The World of Metals and Non-metals
NCERT-Class-7-Science (Curiosity)-Chapter-4
Solutions (Exercise + Intext)
Intext Questions :
Question 1. Identify the objects that are lustrous in appearance and hard. (Page 43)
Objects that are lustrous (shiny) in appearance and hard are usually metals.
Examples include:
- Gold jewellery
- Silver coins
- Iron tools (like hammer, nails)
- Steel utensils
- Copper vessels
These objects are shiny and strong because they are made of metals.
Question 2. Are all metals hard and solid? (Page 43)
No, not all metals are hard and solid. Sodium and potassium are soft and can be cut with a knife, whereas mercury is a liquid metal at room temperature.
Question 3. Which objects did you find become flat on beating with a hammer? (Page 43)
Objects made of metals become flat when beaten with a hammer.
Examples are:
- Aluminium sheet or foil
- Copper sheet
- Iron sheet
- Gold or silver sheet
This happens because metals are malleable, which means they can be beaten into thin sheets.
Question 4. Can you give some examples of metal sheets? (Page 43)
Examples of metal sheets are
- Thin silver foil used on sweets and
- Aluminium foil used for wrapping food.
- Steel sheets – used in cars, appliances, and containers
- Copper sheets – used in electrical work and decorations
Question 5. Where do you find the use of metal wires? (Page 44)
Metal wires are used in electrical fittings, ornaments like bangles and necklaces, and musical instruments like veena, sitar, violin, and guitar.
Question 6. Have you ever seen wires made of coal or sulphur? (Page 45)
No, coal and sulphur are not ductile, so wires cannot be made from them.
Question 7. How is the sound produced when a metal spoon or plate is dropped different from the sound produced by coal or wood? (Page 45)
- When a metal spoon or plate is dropped, it produces a clear, ringing sound.
But when coal or wood is dropped, it produces a dull or soft sound. - This is because metals are sonorous (they produce a ringing sound), while coal and wood are non-sonorous.
Question 8. Can you name some metals that are used for making cooking vessels? Why are they used? (Page 46)
Metals like copper and aluminium are used for making cooking vessels because they are good conductors of heat.
Question 9. What type of material Is used for making the handle of a screwdriver? (Page 47)
The handle of a screwdriver is made of plastic which is a poor conductor of electricity.
Question 10. Why does an electrician wear rubber gloves and shoes while working? (Page 47)
An electrician wears rubber gloves and shoes because rubber is a poor conductor of electricity and protects against electric shock.
Question 11. Which materials make a bulb glow when tested in the experiment? (Page 48)
Materials like iron and copper, which are metals, make the bulb glow.
Question 12. What do we call materials that allow electricity to pass through them easily? (Page 48)
Materials that allow electricity to pass through them easily are called good conductors of electricity.
Question 13. Under what conditions does an iron object develop brown deposits? (Page 48)
An iron object develops brown deposits when it comes into contact with both air and water.
Question 14. How can rusting of iron be prevented? (Page 50)
Rusting of iron can be prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, or coating it with zinc (galvanisation).
Question 15. That happens when magnesium ribbon burns? (Page 51)
When magnesium ribbon burns, it forms a basic oxide that turns red litmus paper blue.
Question 16. Why is sodium stored in kerosene? (Page 52)
- Sodium is stored in kerosene because it is very reactive.
- It reacts quickly with air and moisture and may catch fire.
- Kerosene keeps sodium away from air and water, so it prevents fire and accidents.
Question 17. What happens when sulphur burns in air? (Page 52)
When sulphur burns in air, it forms sulphur dioxide gas, which dissolves in water to form sulphurous acid.
Question 18. Does sulphur behave with water the same way metals do? (Page 53)
No, sulphur does not react with water like metals do.
Question 19. How do non-metals behave? (Page 53)
Non-metals are usually soft, dull, not malleable or ductile, not sonorous, and are poor conductors of heat and electricity. Their oxides are generally acidic.
Question 20. What are some examples of non-metals? (Page 53)
Examples of non-metals are oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon, etc.
Question 21. Are plastic, glass, wood, and rubber classified as metals or non-metals? (Page 53)
No, plastic, glass, wood, and rubber are not classified as metals or non-metals because they are not elements.
Question 22. Why are non-metals important in our lives? (Page 53)
Non-metals are important in our lives because they play a vital role in living, farming, and daily needs.
- Oxygen is needed for breathing.
- Carbon is the basic element of all living things.
- Nitrogen helps plants grow and is used in fertilisers.
- Chlorine is used to purify drinking water.
- Iodine is used as an antiseptic to clean wounds.
Thus, non-metals are essential for life, health, agriculture, and sanitation.
Let Us Enhance Our Learning : Exercise Questions
Question 1. Which metal is commonly used to make food packaging materials as it is cheaper, and its thin sheets can be folded easily into any shape?
(i) Aluminium (ii) Copper
(iii) Iron (iv) Gold
(i) Aluminium
Question 2. Which of the following metal catches fire when it comes in contact with water?
(i) Copper (ii) Aluminium
(iii) Zinc (iv) Sodium
(iv) Sodium
Question 3. State with reason(s) whether the following statements are True [T] or False [F].
(i) Aluminium and copper are examples of non-metals used for making utensils and statues. [ ]
(ii) Metals form oxides when combined with oxygen, the solution of which turns blue litmus paper to red. [ ]
(iii) Oxygen is a non-metal essential for respiration. [ ]
(iv) Copper vessels are used for boiling water because they are good conductors of electricity. [ ]
(i) False. Aluminium and copper are metals and not non-metals which are used for making utensils and statues.
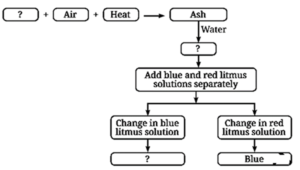
(ii) False. Metallic oxides are basic in nature and the solution of which turns red litmus paper to blue.
(iii) True
(iv) False. Copper vessels are used for boiling water because copper is a good conductor of heat, not electricity.
Question 4. Why are only a few metals suitable for making jewellery?
Only a few metals are suitable for making jewellery because they have special properties.
- They are lustrous, so they look shiny and attractive.
- They are malleable, so they can be easily shaped into different designs.
- They do not rust or corrode easily, so they last for a long time.
Metals like gold, silver, and platinum have these properties, which is why they are used for jewellery.
Question 5. Match the uses of metals and non-metals given in Column I with the jumbled names of metals and non-metals given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Used in electrical wiring | (a) ENXYGO |
| (ii) Most malleable and ductile | (b) NECOHIRL |
| (iii) Living organisms cannot survive without it. | (c) PEPORC |
| (iv) Plants grow healthy when fertilisers containing it are added to the soil. | (d) TENGOINR |
| (v) Used in water purification | (e) OGDL |
(i)-(c), (ii)-(e), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(d), (v)-(b)
(i) Used in electrical wiring - (c) Copper
(ii) Most malleable and ductile - (e) Gold
(iii) Living organisms cannot survive without it-(a) Oxygen
(iv) Plants grow healthy when fertilisers containing it are added to the soil - (d) Nitrogen
(v) Used in water purification - (b) Chlorine
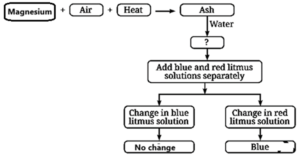
Question 6. What happens when oxygen reacts with magnesium and sulfur. What are the main differences in the nature of products formed?
When oxygen reacts with magnesium and sulfur, different types of products are formed.
- Magnesium burns in oxygen with a bright white flame and forms magnesium oxide, which is a basic oxide.
- Sulfur burns in oxygen with a blue flame and forms sulfur dioxide, which is an acidic oxide.
Main differences in the products formed:
- Magnesium oxide is basic in nature and reacts with acids.
- Sulfur dioxide is acidic in nature and reacts with bases.
So, oxygen forms a basic oxide with a metal (magnesium) and an acidic oxide with a non-metal (sulfur).
Question 7. Complete the following flow chart:
Question 8. You are provided with the following materials. Discuss which material would be your choice to make a pan that is most suitable for boiling water and why?
Iron, copper, sulfur, coal, plastic, wood, cardboard.
I would choose copper to make a pan for boiling water because it is a good conductor of heat and heats water quickly and evenly.
Question 9. You are provided with three iron nails, each dipped in oil, water and vinegar. Which iron nail will not rust, and why?
The iron nail dipped in oil will not rust because oil prevents air and water from reaching the surface of the iron and stops rusting.
Question 10. How do the different properties of metals and non-metals determine their uses in everyday life?
The different properties of metals and non-metals decide how we use them in daily life.
Metals are generally hard, strong, malleable, ductile, shiny, and good conductors of heat and electricity.
Because of these properties:
- Iron and steel are used to make buildings, bridges, and tools.
- Copper and aluminium are used for electrical wires.
- Aluminium is used in aeroplanes because it is light and does not rust.
- Gold and silver are used for jewellery because they are shiny and easy to shape.
Non-metals are usually light, dull, poor conductors of heat and electricity, and many are essential for life.
Because of these properties:
- Oxygen is used for breathing.
- Nitrogen is used in fertilisers for plant growth.
- Chlorine is used to purify water.
- Carbon is used as fuel and is the basis of all living things.
Thus, the special properties of metals and non-metals decide their different uses in everyday life.
Question 11. One of the methods of protecting iron from getting rusted is to put a thin coating of zinc metal over it. Since sulfur does not react with water, can it be used for this purpose? Justify your answer.
No, sulfur cannot be used to protect iron from rusting.
- Rusting happens when iron reacts with oxygen and moisture. Zinc protects iron because it forms a protective layer and also reacts with oxygen more easily than iron, preventing iron from rusting (this process is called galvanisation).
- Although sulfur does not react with water, it does not form a protective coating on iron. In fact, sulfur can react with iron to form iron sulfide, which damages the iron instead of protecting it.
Therefore, sulfur cannot be used to protect iron from rusting, while zinc is suitable for this purpose.
Question 12. An ironsmith heats iron before making tools. Why is heating necessary in this process?
- Heating is necessary because iron becomes soft and more malleable when heated. This makes it easier to shape, bend, and beat into tools.
- If iron is not heated, it is very hard and difficult to mould.
Key Features of Kitabcd Exam Master :
|
Click on below links to get PDF from store
PDF : Chapter-4-The World of Metals and Non-metals– Notes
PDF : Chapter-4-The World of Metals and Non-metals– Exam Master
Main Page : NCERT-Class-7-Science (Curiosity) – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Next Chapter : Chapter-3- Electricity: Circuits and their Components – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-5- Changes Around Us: Physical and Chemical – Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.