Electricity: Circuits and their Components
NCERT-Class-7-Science (Curiosity)-Chapter-3
Solutions (Exercise + Intext)
Intext Questions :
Question 1. Why does the torch lamp glow in one position of its switch? (Page 24)
The torch lamp glows in one position of its switch because only in that position the electric circuit is completed.
- When the switch is ON, the circuit becomes closed. Electric current flows from the battery through the bulb. The bulb then glows.
- When the switch is OFF, the circuit is open, current cannot flow, and the bulb does not glow.
Question 2. In a torch, we generally use more than one cell. Are those placed in any particular order? (Page 25)
Yes, in a torch, cells are placed one after another in a line, with the positive end of one cell touching the negative end of the next. This is called series connection, and it helps increase the total voltage to make the bulb glow brighter.
Question 3. How does a switch turn ON or OFF the torchlight? (Page 32)
A switch turns the torchlight ON or OFF by completing or breaking the electric circuit.
- When the switch is ON, it completes the circuit. Electric current flows from the battery to the bulb, so the torchlight glows.
- When the switch is OFF, it breaks the circuit. Electric current cannot flow, so the torchlight does not glow.
Thus, a switch controls the flow of electricity in the torch.
Question 4. Can we represent the circuits in a simple manner? (Page 33)
Yes, we can represent circuits in a simple way using circuit diagrams.
Question 5. Why does we use metal wires for making electric circuits? Can we not use some other materials for wires? (Page 34)
We use metal wires like copper, aluminum in electric circuits because metals are good conductors of electricity, meaning they allow electricity to flow easily through
them.
- Metals are also strong and flexible, so they can be made into thin wires.
- Insulators like plastic, rubber, wood, and glass cannot be used because they do not allow electricity to flow.
- Some materials like graphite or salt water can conduct electricity, but they are not suitable for making wires because they are weak or not safe.
Therefore, metal wires are best for making electric circuits.
Question 6. Why are electric wires covered with plastic rubber? (Page 34)
- Electric wires are covered with plastic or rubber to insulate them.
- This means the plastic or rubber prevents electricity to flow from outside the wire.
- It also protects the wire from damage, moisture and heat, ensuring safety and preventing electrical shocks or short circuits.
Let Us Enhance Our Learning : Exercise Questions
Question 1. Choose the incorrect statement.
(i) A switch is the source of electric current in a circuit.
(ii) A switch helps to complete or break the circuit.
(iii) A switch helps us to use electricity as per our requirement.
(iv) When the switch is in 'OFF' position, 'there is an air gap between its terminals.
(i) is incorrect.
A switch is not the source of electric current; the battery or cell is the source. A switch only helps to start or stop the flow of current.
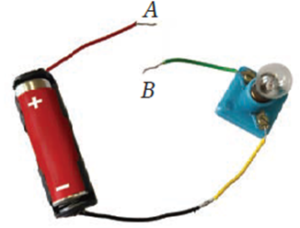
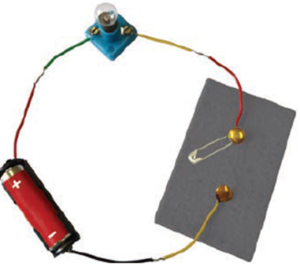
Question 2. Observe the fig. given below. With which material connected between the ends A and B will the lamp not glow?
The lamp will not glow if a non-conducting material (insulator) like plastic, rubber or wood is connected between A and B. These materials do not allow electric current to pass through them.
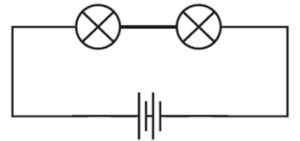
Question 3. In given fig., if the filament of one of the lamps is broken, will the other glow? Justify your answer.
No, the other lamp will not glow.
Both lamps are connected in series. If the filament of one lamp breaks, the circuit becomes open and current cannot flow. So, both lamps will stop glowing.
Question 4. A student forgot to remove the insulator covering from the connecting wires while making a circuit. If the lamp and the cell are working properly, will the lamp glow?
Answer :
No, the lamp will not glow.
The plastic insulator does not allow electric current to pass. So, even if the cell and lamp are fine, the current won't flow and the lamp won't glow.
[/spoiler]Question 5. Draw a circuit diagram for a simple torch using symbols for electric components.
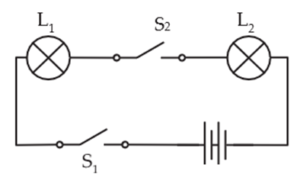
Question 6. In Fig. (i) If S2 is in ‘ON’ position, S1 is in ‘OFF’ position, which lamp(s) will glow?
(ii) If S2 is in ‘OFF’ position, S1 is in ‘ON’ position, which lamp(s) will glow?
(iii) If S1 and S2 both are in ‘ON’ position, which lamp(s) will glow?
(iv) If both S1 and S2 are in ‘OFF’ position, which lamp(s) will glow?
(i) Neither lamps will glow.
(ii) Neither lamps will glow.
(iii) Both lamps L1 and L2 will glow.
(iv) Neither lamps will glow.
Question 7. Vidyut has made the circuit as shown in Fig. Even after closing the circuit, the lamp does not glow. What can be the possible reasons? List as many possible reasons as you can for this faulty operation. What will you do to fi nd out why the lamp did not glow?
Possible reasons why the lamp doesn't glow
- The cell might be dead (no power).
- The bulb might be fused or damaged.
- The wires might be loose or broken.
- The switch might not be working.
- There might still be plastic covering (insulator) on the wire ends.
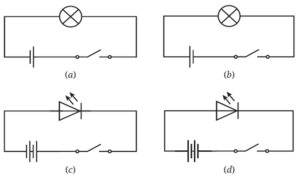
Question 8. In Fig., in which case(s) the lamp will not glow when the switch is closed?
In case (b) The wires are not connected to the lamp in the proper order. So, the lamp will not glow.
In case (d) The LED is connected in the wrong direction. LEDs only work in one direction, so it will not glow.
So, the lamp will not glow in cases (b) and (d).
Question 9. Suppose the ‘+’ and ‘–’ symbols cannot be read on a battery. Suggest a method to identify the two terminals of this battery.
We can identify the terminals of the battery using a simple electrical test:
Method (using a bulb/LED and wires):
- Take a small bulb (or LED), two wires, and the battery.
- Connect the wires to the two ends of the battery in any way.
- If the bulb glows, the connection is correct.
Now note the connection:
- The end of the battery connected to the metal tip (base) of the bulb is the positive (+) terminal.
- The end connected to the side metal casing of the bulb is the negative (–) terminal.
If using an LED:
- The LED glows only in one direction.
- The battery end connected to the longer leg of the LED is the positive terminal.
Thus, by observing which connection makes the bulb/LED glow, we can identify the + and – terminals of the battery.
Question 10. You are given six cells marked A, B, C, D, E, and F. Some of these are working and some are not. Design an activity to identify which of them are working.
(i) List the items that you require.
(ii) Write the procedure that you will follow.
(iii) With the items, carry out the activity to identify the cells that are working.
Activity to identify the working cells
(i) Items required :
- Six cells labeled A, B, C, D, E, and F
- A small torch bulb (or LED)
- Two connecting wires
- A switch (optional)
(ii) Procedure :
- Set up a simple electric circuit by connecting the bulb, two wires, and one cell.
- Take cell A and connect it in the circuit properly.
- Observe the bulb: If the bulb glows, the cell is working. If the bulb does not glow, the cell is not working.
- Disconnect cell A and repeat the same steps with cells B, C, D, E, and F, one by one.
- Record the observation for each cell.
(iii) Observation / Result :
- Cells for which the bulb glows are working cells.
- Cells for which the bulb does not glow are not working.
By testing each cell individually in a simple circuit and observing whether the bulb glows, we can easily identify which of the cells A–F are working.
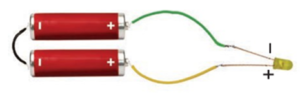
Question 11. An LED requires two cells in series to glow. Tanya made the circuit as shown in Fig. Will the lamp glow? If not, draw the wires for correct connections.
Key Features of Kitabcd Exam Master :
|
Click on below links to get PDF from store
PDF : Chapter-3- Electricity: Circuits and their Components– Notes
PDF : Chapter-3- Electricity: Circuits and their Components– Exam Master
Main Page : NCERT-Class-7-Science (Curiosity) – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Next Chapter : Chapter-2- Exploring Substances: Acidic, Basic, and Neutral – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-4- The World of Metals and Non-metals – Online Solutions

We reply to valid query.