Biomolecules
Maharashtra Board-Class-12-Chemistry-Chapter-14
Question 1. Select the most correct choice.
(i) CH2OH-CO-(CHOH)4-CH2OH is an example of
(a) Aldohexose
(b) Aldoheptose
(c) Ketotetrose
(d) Ketoheptose
(d) Ketoheptose
(ii) Open chain formula of glucose does not contain
(a) Formyl group
(b) Anomeric hydroxyl group
(c) Primary hydroxyl group
(d) Secondary hydroxyl group
(b) Anomeric hydroxyl group
(iii) Which of the following does not apply to CH2NH2-COOH
(a) Neutral amino acid
(b) L - amino acid
(c) Exists as zwitter ion
(d) Natural amino acid
(b) L - amino acid
(iv) Tryptophan is called essential amino acid because
(a) It contains aromatic nucleus.
(b) It is present in all the human proteins.
(c) It cannot be synthesised by human body.
(d) It is essential constituent of enzymes.
(c) It cannot be synthesised by human body.
(v) A disulfide link gives rise to the following structure of protein.
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Quaternary
(c) Tertiary
(vi) RNA has
(a) A - U base pairing
(b) P-S-P-S backbone
(c) double helix
(d) G - C base pairing
(a) A - U base pairing
Question 2. Give scientific reasons :
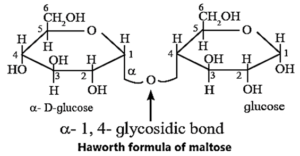
(i) The disaccharide sucrose gives negative Tollens test while the disaccharide maltose gives positive Tollens test.
- (a) The structure of sucrose contains glycosidic linkage between C-1 of α-glucose and C-2 of β-fructose. Since the potential aldehyde and ketone groups of both the monosaccharide units are involved in the formation of the glycosidic bond (i.e., α, β-1,2- glycosidic bond), sucrose is a non-reducing sugar and gives negative Tollen's test.
- (b) The glycosidic bond in maltose is in between C-1 of one glucose ring and C-4 of the other (i.e., α-1,4-glycosidic linkage). The hemiacetal group at C-1 of the second ring is not involved in the glycosidic linkage. Hence, maltose is a reducing sugar and gives positive Tollen's test.
(ii) On complete hydrolysis DNA gives equimolar quantities of adenine and thymine.
On complete hydrolysis DNA yields 2-deoxy-D-ribose, adenine, thymine, guanine, cystosine and phosphoric acid. Since adenine always forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine, the hydrolysis of DNA gives equimolar quantities of adenine and thymine.
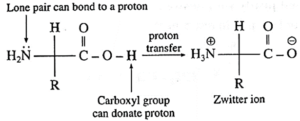
(iii) α-Amino acids have high melting points compared to the corresponding amines or carboxylic acids of comparable molecular mass.
- α-Amino acids have high melting points compared to the corresponding amines or carboxylic acids of comparable molecular mass due to the presence of both acidic (carboxylic group) and basic (amino group) groups in the same molecule.
- In aqueous solution, proton transfer from acidic group to amino (basic) group of amino acid forms a salt, which is a dipolar ion called zwitter ion.
Thus, a-amino acids have high melting points compared to the corresponding amines or carboxylic acids of comparable molecular mass.
(iv) Hydrolysis of sucrose is called inversion.
- Sucrose is dextro rotatory. On hydrolysis it gives equimolar mixture of D-(+) glucose and D-(-) fructose. Since the laevorotation of fructose (-92.4°) is more than dextrorotation of glucose (+ 52.7°), the hydrolysis product has net laevorotation.
- Thus, hydrolysis of sucrose brings about a change in the sign of rotation, from dextro (+) to laevo (-) and the product is called as invert sugar and so the hydrolysis of sucrose is called inversion.
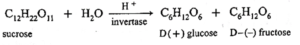
(v) On boiling egg albumin becomes opaque white.
- Proteins when subjected to high temperature undergo disruption of noncovalent interactions which are responsible for the specific shape of protein. That is, it undergoes denaturation.
- Denaturation disturbs the specific structure of egg albumin which causes a change in the physical properties.
Thus, on boiling egg albumin becomes opaque white.
Question 3. Answer the following
(i) Some of the following statements apply to DNA only, some to RNA only and some to both. Lable them accordingly.
(a) The polynucleotide is double stranded. (…….. )
(b) The polynucleotide contains uracil. (…….. )
(c) The polynucleotide contains D-ribose (…….. ).
(d) The polynucleotide contains Guanine ( ……..).
(a) The polynucleotide is double stranded. (DNA)
(b) The polynucleotide contains uracil. (RNA)
(c) The polynucleotide contains D-ribose (RNA).
(d) The polynucleotide contains Guanine (RNA, DNA).
(ii) Write the sequence of the complementary strand for the following segments of a DNA molecule.
(a) 5' - CGTTTAAG - 3'
(b) 5' - CCGGTTAATACGGC - 3'
(i) 5' - ACGTAC-3'
The complementary strand runs in opposite direction from the 3' end to the 5' end. It has the base sequence decided by complementary base pairs A - T and C - G.

(ii) DNA molecule : 5-CGTTTAAG-3'
The complementary strand runs in opposite direction from the 3’ end to the 5’ end. It has the base sequence decided by complementary base pairs A-T and C-G.
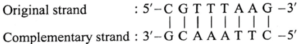
(iii) Write the names and schematic representations of all the possible dipeptides formed from alanine, glycine and tyrosine.
(i) Dipeptide from glycine :
Carboxylic group of glycine reacting with amino group another molecule of glycine to form dipeptide
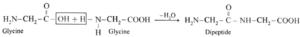
(ii) Dipeptide from alanine :
Carboxylic group of alanine reacting with amino group of another molecule of alamine to form dipeptide.
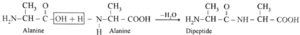
(iii) Dipeptide from glycine and alanine :
Carboxylic group of glycine reacting with amino group another molecule of alanine to form dipeptide
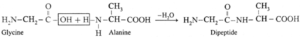
(iv) Dipeptide formed from alanine and tyrosine :

(v) Dipeptide formed from glycine and tyrosine :

(iv) Give two evidences for presence of formyl group in glucose.
(i) Glucose reacts with hydroxyl amine in an aqueous solution to form glucose oxime. This indicates the presence of -CHO (formyl group) in glucose.
(ii) Glucose on oxidation with mild oxidising agent like bromine water gives gluconic acid which shows carbonyl group in glucose is aldehyde (formyl group) group.
Question 4. Draw a neat diagram for the following:
(i) Haworth formula of glucopyranose

(ii) Zwitter ion
(iii) Haworth formula of maltose
(iv) Secondary structure of protein
(i) ∝-Helix : In ∝-helix structure, a polypeptide chain gets coiled by twisting into a right handed or clockwise spiral known as ∝-helix. The characteristic features of ∝-helical

(ii) β-Pleated sheet : The secondary structure is called β-pleated sheet when two or more polypeptide chains, called strands, line up side-by-side (Fig.)

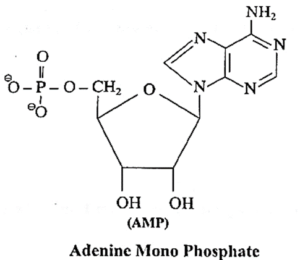
(v) AMP
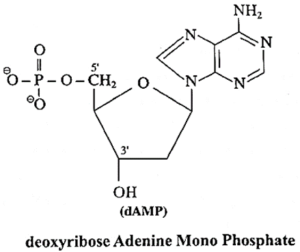
(vi) dAMP
(vii) One purine base from nucleic acid

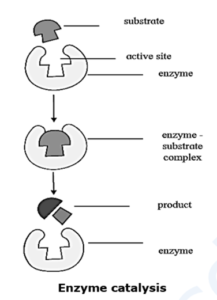
(viii) Enzyme catalysis
PDF : Class-12-Chemistry-Chapter-14-Biomolecules-Text Book
PDF : Class-12-Chemistry-Chapter-14-Biomolecules- Notes
PDF : Class-12-Chemistry-Chapter-14-Biomolecules- Solution
All 16 Chapters Notes -Class-12-Chemistry (16-PDF)
All 16 Chapters Solutions -Class-12-Chemistry (16-PDF)
All 16 Chapters Notes+Solutions -Class-12-Chemistry (32-PDF)
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Chemistry – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 13- Amines – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-15-Introduction to Polymer Chemistry- Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.