How Nature Works in Harmony
NCERT-Class-8-Science (Curiosity)-Chapter-12
Solutions (Exercise + Intext)
NCERT Probe & Ponder/Intext Questions :
Question 1. How might the loss of forest cover and changes in rainfall patterns lead to elephants to enter human farms and villages?
- Loss of forest cover destroys the natural habitat of elephants and reduces the availability of food and shelter.
- Changes in rainfall patterns dry up forest water sources and affect the growth of plants elephants depend on.
- In search of food and water, elephants move out of forests.
- Farms have water and nutritious crops like rice, sugarcane, and bananas, which attract elephants as easy food.
- With forests unable to support them, elephants migrate toward human settlements, leading to human–elephant conflict.
Thus, deforestation and altered rainfall push elephants out of forests and into farms and villages in search of food and water.
Question 2. Imagine you are a tree in a dense forest. What kind of relationships would you have with water, sunlight, other animals, and other components of the forest?
If I were a tree in a dense forest,
- I would depend on sunlight to make my food through photosynthesis and on water from rain and soil to stay alive and grow.
- I would share relationships with animals by giving them shelter, shade, fruits, or leaves, while they might help me by spreading my seeds.
- I would interact with other plants and trees by competing for light and space, but also by sharing nutrients through the soil with the help of microorganisms.
- I would also be connected to soil, air, and microbes, which provide nutrients, carbon dioxide, and help in decomposing matter to keep the forest ecosystem balanced.
Question 3. Do you think the Earth can thrive without humans? Can humans survive without the earth?
- Yes, the Earth can thrive without humans. Nature existed and maintained balance long before humans appeared, and ecosystems can recover when human pressure is removed.
- Humans, however, cannot survive without the Earth. We depend on it for air, water, food, and all natural resources, so without the Earth and its ecosystems, human life would not be possible.
Question 4. If two kinds of birds compete for the same fruit, how might their way of living change over time?
- If two kinds of birds compete for the same fruit, their way of living may gradually change to reduce competition.
- One species might start eating a different type of fruit, feed at a different time of day, or use another part of the tree.
- Over time, these changes help both species survive by sharing resources more efficiently, a process called resource partitioning.
Question 5. Can human actions cause natural disasters?
- Human actions can increase the frequency and severity of some natural disasters, but they usually do not create them entirely.
- For example, deforestation can lead to floods and landslides, climate change caused by greenhouse gas emissions can intensify cyclones, droughts, and heatwaves, and unplanned urbanization can worsen flooding.
- Thus, while natural processes cause disasters, human activities often make their impacts more destructive.
Keep The Curiosity Alive :
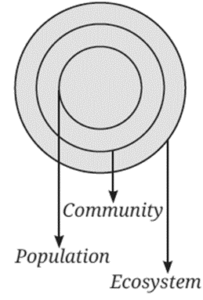
Question 1. Refer to the given diagram (Fig.) and select the wrong statement.
(i) A community is larger than a population.
(ii) A community is smaller than an ecosystem.
(iii) An ecosystem is part of a community.
(iii) An ecosystem is part of a community.
Question 2. A population is part of a community. If all decomposers suddenly disappear from a forest ecosystem, what changes do you think would occur? Explain why decomposers are essential.
- If all decomposers suddenly disappeared from a forest ecosystem, dead plants and animals would start accumulating because there would be nothing to break them down.
- Nutrients locked in this dead matter would not return to the soil, making the soil poor and less fertile.
- As a result, plant growth would decline, and animals that depend on plants for food would also be affected.
- Decomposers are essential because they recycle nutrients back into the soil and maintain the balance and continuity of the ecosystem.
Question 3. Selvam from Cuddalore district, Tamil Nadu, shared that his village was less affected by the 2004 Tsunami compared to nearby villages due to the presence of mangrove forests. This surprised Sarita, Shabnam, and Shijo. They wondered if mangroves were protecting the village. Can you help them understand this?
Yes, mangroves protected the village.
- Mangrove forests act as natural barriers, slowing down strong winds and waves during storms and tsunamis.
- Their roots stabilize soil, reducing erosion, and they absorb water impact, protecting coastal areas.
The Sundarbans' mangroves, a World Heritage Site, demonstrate this protective role.
Question 4. Look at this food chain:
Grass -> Grasshopper -> Frog -> Snake
If frogs disappear from this ecosystem, what will happen to the population of grasshoppers and snakes? Why?
- If frogs disappear from the ecosystem, the population of grasshoppers will increase because frogs feed on grasshoppers and other insects.
- At the same time, the population of snakes will decrease because frogs are an important food source for snakes.
- This happens because removing frogs disturbs the food chain and upsets the balance of the ecosystem.
Question 5. In a school garden, students noticed fewer butterflies the previous season. What could be the possible reasons? What steps can students take to have more butterflies on campus?
Possible reasons for fewer butterflies:
- Loss of flowering plants that provide nectar.
- Use of chemical pesticides that kill caterpillars and butterflies.
- Lack of host plants needed for laying eggs.
- Changes in weather, such as irregular rainfall or high temperatures.
Steps students can take to increase butterflies:
- Plant more native flowering plants and shrubs.
- Grow host plants for caterpillars.
- Avoid or reduce the use of chemical pesticides.
- Provide a safe, clean, and green environment with water and shelter.
These steps help create a butterfly-friendly garden and support biodiversity on campus.
Question 6. Why is it not possible to have an ecosystem with only producers and no consumers or decomposers?
It is not possible to have an ecosystem with only producers because consumers and decomposers are essential for balance and survival.
- Consumers control the population of producers and transfer energy through food chains.
- Decomposers break down dead plants and animals and recycle nutrients back into the soil, which producers need to grow.
Without consumers and decomposers, nutrients would not be recycled and the ecosystem would eventually collapse.
Question 7. Observe two different places near your home or school (e.g., a park and a roadside). List the living and non-living components you see. How are the two ecosystems different?
Place 1: Park :
- Living components (Biotic): Trees, shrubs, grass, flowering plants, birds, butterflies, insects, squirrels, earthworms, humans.
- Non-living components (Abiotic): Soil, water, sunlight, air, temperature, stones.
Place 2: Roadside :
- Living components (Biotic): Small plants and weeds, a few trees, insects, birds, dogs, humans.
- Non-living components (Abiotic): Dust, air, sunlight, noise, smoke, road surface, stones.
Differences between the two ecosystems:
- The park has more greenery, cleaner air, and greater biodiversity, making it a healthier ecosystem.
- The roadside has fewer plants and animals due to pollution, noise, and human disturbance.
Therefore, the park ecosystem is more balanced and stable than the roadside ecosystem.
Question 8. ‘Human-made ecosystems like agricultural fields are necessary, but they must be made sustainable.’ Comment on the statement
- Human-made ecosystems such as agricultural fields are necessary because they provide food and support human survival.
- However, if they are not managed properly, practices like excessive use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and overuse of water can damage soil, reduce biodiversity, and harm the environment.
- Making agriculture sustainable through crop rotation, organic farming, efficient irrigation, and conservation of soil and water helps maintain productivity while protecting nature.
- Thus, human-made ecosystems are essential, but they must be developed and managed sustainably to ensure long-term benefits for both humans and the environment.
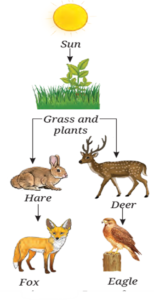
Question 9. If the Indian hare population (Fig.) drops because of a disease, how would it affect the number of other organisms?
- If the Indian hare population drops due to a disease, it will disturb the food chain.
- Foxes, which feed on hares, will decrease in number due to lack of food.
- Grass and plants may increase because fewer hares will be grazing on them.
- Other herbivores like deer may face more competition for food, which can also affect predators like the eagle, thus upsetting the balance of the ecosystem.
Key Features of Kitabcd Exam Master :
|
Click on below links to get PDF from store
PDF : Class 8 -Curiosity-Chapter-12-How Nature Works in Harmony– Notes
PDF : Class 8 -Curiosity-Chapter-12-How Nature Works in Harmony– Exam Master
PDF Set :
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Notes Set (13-PDF)-Rs.58
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Exam Master Set (13-PDF)-Rs.74
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Notes + Exam Master Set (26-PDF)-Rs.116
Main Page : NCERT-Class-8-Science (Curiosity) – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-11-Light: Mirrors and Lenses– Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-13- How Nature Works in Harmony – Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.