Light: Mirrors and Lenses
NCERT-Class-8-Science (Curiosity)-Chapter-10
Solutions (Exercise + Intext)
NCERT Probe & Ponder/Intext Questions :
Question 1. Can we make mirrors which can give enlarged or diminished images?
Yes, we can make mirrors that give enlarged or diminished images.
- Concave mirror: It can give an enlarged image when the object is placed close to the mirror (between the pole and focus). Example: shaving mirror, dentist’s mirror.
- Convex mirror: It always gives a diminished image of the object. Example: rear-view mirrors in vehicles.
So, by using concave and convex mirrors, we can get enlarged or diminished images.
Question 2. On side-view mirrors of vehicles, there is a warning that says “Objects in mirror are closer than they appear”. Why is this warning written there?
The warning “Objects in mirror are closer than they appear” is written because side-view mirrors are convex mirrors.
- A convex mirror always forms a diminished (smaller) image of objects. Since the image looks smaller, our eyes judge the object to be farther away than it actually is. In reality, the object (vehicle) is closer than it appears in the mirror.
Therefore, this warning is given to prevent accidents and help drivers judge the correct distance of nearby vehicles.
Question 3. Why is there a curved line on some reading glasses?
The curved line seen on some reading glasses is because they are bifocal lenses.
These glasses have two different lens powers in one frame:
- The upper part is used for seeing distant objects.
- The lower part is used for reading or near objects.
The curved line separates these two parts and shows where the lens power changes. This helps people who have difficulty seeing both near and far objects clearly
Question 4. How can we distinguish between concave and convex mirrors? (Page 155)
We can distinguish between concave and convex mirrors by observing the type of image formed:
- Concave mirror: It can form a real and inverted image (on a screen) when the object is far away. It can also form a virtual and enlarged image when the object is very close.
- Convex mirror: It always forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image and cannot form a real image on a screen.
So, if a mirror can form a real image on a screen, it is a concave mirror; if it always gives a small, upright image, it is a convex mirror.
Question 5. We have observed images formed by three types of mirrors-plane, concave and convex. But are there any laws which govern the image formation? (Page 157)
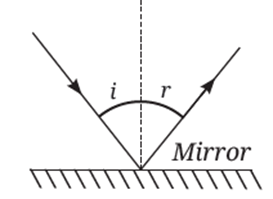
Yes, image formation by all types of mirrors (plane, concave, and convex) is governed by the laws of reflection.
There are two laws of reflection:
- The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
These two laws apply to plane mirrors as well as curved mirrors (concave and convex) and explain how images are formed by mirrors.
Question 6. Are laws of reflection applicable to spherical mirrors also? (Page 160)
Yes, the laws of reflection are applicable to spherical mirrors also.
These laws state that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal all lie in the same plane. These laws hold true for all types of reflecting surfaces, including spherical mirrors like concave and convex mirrors.
Question 7. What changes can be seen in the objects when viewed through lenses? (Page 163)
When objects are viewed through lenses, the following changes can be seen:
- Size of the object may change: it may appear enlarged or diminished.
- Position of the image may change: the image may appear nearer or farther than the object.
- Nature of the image may change: the image can be real or virtual.
- Orientation may change: the image can be erect or inverted (in some cases).
Thus, lenses can change how big an object looks, where it appears, and the type of image formed.
Question 8. Do lenses also converge or diverge the light beam? (Page 163)
Yes, lenses can both converge and diverge light beams. Convex lenses converge (focus) light, while concave lenses diverge (spread out) light.
Question 9. Since convex lens converges a light beam, can it also burn a paper. (Page 164)
Yes, a convex lens can burn a paper.
- A convex lens converges parallel rays of sunlight to a small bright point called the focus. At this point, a large amount of heat energy is concentrated in a very small area. If a piece of paper is placed at the focus, it gets heated strongly and starts burning.
This happens because sunlight carries heat energy, and the convex lens concentrates this energy at one point.
Question 10. Where all are the lenses used? (Page 165)
Lenses are used in a variety of applications, both in everyday life and in scientific instruments. These include eyeglasses, cameras, microscopes, telescopes, and projectors, as well as simple magnifying glasses and spyholes in doors.
Keep The Curiosity Alive :
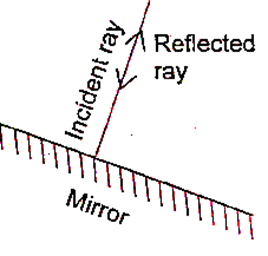
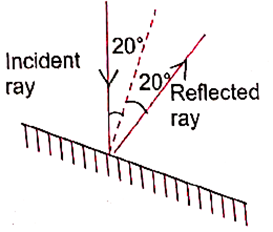
Question 1. A light ray is incident on a mirror and gets reflected by it (Fig.). The angle made by the incident ray with the normal to the mirror is 40°. What is the angle made by the reflected ray with the mirror?
(i) 40° (ii) 50° (iii) 45° (iv) 60°
(ii) 50°
Explanation : The angle of incidence is given as 40° (measured with the normal).
According to the law of reflection:
Angle of reflection = Angle of incidence = 40° (with the normal)
The mirror surface is perpendicular to the normal, so:
Angle with mirror = 900 - 400 = 500
Answer: The reflected ray makes an angle of 50° with the mirror.
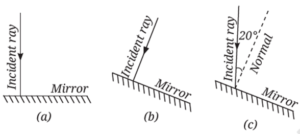
Question 2. Fig. shows three different situations where a light ray falls on a mirror:
(i) The light ray falls along the normal.
(ii) The mirror is tilted, but the light ray still falls along the normal to the tilted surface.
(iii) The mirror is tilted, and the light ray falls at an angle of 20° from the normal.
Draw the reflected ray in each case (Use a ruler and protractor for accurate drawing). What is the angle of reflection in each case?
(i) Light ray falls along the normal
Angle of incidence = 0°
Angle of reflection = 0°
The ray retraces its path. It reflects straight back along the same line.
(ii) Mirror is tilted, but light ray still falls along the normal to the tilted surface
Even though the mirror is tilted, the ray is still perpendicular to the surface.
Angle of incidence = 0°
Angle of reflection = 0°
The ray again retraces its path – the tilt doesn't affect the reflection if the ray is normal to the surface.
(iii) Mirror is tilted, and light ray falls at 20° from the normal
Angle of incidence = 20°
By the law of reflection:
Angle of reflection = 20°
The reflected ray will make a 20° angle with the normal, on the opposite side.
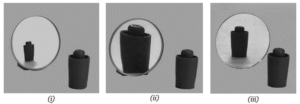
Question 3. In Fig., the cap of a sketch pen is placed in front of three types of mirrors.
Match each image with the correct mirror.
| Image | Mirror |
| (i) | Plane mirror |
| (ii) | Convex mirror |
| (iii) | Concave mirror |
| Image | Mirror |
| (i) | Convex mirror |
| (ii) | Concave mirror |
| (iii) | Plane mirror |
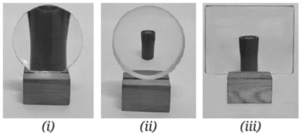
Question 4. In Fig. the cap of a sketch pen is placed behind a convex lens, a concave lens, and a flat transparent glass piece — all at the same distance.
Match each image with the correct type of lens or glass.
| Image | Lens/glass type |
| (i) | Flat transparent glass piece |
| (ii) | Convex lens |
| (iii) | Concave lens |
| Image | Lens/glass type |
| (i) | Convex lens |
| (ii) | Concave lens |
| (iii) | Flat transparent glass piece |
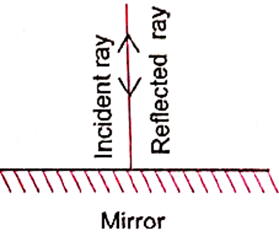
Question 5. When the light is incident along the normal on the mirror, which of the following statements is true:
(i) Angle of incidence is 90°
(ii) Angle of incidence is 0°
(iii) Angle of reflection is 90°
(iv) No reflection of light takes place in this case
(ii) Angle of incidence is 0°
Explanation : When light hits a surface at a 90° angle (perpendicular), it is considered to be incident normally.
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection:
In reflection, the angle of the reflected light is always equal to the angle of
the incident light. Since the light is hitting the mirror normally (at a 0° angle), the reflected light will also be at a 0° angle.
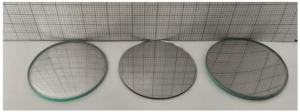
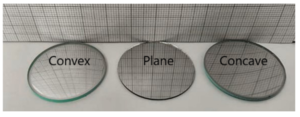
Question 6. Three mirrors — plane, concave and convex are placed in Fig. On the basis of the images of the graph sheet formed in the mirrors, identify the mirrors and write their names above the mirrors.
Question 7. In a museum, a woman walks towards a large convex mirror (Fig.). She will see that:
(i) her erect image keeps decreasing in size.
(ii) her inverted image keeps decreasing in size.
(iii) her inverted image keeps increasing in size and eventually it becomes erect and magnified.
(iv) her erect image keeps increasing in size.
(i) her erect image keeps decreasing in size.
Explanation : Convex mirror always forms virtual, erect and diminished image.
Question 8. Hold a magnifying glass over text and identify the distance where you can see the text bigger than they are written. Now move it away from the text. What do you notice? Which type of lens is a magnifying glass?
A magnifying glass produces a magnified, upright image when the object is placed inside its focal length. A magnifying glass is a convex lens.
Explanation :
- When you hold a magnifying glass close to the text (within a certain short distance), the letters appear bigger and clear.
- This happens when the text is placed within the focal length of the lens.
- Now, when you move the magnifying glass away from the text, the letters first become less clear, and after some distance they may appear inverted and smaller or blurred.
Question 9. Match the entries in Column I with those in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Concave mirror | (a) Spherical mirror with a reflecting surface that curves inwards. |
| (ii) Convex mirror | (b) It forms an image which is always erect and diminished in size. |
| (iii) Convex lens | (c) Object placed behind it may appear inverted at some distance. |
| (iv) Concave lens | (d) Object placed behind it always appears diminished in size. |
Correct matching is:
(i) Concave mirror - (a) Spherical mirror with a reflecting surface that curves inwards.
(ii) Convex mirror - (b) It forms an image which is always erect and diminished in size.
(iii) Convex lens - (c) Object placed behind it may appear inverted at some distance.
(iv) Concave lens - (d) Object placed behind it always appears diminished in size.
Question 10. The following question is based on Assertion/Reason.
Assertion: Convex mirrors are preferred for observing the traffic behind us.
Reason: Convex mirrors provide a significantly larger view area than plane mirrors.
Choose the correct option:
(i) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(ii) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(iii) Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(iv) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
(i) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
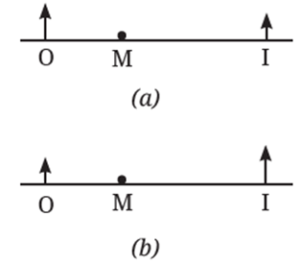
Question 11. In Fig., note that O stands for object, M for mirror, and I for image.
Which of the following statements is true?
(i) Figure (a) indicates a plane mirror and Figure (b) indicates a concave mirror.
(ii) Figure (a) indicates a convex mirror and Figure (b) indicates a concave mirror.
(iii) Figure (a) indicates a concave mirror and Figure (b) indicates a convex mirror.
(iv) Figure (a) indicates a plane mirror and Figure (b) indicates a convex mirror.
(ii) Figure (a) indicates a convex mirror and Figure (b) indicates a concave mirror.
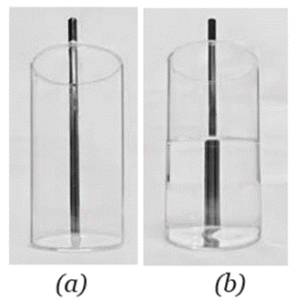
Question 12. Place a pencil behind a transparent glass tumbler (Fig. a). Now fill the tumbler halfway with water (Fig. b). How does the pencil appear when viewed through the water? Explain why its shape appears changed.
When we place a pencil behind a transparent glass tumbler and fill the tumbler
halfway with water, the pencil will appear to be bent or broken at the point where it
enters the water. The submerged portion of the pencil might also appear slightly thicker or shifted from its actual position.
This happens due to refraction of light. Light rays coming from the pencil change their direction when they pass from water to air through the glass. Because of this bending of light, the part of the pencil inside the water appears shifted from its actual position, making the pencil look bent or broken at the surface of the water.
Key Features of Kitabcd Exam Master :
|
Click on below links to get PDF from store
PDF : Class 8 -Curiosity-Chapter-10-Light: Mirrors and Lenses– Notes
PDF : Class 8 -Curiosity-Chapter-10-Light: Mirrors and Lenses– Exam Master
PDF Set :
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Notes Set (13-PDF)-Rs.58
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Exam Master Set (13-PDF)-Rs.74
Class -8-Science (Curiosity) -All 13 Chapters Notes + Exam Master Set (26-PDF)-Rs.116
Main Page : NCERT-Class-8-Science (Curiosity) – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-9-The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions– Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-11- Keeping Time with the Skies – Online Notes

We reply to valid query.