Transition and Inner transition Elements
Maharashtra Board-Class-12-Chemistry-Chapter-8
Solutions
Question 1. Choose the most correct option.
(i) Which one of the following is dimagnetic
(a) Cr2+
(b) Fe3+
(c) Cu2+
(d) Sc3+
(d) Sc3+
(ii) Most stable oxidation state of Titanium is
(a) +2
(b) +3
(c) +4
(d) +5
(c) +4
(iii) Components of Nichrome alloy are are
(a) Ni, Cr, Fe
(b) Ni, Cr, Fe, C
(c) Ni, Cr
(d) Cu, Fe
(c) Ni, Cr
(iv) Most stable oxidation state of Ruthenium is
(a) +2
(b) +4
(c) +8
(d) +6
(b) +4
(v) Stable oxidation states for chromium are
(a) +2, +3
(b) +3, +4
(c) +4, +5
(d) +3, +6
(d) +3, +6
(vi) Electronic configuration of Cu and Cu+1
(a) 3d10, 4s0; 3d9, 4s0
(b) 3d9, 4s1; 3d94s0
(c) 3d10, 4s1; 3d10, 4s0
(d) 3d8, 4s1; 3d10, 4s0
(c) 3d10, 4s1; 3d10, 4s0
(vii) Which of the following have d0s0 configuration
(a) Sc3+
(b) Ti4+
(c) V5+
(d) all of the above
(d) all of the above
(viii) Magnetic moment of a metal complex is 5.9 B.M. Number of unpaired electrons in the complex is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
(d) 5
(ix) In which of the following series all the elements are radioactive in nature
(a) Lanthanides
(b) Actinides
(c) d-block elements
(d) s-block elements
(b) Actinides
(x) Which of the following sets of ions contain only paramagnetic ions
(a) Sm3+, Ho3+, Lu3+
(b) La3+, Ce3+, Sm3+
(c) La3+, Eu3+, Gd3+
(d) Ce3+, Eu3+, Yb3+
(d) Ce3+, Eu3+, Yb3+
(xi) Which actinoid, other than uranium, occur in significant amount naturally?
(a) Thorium
(b) Actinium
(c) Protactinium
(d) Plutonium
(a) Thorium
(xii) The flux added during extraction of Iron from teamatite are its?
(a) Silica
(b) Calcium carbonate
(c) Sodium carbonate
(d) Alumina
(b) Calcium carbonate
Question 2. Answer the following
(i) What is the oxidation state of Manganese in (i) MnO42- (ii) MnO4- ?
Oxidation state of Manganese in (i) MnO42- is +6 (ii) MnO4- is +7
(ii) Give uses of KMnO4
Potassium permanganate is used :
(iii) Why salts of Sc3+, Ti4+, V5+ are colourless ?
(a) Sc3+ salts are colourless : (b) Ti4+ salts are colourless : (c) V5+ salts are colourless :
(iv) Which steps are involved in manufacture of potassium dichromate from chromite ore ?
Steps in manufacture of potassium dichromite from chromite ore are :
(v) Balance the following equation
(i) KMnO4 + H2C2O4 + H2SO4 → MnSO4 + K2SO4 + H2O + O2
2KMnO4 + 5H2C2O4 + 3H2SO4 → 2MnSO4 + K2SO4 + 10CO2 + 8H2O
(ii) K2Cr2O7 + KI + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 7H2O + 3I2
K2Cr2O7 + 6Kl + 7H2SO4 → 4K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 7H2O + 3I2
(vi) What are the stable oxidation states of plutonium, cerium, manganese, Europium ?
Plutonium : +3 to +7 Cerium : +3, +4 Manganese : +2, +4, +6, +7 Europium : +2, 34
(vii) Write probable electronic configuration of chromium and copper.
(a) Chromium (24Cr) has electronic configuration, 24Cr (Expected) : 1s22s22p63s23p63d44s2 (Observed) : 1s22s22p63s23p63d54s1 Explanation : (b) Copper (29Cu) has electronic configuration, 29Cu (Expected) : 1s22s22p63s23p63d94s2 (Observed) : 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s1 Explanation :
(viii) Why nobelium is the only actinoid with +2 oxidation state?
Nobelium has the electronic configuration 102No : [Rn] 5f146d07s2 No2+ : [Rn] 5f146d0 Since the 4f subshell is completely filled and 6d0 is empty, +2 oxidation state is the stable oxidation state. Other actinoids in +2 oxidation state are not as stable due to incomplete 4f subshell.
(ix) Explain with the help of balanced chemical equation, why the solution of Ce(IV) is acidic.
Ce4 undergoes hydrolysis as, Ce4+ + 2H2O -> Ce(OH)4 + 4H+. Due to the presence of H+ in the solution, the solution is acidic. Hence, the solution of Ce(IV) is acidic in nature.
(x) What is meant by ‘shielding of electrons’ in an atom?
(xi) The atomic number of an element is 90. Is this element diamagnetic or paramagnetic?
The 90th element thorium has electronic configuration, [Rn] 6d27s2. Since it has 2 unpaired electrons it is paramagnetic.
Question 3. Answer the following
(i) Explain the trends in atomic radii of d block elements.

(ii) Name different zones in the Blast furnace. Write the reactions taking place in them.
There are three zones of temperature in the Blast furnace in which three main chemical reactions take place. (a) Zone of combustion : This is 5 - 10 m from the bottom. The hot air blown through the tuyers, oxidises coke to CO which is an exothermic reaction, due to which the temperature of furnace rises. C + \(\frac{1}{2}\)O2 → CO ΔH = —220 kJ Some part of CO dissociates to give finely divided carbon and O2. 2CO → 2C + O2 The hot gases with CO rise up in the furnace and heats the charge coming down. CO acts as a fuel as well as a reducing agent. (b) Zone of reduction (22-25 m near the top) : At about 900 K, CO reduces Fe2O3 to spongy (or porous) iron. Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2 Carbon also reduces partially Fe2O3 to Fe. Fe2O3 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO (c) Zone of slag formation (20 m unit) : At 1200 K limestone, CaCO3 in the charge, decomposes and forms a basic flux CaO which further reacts at 1500 K with gangue (SiO2, Al2O3) and forms a slag of CaSiO3 and Ca3AlO3. CaCO3 → CaO + CO2 CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3 12CaO + 2Al2O3 → 4Ca3AlO3 + 3O2 The slag is removed from the bottom of the furnace through an outlet. (d) Zone of fusion (15 m ht): The impurities in ore like MnO2 and Ca3(PO4)2 are reduced to Mn and P while SiO2 is reduced in Si. The spongy iron moving down in the furnace melts in the fusion zone and dissolves the impurities like C, Si, Mn, phosphorus and sulphure. The molten iron collects at the bottom of furnace. The lighter slag floats on the molten iron and prevents its oxidation. The molten iron is removed and cooled in moulds. It is called pig iron or cast iron. It contains about 4 % carbon.
(iii) What are the differences between cast iron, wrought iron and steel.
Manufacturing automotive parts, pots, pans, utensils
Cast iron
Wrought iron
Steel
Hard and brittle
Very soft
Neither too hard nor too soft.
Contains 4% carbon.
Contains less than 0.2% carbon.
Contains 0.2 to 2% carbon
Used for making pipes,
Used for making pipes, bars for stay bolts, engine bolts and rivetts.
Used in buildings infrastructure, tools, ships, automobiles, weapons etc.
(iv) Iron exhibits +2 and +3 oxidation states. Write their electronic configuration. Which will be more stable ? Why ?
The electronic configuration of Fe2+ and Fe3+ : Fe2+: 1s22s22p63s23p63d6 Fe3+: 1s22s22p63s23p63d5 Due to loss of two electrons from the 4s-orbital and one electron from 3d-orbital, iron attains 3+ oxidation state. Since in Fe3+, the 3d-orbital is half filled, it gets extra stability, hence Fe3+ is more stable than Fe2+.
(v) Give the similarities and differences in elements of 3d, 4d and 5d series.
Similarity : Differences :
(vi) Explain trends in ionisation enthalpies of d block elements.
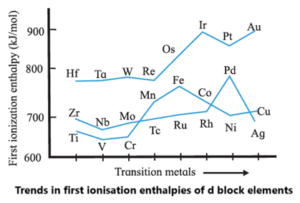
(vii) What is meant by diamagnetic and paramagnetic? Give one example of diamagnetic and paramagnetic transition metal and lanthanoid metal.
Diamagnetic substances : When a magnetic field is applied, substances which are repelled by the magnetic fields are called diamagnetic substances. Paramagnetic substances : When a magnetic field is applied, substances which are attracted towards the applied magnetic field are called paramagnetic substances. Examples :
Transition metal
Lanthanoid metal
Diamagnetic
Zinc
Ytterbium
Paramagnetic
Titanium
Cerium
(viii) Why the ground-state electronic configurations of gadolinium and lawrentium are different than expected?
(ix) Write steps involved in metallurgical process.
The various steps and principles involved in the extraction of pure metals from their ores are as follows :
(x) Cerium and Terbium behaves as good oxidising agents in +4 oxidation state. Explain.
(xi) Europium and xtterbium behave as good reducing agents in +2 oxidation state explain.
PDF : Chapter-8-Transition and Inner transition Elements-Text Book
PDF : Chapter-8-Transition and Inner transition Elements- Notes
PDF : Chapter-8-Transition and Inner transition Elements- Solution
All 16 Chapters Notes -Class-12-Chemistry (16-PDF)
All 16 Chapters Solutions -Class-12-Chemistry (16-PDF)
All 16 Chapters Notes+Solutions -Class-12-Chemistry (32-PDF)
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Chemistry – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-8-Elements of Groups 16, 17 and 18 – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-9-Coordination Compounds – Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.