire. Will the coil still deflect the compass? If yes, will the deflection be more or less than before?
- Yes, the coil will deflect the compass even after the iron nail has been slid out.
- The coil gets magnetic force when current flows through it.
- If iron nail is inserted inside the coil, the strength of the magnet increases.
- Deflection in the compass will be less when Neha slides the iron nail out, due to less strong electromagnet formed by the coil alone.
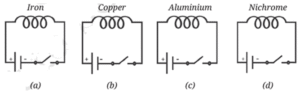
Question 11. We have four coils, of similar shape and size, made up from iron, copper, aluminium, and nichrome as shown in Fig.
When current is passed through the coils, compass needles placed near the coils will show deflection.
(i) Only in circuit (a)
(ii) Only in circuits (a) and (b)
(iii) Only in circuits (a), (b), and (c)
(iv) In all four circuits
(iv) In all four circuits
Explanation :The compass needles placed near the coils will show deflection in all the four cases. The deflection however will not be equal in all the four cases. The magnetic strength of the electromagnet depends on the nature of the material used. Some magnetic substances like iron, nickel and cobalt make strong electromagnets, while aluminium and nichrome may be of the same shape and size may not make equally strong magnets. Therefore, the deflection of the compass needles will vary depending on the strength of the electromagnet.
Key Features of Kitabcd Exam Master :
|
Click on below links to get PDF from store
PDF : Curiosity-Chapter-4-Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects– Notes
PDF : Curiosity-Chapter-4-Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects– Exam Master
PDF Set :
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Notes Set (13-PDF)-Rs.58
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Exam Master Set (13-PDF)-Rs.74
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Notes + Exam Master Set (26-PDF)-Rs.116
Main Page : NCERT-Class-8-Science (Curiosity) – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-3- Health: The Ultimate Treasure – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-5- Exploring Forces – Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.