Control and Coordination
Maharashtra Board-Class-12th-Biology-Chapter-9
Solutions
Question 1. Multiple choice questions.
(1) The nervous system of mammals uses both electrical and chemical means to send signals via neurons. Which part of the neuron receives impulse?
(a) Axon
(b) Dendron
(c) Nodes of Ranvier
(d) Neurilemma
(b) Dendron
(2) ___________ is a neurotransmitter.
(a) ADH
(b) Acetyl CoA
(c) Acetyl choline
(d) Inositol
(c) Acetyl choline
(3) The supporting cells that produce myelin sheath in the PNS are _________.
(a) Oligodendrocytes
(b) Satellite cells
(c) Astrocytes
(d) Schwann cells
(d) Schwann cells
(4) A collection of neuron cell bodies located outside the CNS is called __.
(a) Tract
(b) Nucleus
(c) Nerve
(d) Ganglionl
(d) Ganglionl
(5) Receptors for protein hormones are located
(a) in cytoplasm
(b) on cell surface
(c) in nucleus
(d) on Golgi complex
(b) on cell surface
(6) If parathyroid gland of man are removed, the specific result will be
(a) onset of aging
(b) disturbance of Ca++
(c) onset of myxoedema
(d) elevation of blood pressure
(b) disturbance of Ca++
(7) Hormone thyroxine, adrenaline and non-adrenaline are formed from --.
(a) Glycine
(b) Arginine
(c) Ornithine
(d) Tyrosine
(d) Tyrosine
(8) Pheromones are chemical messengers produced by animals and released outside the body. The odour of these substance affects
(a) skin colour
(b) excretion
(c) digestion
(d) behavior
(d) behavior
(9) Which one of the following is a set of discrete endocrine gland
(a) Salivary, thyroid, adrenal, ovary
(b) Adrenal, testis, ovary, liver
(c) Pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, thymus
(d) pituitary, pancreas, adrenal, thymus
(c) Pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, thymus
(10) After ovulation, Graafian follicle changes into
(a) Corpus luteum
(b) Corpus albicans
(c) Corpus spongiosum
(d) Corpus callosum
(a) Corpus luteum
(11) Which one of the following pair correctly matches a hormone with a disease resulting from its deficiency?
(a) Parathyroid hormone – Diabetes insipidus
(b) Leutinising hormone – Diabetes mellitus
(c) Insulin - Hyperglycemia
(d) Thyroxine – Tetany
(c) Insulin - Hyperglycemia
(12) ___________ is in direct contact of brain in human
(a) Cranium
(b) Duramater
(c) Arachnoid
(d) Piamater
(d) Piamater
Question 2 Very short answer questions.
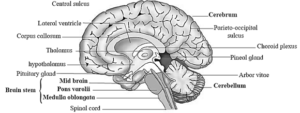
(1) What is the function of red nucleus?
Red nucleus plays an important role in controlling posture and muscle tone. modifying some motor activities and motor coordination.
(2) What is the importance of Corpora quadrigemina?
Corpora quadrigemina consists of 4 solid rounded structures. viz. superior and inferior colliculi. Superior colliculi control visual reflexes while inferior colliculi control auditory reflexes.
(3) What does the cerebellum of brain control?
Cerebellum of brain is an important centre which maintains equilibrium of body posture. balancing orientation, moderation of voluntary movements and maintenance of muscle tone
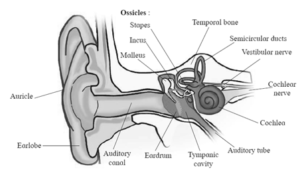
(4) Name the three ossicles of the middle ear
(i) Malleus [hammer], (ii) incus [anvil] and (iii) stapes [stirrup] are the three ossicles of the middle ear
(5) Name the hormone which is anti abortion hormone
Progesterone is anti-abortion hormone
(6) Name an organ which acts as temporary endocrine gland.
Placenta is a temporary endocrine gland.
(7) Name the type of hormones binding to DNA and alter gene expression.
Steroid hormones
(8) What is the cause of abnormal elongation of long bones of arms and legs and of lower jaw.
Hypersecretion of growth hormones in adults causes abnormal elongation of long bones of arms and legs and of lower jaw i.e. acromegaly.
(9) Name the hormone secreted by the pineal gland.
Pineal gland secretes a hormone called melatonin also known as sleep hormone.
(10) Which endocrine gland plays important, role in improving immunity?
The endocrine gland, thymus plays an important role in improving immunity.
Question 3. Match the organism with the type of nervous system found in them.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Neurons | a. Earthworm |
| 2. Ladder type | b. Hydra |
| 3. Ganglion | c. Flatworm |
| 4. Nerve net | d. Human |
Column A
Column B
1. Neurons
Human
2. Ladder type
Flatworm
3. Ganglion
Earthworm
4. Nerve net
Hydra
Question 4. Very short answer questions.
(1) Describe the endocrine role of islets of Langerhans.
Endocrine cells of pancreas form groups of cells called Islets of Langerhans. There are four kinds of cells in islets of Langerhans which secrete hormones.
(2) Mention the function of testosterone?
Testosterone is a steroid sex hormone secreted by testes and cortex of adrenal glands. It controls the secondary sexual characters in males.
(3) Give symptoms of the disease caused by hyposecretion of ADH.
Polydipsia, i.e. frequent thirst and polyuria i.e. frequent urination are the symptoms of the dlsease caused by hyposecretion of ADH.
Question 5. Short answer questions
(1) Rakesh got hurt on his head when he fell down from his motorbike. Which inner membranes must have protected his brain? What other roles do they have to play?
When Rakesh fell down from his motorbike, the inner membranes that protected his brain were meninges, viz. dura mater, arachnoid membrane and pia mater. Morevover, CSF must have also acted as a shock absorber.
(2) Give reason - Injury to medulla oblongata may prove fatal.
(3) Distinguish between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system on the basis of the effect they have on:
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Heart beat
Increases
Decreases
Urinary Bladder
Relaxes and stores urine
Contracts causing micturition
(4) While holding a tea cup Mr. Kothari’s hands rattle. Which disorder he may be suffering from and what is the reason for this?
(5) List the properties of the nerve fibres.
(6) How does tongue detect the sensation of taste?
(7) State the site of production and function of Secretin, Gastrin and Cholecystokinin
(i) Secretin : (ii) Gastrin : (iii) Cholecystokinin :
(8) An adult patient suffers from low heartrate, low metabolic rate and low body temperature. He also lacks alertness, intelligence and initiative. What can be this disease? What can be its cause and care?
(9) Where is the pituitary gland located? Enlist the hormones secreted by anterior pituitary.
It secretes following hormones :
(10) Explain how the adrenal medulla and sympathetic nervous system function as a closely integrated system.
(11) Name the secretion of alpha, beta and delta cells of islets of langerhans. Explain their role.
(i) Alpha cells : (ii) Beta cells : (iii) Delta cells :
(12) Which are the 2 types of goitre? What are their causes?
Goitre is the enlargement of thyroid gland. It is easily visible at the base of neck when a person is suffering from it. Goitre is of two types.
(13) Name the ovarian hormone and give their functions.
Ovaries produce following hormones :
Question 6. Answer the following.
(1) Complete the table.
| Location | Cell Type | Function |
| PNS | Produce myelin sheath | |
| PNS | Satellite cells | |
| Oligodendrocytes | Form myelin sheath around
central axon |
|
| CNS | Phagocytose pathogens | |
| CNS | Form the epithelial lining of brain cavities and central canal. |
Location
Cell Type
Function
PNS
Schwann cells
Produce myelin sheath
PNS
Satellite cells
Supply nutrients to surrounding neurons, protect and cushion nearby neurons.
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath around central axon
CNS
Microglia
Phagocytose pathogens
CNS
Ependyma cells
Form the epithelial lining of brain cavities and central canal.
Question 7. Long answer questions.
(1) Explain the process of conduction of nerve impulses upto development of action potential
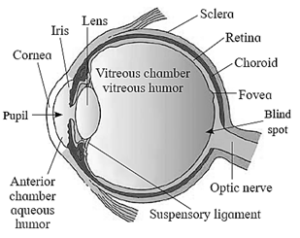
(2) Draw the neat labelled diagrams of.
(a) Human ear
(b) Sectional view of human eye
(c) L. S. of human brain
(d) Multipolar Neuron
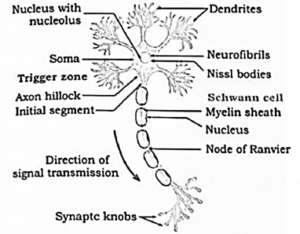
(3) Answer the questions after observing the diagram given below.

(a) What do the synaptic vesicles contain?
Synaptic vesicles contain a neurotransmitter — acetyl choline.
(b) What process is used to release the neurotransmitter?
Exocytosis.
(c) What should be the reason for the next impulse to be conducted?
Removal of neurotransmitter by the action of acetyl cholinesterase.
(d) Will the impulse be carried by postsynaptic membrane carried even if one pre-synaptic neuron is there?
Yes. As far as impulse is transmitted by pre-synaptic neuron, it will be received by post-synaptic neuron.
(e) Can you name the channel responsible for their transmission?
Ca++ channel is responsible for their transmission
(4) Explain the Reflex Pathway with the help of a neat labelled diagram.
Reflex action : Reflex action is defined as a quick, automatic involuntary and often unconscious action brought about when the receptors are stimulated by external or internal stimuli. Reflex arc : Reflex actions are controlled by CNS. Reflex arc is the structural or functional unit of reflex action. Simple reflex arc is formed of the following five components.
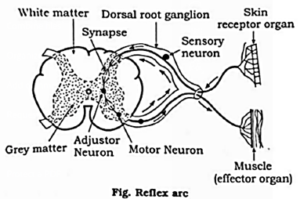
(5) Krishna was going to school and on the way he saw a major bus accident. His heart beat increased and hands and feet become cold. Name the part of the nervous system that had a role to play in this reaction.
(6) What will be the effect of thyroid gland atrophy on the human body?
(7) Write the names of hormones and the glands secreting them for the regulation of following functions.
(a) Growth of thyroid and secretion of thyroxine.
TSH by adenohypophysis
(b) Helps in relaxing pubic ligaments to facilitate easy birth of young ones.
Relaxin by degenerating corpus luteum of the ovary.
(c) Stimulate intestinal glands to secrete interstinal juice.
Secretin by duodenal mucosa
(d) Controls calcium level in the blood
Calcitonin [hypocalcemic hormone] by thyroid and parathormone [hypcrcalcemic hormone] by parathyroid glands.
(e) Controls tubular absorption of water in kidneys.
ADH by hypothalamus
(f) Urinary elimination of water.
Atrial natriuretlc factor by atria of heart.
(g) Sodium and potassium ion metabolism.
Aldosterone by adrenal cortex
(h) Basal Metabolic rate.
T3 and T4 by thyroid gland.
(i) Uterine contraction.
Oxytocin by hypothalamus.
(j) Heart beat and blood pressure.
Adrenaline. non-adrenaline [stimulation] and acctylcholine [inhibition] by adrenal medulla.
(k) Secretion of growth hormone.
GHRF by hypothalamus.
(l) Maturation of Graafian follicle.
FSH by anterior pituitary.
(8) Explain the role of hypothalamus and pituitary as a coordinated unit in maintaining homeostasis?
Following are the releasing and inhibiting factors produced by hypothalamus :
(9) What is adenohypophysis? Name the homones secreted by it?
It secretes following hormones :
(10) Describe in brief, an account of disorders of adrenal gland.
Disorders of adrenal cortical secretions are caused due to hyporsecretion and hypersecretion of adrenal corcoid harmones. Hyposecretion of corticosteroids causes Addison's disease : Hypersecretion of corticoid Cushing's disease :
(11) Explain action of steroid hormones an proteinous hormones.
The hormones always act on their target organs or tissues to induce their effects. The target tissues have specific binding sites or receptor sites which contain hormone receptors. Steroid hormones : Protein hormones :
(12) Describe in brief an account of disorders of the thyroid.
Disorders of thyroid gland are of three types. viz. hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism and simple goitre.
Notes, Solutions, Text Book-PDF
PDF : Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-9-Control and Coordination-Text Book
PDF : Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-9-Control and Coordination- Notes
PDF : Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-9-Control and Coordination- Solution
PDF SET :
All Chapters Notes-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-130
All Chapters Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-128
All Chapters Notes+Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(30-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-240
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Biology – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-8-Respiration and Circulation– Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-10-Human Health and Diseases – Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.