Human Health and Diseases
Maharashtra Board-Class-12th-Biology-Chapter-10
Solutions
Question 1 Multiple Choice Questions
(1) Which of the following is NOT caused by unsterilized needles?
(a) Elephantiasis
(b) AIDS
(c) Malaria
(d) Hepatitis B
Answer :
(a) Elephantiasis
(2) Opium derivative is ..............
(a) Codeine
(b) Caffeine
(c) Heroin
(d) Psilocybin
Answer :
(c) Heroin
(3) The stimulant present in tea is .............
(a) tannin
(b) cocaine
(c) caffeine
(d) crack
Answer :
(c) caffeine
(4) Which of the following is caused by smoking?
(a) Liver cirrhosis
(b) Pulmonary tuberculosis
(c) Emphysema
(d) Malaria
Answer :
(c) Emphysema
(5) An antibody is ...............
(a) molecule that binds specifically an antigen
(b) WBC which invades bacteria
(c) secretion of mammalian RBC
(d) cellular component of blood
Answer :
(a) molecule that binds specifically an antigen
(6) The antiviral proteins released by a virus-infected cell are called ............
(a) histamines
(b) interferons
(c) pyrogens
(d) allergens
Answer :
(b) interferons
(7) Both B-cells and T-cells are derived from ....................
(a) lymph nodes
(b) thymus glands
(c) liver
(d) stem cells in bone marrow
Answer :
(b) thymus glands
(8) Which of the following diseases can be contracted by droplet infection?
(a) Malaria
(b) Chicken pox
(c) Pneumonia
(d) Rabies
Answer :
(c) Pneumonia
(9) Confirmatory test used for detecting HIV infection is .................
(a) ELISA
(b) Western blot
(c) Widal test
(d) Eastern blot
Answer :
(b) Western blot
(10) Elephantiasis is caused by ............
(a) W. bancrofti
(b) P. vivax
(c) Bedbug
(d) Elephant
Answer :
(a) W. bancrofti
(11) Innate immunity is provided by ...........
(a) phagocytes
(b) antibody
(c) T- Lymphocytes
(d) B- Lymphocytes
Answer :
(c) T- Lymphocytes
Question 2 Very Short Answer Questions
(1) What is the source of cocaine?
Answer :
Cocaine is an alkaloid obtained from coca plant- Erythroxylum coca.
(2) Name one disease caused by smoking?
Answer :
Emphysema. (Damaged and enlarged lungs causing breathlessness).
(3) Which cells stimulate B-cells to form antibodies?
Answer :
Helper T-cells stimulate B-cells to form antibodies
(4) What does the abbreviation AIDS stand for?
Answer :
AIDS stands for Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome.
(5) Name the causative agent of typhoid\ fever?
Answer :
Salmonella typhi
(6) What is Rh factor?
Answer :
Antigen ‘D’ present on the surface of RBCs is known as Rh factor.
(7) What is schizont?
Answer :
Schizont is a ring-like form produced from merozoites inside the erythrocytes of human beings, infected by Plasmodium, which again forms new merozoites.
(8) Name the addicting component found in tobacco.
Answer :
Nicotine
(9) Name the pathogen causing Malaria.
Answer :
Plasmodium vivax.
(10) Name the vector of Filariasis.
Answer :
Female Culex mosquito.
(11) Give the name of the causative agent of ringworm.
Answer :
Trichophyton.
(12) Define health.
Answer :
Health: Health is defined as the state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
Question 3 Short Answer Questions:
(1) What are acquired diseases?
Answer :
- Acquired diseases, developed after an individual's birth, are divided into communicable or infectious diseases and non-communicable or non-infectious diseases.
- Communicable diseases are transmitted directly or indirectly from infected individuals to healthy ones, caused by pathogens like viruses, bacteria, fungi, and helminth worms.
- Non-communicable or non-infectious diseases cannot be transmitted directly or indirectly.
(2) Differentiate between antigen and antibody.
Answer :
| Antigen | Antibody |
| Antigens are foreign proteins which are capable of producing infection. | Antibodies are immunoglobulins produced by the body to act against the antigens. |
| The structure of antigens is variable dependent upon the type of pathogen. | The structure of antibody is Y-shaped. |
| The antigen is the ‘non-self’ molecule. | The antibody is ‘self’ molecule. |
| The antigens have epitope sites which bind with the antibody molecule. | The antibodies have paratope sites which bind with the antigen molecule: |
(3) Name the infective stage of Plasmodium. Give any two symptoms of malaria.
Answer :
(a) Infective stage of Plasmodium : Sporozoite.
(b) Symptoms of malaria :
- (i) Cyclic occurrence of high fever followed by sweating and sudden shievering.
- (ii) Vomiting and convulsions.
(4) Explain the mode of infection and cause of elephantiasis.
Answer :
Mode of infection, i.e. transmission of elephantiasis :
- The parasite Wuchereria bancrofti is transmitted from a patient to other normal human being by female Culex mosquito.
- The filarial larvae leave mosquito body and arrive on the human skin where they penetrate the skin and enter inside.
- They undergo two moultings to become adults. Later they settle ln the lymphatic system. They incubate for about 8- 16 months.
- When they settle in lymphatic system, this infection is called lymphatic filariasis.
- The worms start infecting lymphatic circulation resulting into enlargement of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. The extremities like legs or limbs become swollen which resembles elephant legs.
- Therefore, it is called elephantiasis.
- This condition is lymphoedema, i.e. accumulation of lymph fluid in tissue causing swelling.
(5) Why is smoking a bad habit?
Answer :
Smoking: A Dangerous Habit.
- Inhalation of cigarette smoke contains nicotine, toxic substances, and carbon monoxide.
- It can lead to respiratory issues like asthma, hypertension, heart disease, stroke, and lung damage.
- Carcinogenic substances can cause cancer in larynx, trachea, lung, etc.
Smoking affects others due to passive smokers. - Mutagenic chemicals in smoke can cause ovaries mutations in women.
Therefore, smoking is a very bad habit.
(6) What do the abbreviations AIIMS and CMIS denote?
Answer :
- AMIS is Antibody-mediated immune system or humoral immunity
- CMIS is cell-mediated immune system.
(7) What is a carcinogen? Name one chemical carcinogen with its target tissue.
Answer :
(a) Carcinogen is the substance or agent that causes cancer.
(b) Urinary ‘bladder cancer caused by 2-naphthylamine and 4-aminobiphenyl.
(8) Distinguish between active immunity and passive immunity.
Answer :
| Active immunity | Passive immunity |
| Active immunity is produced in response to entry of pathogens and their antigenic stimuli. | Passive immunity is produced due to antibodies that are transferred to the body. |
| Active immunity is the long lasting immunity. | Passive immunity is short-lived immunity. |
| In active immunity, the body produces its own antibodies. | In passive immunity, antibodies are given to the body from outside. |
| Natural acquired active immunity is obtained due to infections by pathogens. | Passive immunity, acquired naturally, is derived from antibodies of the mother, which are transmitted to the baby through placenta or colostrum. |
| Artificial acquired active immunity is obtained through vaccinations. These vaccines contain dead or live but attenuated pathogens. | Artificial acquired passive immunity is obtained through vaccinations, which contain readymade antibodies prepared with the help of other animals like horses. |
Question 4 Short Answer Questions
(1) Differentiate between B-cells and T-cells.
Answer :
| B-cells | T-cells |
| B-cells are type of lymphocyte whose origin is in bone marrow but maturation is in blood. | T-cells are type of lymphocytes which originate in bone marrow but maturation occurs in thymus. |
| B-cells are type of lymphocytes which are Involved in humoral mediated immunity. | T-cells are type of lymphocytes which are involved in cell-mediated immunity. |
| 20% of lymphocytes present in the blood are B-cells. | 80% of lymphocytes present in the blood are T-cells. |
| Two types of B-cells are Memory cells and Plasma cells. | T-cells are of following subtypes : Cytotoxic T-cells, helper T-cells, suppressor T-cells. |
| They are involved in antibody mediated
immunity. (AMI) |
They are involved in cell-mediated immunity (CMI). |
| B-cells produced antibodies With which they fight against pathogens. | T-cells do not produce antibodies. |
| B-cells have membrane bound immunoglobulins located on the surface. | There is a presence of T cell receptors on the T-cell surface. |
(2) What are the symptoms of malaria? How does malaria spread?
Answer :
(a) Symptoms of malaria :
- Cyclical occurrence of sudden coldness followed by rigor and then fever and sweating lasting for four to six hours. This is called a classic symptom of malaria.
- Splenomegaly or enlarged spleen, severe headache, cerebral ischemia, hepatomegaly, i.e. enlarged liver, hypoglycaemia and haemoglobinuria with renal failure may occur in severe infections.
(b) Spread / Transmission of malaria :
- Malaria parasite is transmitted through the female Anopheles mosquito and hence it is known as mosquito-borne disease. Mosquito acts as a vector.
- There are four species of Plasmodium, viz., P. vivax, R. falciparum, R. ovale and P. malariae which transmit malaria.
(3) Write a short note on AIDS.
Answer :
- AIDS or the acquired immuno deficiency syndrome, is fatal viral disease caused by a retrovirus (ss RNA) known as the human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) which weakens the body’s immune system. It is called a modern pandemic.
- The HIV attacks the immune system which in turn causes many opportunistic infections, neurological disorders and unusual malignancies ultimately leading to death.
- It was first observed in the USA in 1981 and confirmed in India in 1986.
- HIV is transmitted through body fluids like saliva, tears, nervous system tissue, spinal fluid, blood, semen, vaginal fluid, and breast milk.
- Transmission occurs through sexual contact, blood and blood products, and contaminated syringes and needles.
(4) Give the symptoms of cancer.
Answer :
Symptoms of cancer :
- Presence of lump or tumour.
- White patches in the mouth.
- Change in a wart or mole on the skin.
- Swollen or enlarged lymph nodes.
- Vertigo, headaches or seizures if cancer affect the brain.
- Coughing and shortness of breath if lungs are affected due to cancer.
(5) Write a note on antigens on blood cells.
Answer :
- About 30 known antigens on the surface of human red blood cells determine blood group types, including ABO, Rh, Duffy, Kidd, Lewis, P. MNS, and Bombay.
- These blood groups are genetically determined by the presence of a specific antigen. Landsteiner identified two antigens, antigen A and antigen B, and another antigen, Antigen D, which determines the Rh status of the blood.
- These antigens are responsible for blood group types and specific transfusions.
- Non-compatible antigens and antibodies in the serum can cause agglutination reactions, so proper blood group checks are crucial during transfusions.
(6) Write a note on antigens-antibody complex.
Answer :
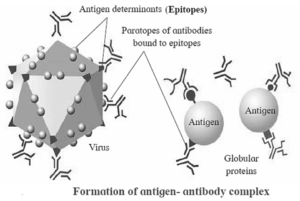
- Antigen and antibody have specificity, with each antibody binding to a specific antigen.
- Antigens have antigenic determinants or epitopes, which react with antibodies' paratopes.
- Antigen binding sites are on variable regions, with small variations, making each antibody highly specific.
- This allows the antibody to recognize the specific antigen, forming an antigen-antibody complex.
- The variable regions allow the antibody to bind to the specific antigen in a lock and key manner.
(7) What are the various public health measures, which you would suggest as safeguard against infectious diseases?
Answer :
- Infectious diseases spread through pathogens, making it crucial to reduce the risk of infection.
- This can be achieved by washing hands frequently, especially when in contact with food and water. Handwashing before, during, and after food preparation, eating, and toilet use is essential.
- Vaccinations are essential for protection against many diseases, especially during epidemics. It is essential to stay at home if symptoms of an infection appear, as going out can infect other healthy individuals.
- Proper diet and exercise can improve immunity.
- Hygiene should be maintained in kitchens and dining areas, especially when eating uncovered or leftover food.
- Daily cleaning of bathrooms and toilets is essential due to high concentrations of bacteria.
- Responsible sexual behavior is essential to avoid sexually transmitted diseases. Sharing personal items like toothbrushes, combs, towels, undergarments, or razor blades is not recommended.
- Traveling should be avoided to avoid infecting others and aggravate illness.
- Special immunizations may be necessary during certain travels, such as the anti-cholera vaccine for Pandharpur during Ashadhi.
(8) How does the transmission of each of the following diseases take place?
(a) Amoebiasis
Answer :
Amoebiasis is usually transmitted by the following ways :
- The faecal-oral route.
- Through contact with dirty hands or objects.
- Ry anal-oral1 contact.
- Through contaminated food and water.
(b) Malaria
Answer :
- Malaria parasite is transmitted through the female Anopheles mosquito and hence it is known as mosquito-borne disease. Mosquito acts as a vector.
- There are four species of Plasmodium, viz., P. vivax, R. falciparum, R. ovale and P. malariae which transmit malaria.
(c) Ascariasis
Answer :
- Unsafe and unhygienic food and drinks contaminated with the eggs of Ascaris are the main mode of transmission.
- Eggs hatch inside the intestine of the new host.
- The larvae pass through various organs and settle as adults in the digestive system.
(d) Pneumonia
Answer :
- Pneumonia usually spreads by direct person to person contact.
- It is also spread via droplet infection, i.e. droplets released by infected person.
- Using clothes and utensils of the patient.
(9) What measure would you take to prevent water-borne diseases?
Answer :
- To prevent water-borne diseases, use safe, clean, and potable water. Filter, boil, and store in covered containers.
- Install water purifier systems at home if possible.
- Ideally, use bottled water or carry your own container while traveling.
- Maintain personal hygiene and clean containers near water storage.
- Megacities offer chlorinated and purified water for citizens. But villages and smaller rural set ups use river water which may be highly contaminated with pathogens. Such water should be purified before consumption to prevent water-borne diseases.
(10) Write a short note on typhoid.
Answer :
Typhoid is an infective disease caused by Salmonella typhi, a Gram-ve bacterium found in the intestinal lumen of infected individuals. The bacterium's "O"-antigen and "H"-antigen on its surface coat make it pathogenic.
Signs and Symptoms of typhoid are as follows :
- Prolonged and high fever with nausea, fatigue, headache.
- Abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhoea.
- In severe cases rose-coloured rash is seen on skin. Tongue shows white coating and
- there is cough. Anorexia or loss of appetite is seen. In chronic cases there is
- breathlessness, irregular heartbeats and haemorrhage.
Poor hygiene habits and poor sanitation and insects like houseflies and cockroaches
spread typhoid. Typhoid is diagnosed by Widal test.
Antibiotics like Chloromycetin can cure typhoid. Preventive vaccines such as oral
Ty21a vaccine and injectable typhim vi and typherix against typhoid are also available. Chronic cases need surgical removal of gall bladder.
Question 5 Match the following
| Column I | Column I |
| AIDS | Antibody production |
| Lysozyme | Activation of B-cells |
| B-cells | Immunoglobulin |
| T-helper cells | Tears |
| Antibody | Immuno deficiency |
Answer :
| Column I | Column I |
| AIDS | Immuno deficiency |
| Lysozyme | Tears |
| B-cells | Antibody production |
| T-helper cells | Activation of B-cells |
| Antibody | Immunoglobulin |
Question 6 Long Answer Questions
(1) Describe the structure of antibody.
Answer :

- Antibodies are glycoproteins produced by plasma cells, which are formed by B-lymphocytes.
- They are highly specific to specific antigens and are 'Y'-shaped with four polypeptide chains.
- Disulfide bonds hold the chains together, creating a 'Y'-shaped structure.
- The hinge region holds the arms and stem of the antibody, while each chain has two distinct regions: the variable region and the constant region.
- Variable regions have a paratope, an antigen-binding site, which recognizes and binds to the specific antigen, forming an antigen-antibody complex.
- Antibodies are bivalent, carrying two antigen binding sites.
(2) Write a note on Vaccination.
Answer :
- Vaccines are prepared from inactivated pathogens, proteins, sugars, dead forms, toxoids, or attenuated pathogens.
- They are administered to protect against specific pathogens, teaching the immune system to recognize and eliminate pathogenic organisms.
- The body's antibodies are formed in response to the vaccine, preparing it for potential attacks.
- Vaccination is a primary prevention method that reduces illness risks by protecting people by exposing pathogens in a safe form.
- It controls the spread of diseases like measles, polio, tetanus, and whooping cough, which once threatened many lives.
- Vaccination also controls epidemic outbreaks, with some hazardous diseases like smallpox and polio completely eradicated by vaccination.
(3) What is cancer? Differentiate between bening tumor and malignant tumor. Name the main five types of cancer.
Answer :
(a) Cancer: Cancer is a disease caused by uncontrolled cell division due to disturbed
cell cycle.
(b) Bening tumor and malignant tumor :
| Bening tumor | Malignant tumor |
| Benign tumour is localized and it does not spread to neighbouring areas. | Malignant tumour starts as local but spreads rapidly to neighbouring areas. |
| Benign tumour is enclosed in connective tissue sheath. | Malignant tumour is not enclosed in connective tissue sheath. |
| Benign tumour compresses the surrounding normal tissue. | Malignant tumour invades and destroys the surrounding tissue. |
| Benign tumours can be removed surgically. | Malignant tumours need further treatment after removal. |
| Except for brain tumour, benign tumours are usually not fatal. | Malignant tumours are fatal. |
| Benign tumours do not show metastasis. | Malignant tumours show metastasis. |
| Benign tumours are well differentiated. | Malignant tumours are poorly differentiated. |
| Benign tumours show slow and progressive growth. | Malignant tumours show rapid and erratic growth. |
(c) Types of Cancer :
According to the tissue affected, the cancers are classified into five main types. These are as follows :
- Carcinoma : Cancer of epithelial tissue covering or lining the body organs is known as carcinoma. E.g. breast cancer, lung cancer, cancer of stomach, skin cancer, etc.
- Sarcoma: Cancer of connective tissue is called sarcoma. Following are the types of sarcoma : osteosarcoma (bone cancer), myosarcoma (muscle cancer), chondrosarcoma (cancer of cartilage) and liposarcoma (cancer of adipose tissue).
- Lymphoma: Cancer of lymphatic tissue is called lymphoma. Lymphatic nodes, spleen and tissues of immune system are affected due to lymphoma.
- Leukaemia : Leukaemia is blood cancer. In this condition, excessive formation of leucocytes take place in the bone marrow. There are millions of abnormal immature leucocytes which cannot fight infections. Monocytic leukaemia, lymphoblastic leukaemia, etc. are the types of leukaemia.
- Adenocarcinoma : Cancer of glandular tissues such as thyroid, pituitary, adrenal, etc. is called adenocarcinoma.
(4) Describe the different type of immunity.
Answer :
There are two basic types of immunity, viz. innate immunity and acquired immunity.
Innate immunity :
- Innate immunity is natural, inborn immunity, which helps the body to fight against the invasion of microorganisms.
- Innate immunity is non-specific because it does not depend on previous exposure to foreign substances.
- Innate immunity mechanisms consist of various types of barriers such as anatomical barriers, physiological barriers, phagocytic barriers and inflammatory barriers. They prevent entry of foreign agents into the body.
Acquired immunity :
- The immunity that an individual acquires during his life is called acquired immunity or adaptive immunity or specific immunity.
- It helps the body to adapt by fighting against specific antigens hence it is called adaptive immunity. Since it is produced specifically against an antigen, it is called specific immunity.
- Acquired immunity takes long time for its activation.
- This type of immunity is seen only in
(5) Describe the ill –effects of alcoholism on health.
Answer :
- Alcohol is toxic and can cause liver detoxification, affecting the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and causing inflammation, ulceration, and painful conditions.
- High doses can induce a comatose condition. Alcoholics also experience hypertension and cardiac problems, and can cause cirrhosis.
- They may also experience numbness in their cerebrum, making it difficult to think.
- Social health is significantly impacted, as alcoholics can cause problems to family, friends, and society.
- Alcohol's worst effects include liver damage, hypertension, and cardiac problems.
(6) In your view, what motivates the youngsters to take to alcohol or drugs and how can this be avoided?
Answer :
- Addiction of drugs or alcohol among youngsters is often due to insufficient parental supervision, excessive pressure, lack of communication, poorly defined family rules, continuous family conflicts, and favorable parental attitudes towards alcohol and drug use.
- These factors can lead to a lack of planning for the future, exposure to harmful habits at home, and the inability to cope with the present, ultimately leading to addiction and risk-taking behavior among youngsters.
(7) Do you think that friends can influence one to take alcohol/drugs? If yes, how may one protect himself/herself from such an influence?
Answer :
- Friends can influence a person to take alcohol and drugs if they are timid and non-communicative with their parents and teachers. This influence depends on the individual's personality and can occur in the adolescent age. The confusion in the mind and role of hormones in the psyche and thought process makes it difficult to understand the hazards of such habits. Additionally, curiosity about experimentation due to bad media influences can also contribute to this behavior.
- If there is complete trust and friendship with sensible parents, such influence may not work. To protect oneself, one should denial and communicate incidents to an elder who can confide in them. It is important to inform friends about the ill-effects of alcohol and drugs and make them aware of these aspects.
- In conclusion, friends can influence a person to take alcohol and drugs if they are timid and non-communicative with their parents and teachers. The influence of friends on a person's behavior is influenced by various factors, including the individual's personality, the confusion in the mind and the role of hormones in the psyche and thought process, and the curiosity to experiment with these substances due to the negative influence of media. Trust and friendship with sensible parents are crucial for preventing such influence.
Notes, Solutions, Text Book-PDF
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-10-Human Health and Diseases-Text Book
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-10-Human Health and Diseases- Notes
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-10-Human Health and Diseases- Solution
PDF SET :
All Chapters Notes-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-130
All Chapters Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-128
All Chapters Notes+Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(30-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-240
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Biology – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-9-Control and Coordination– Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter 11-Enhancement of Food production – Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.