Reproduction in Lower & Higher Plants
Maharashtra Board-Class-12th-Biology-Chapter-1
Notes-Part-1
|
Topics to be Learn : Part-1
|
Reproduction : Reproduction is production of young ones like parents.
Essential Process related to continuity of species.
To maintain continuity of life, organisms produce offspring showing similar characters.
Two types of reproduction —
- Asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction :
- Asexual reproduction does not involve fusion of two compatible gametes or sex cells.
- Production of genetically identical progeny, i.e. Clones.
- Progeny from single organism.
- Inheritance of genes of parent by progeny.
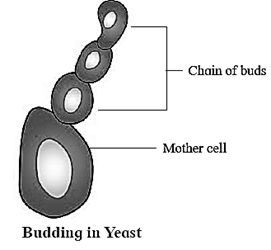
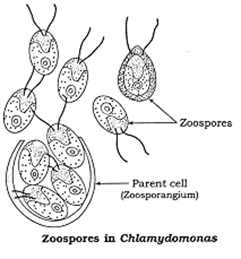
Modes of Asexual Reproduction : 1-Fragmentation : Fragmentation: It is a type of asexual reproduction observed in lower plants, e.g. algae. Multicellular organisms break into small pieces called fragments which develop into new plant. These fragments are formed due to different reasons like accidental breakdown, death and decay of cells, etc. 2-Budding : Budding in plants is an artificial method of propagation in which a single bud is joined or grafted on the stock plant. It is a type of asexual reproduction. 3-Spore formation : It is of very common occurrence in lower plants. 4-Fission 5-Conidia formation 6-Gemmule formation
Vegetative reproduction : The plants reproduce asexually from their vegetative plant parts and thus new plants formed are genetically similar to their parents.
- It is very useful in agriculture and horticulture.
- Artificial methods like cutting and grafting are useful for propagation of desired varieties as per human needs.
Artificial methods of vegetative reproduction : In artificial method cutting and grafting are two methods used to propagate desired varieties of plants- (1) Cutting : small pieces of plant parts having one or more buds are selected for propagation, e.g, Stem cutting - Rose, Root, Cutting—Blackberry and Leaf cutting- Sansevieria (2) Grafting (3) Tissue Culture
Sexual Reproduction : It involves fusion of two compatible gametes and thus it results in production of genetically dissimilar offspring.
- Variations are set in, which are important from point of view of survival and evolution of species.
- Takes place after certain maturity.
- In higher plants, flowering indicates beginning of reproductive phase
Flowers : Flower is a specialized reproductive structure which produces haploid gametes and ensures that act of fertilization will take place. 1) Accessory whorls: 2) Essential whorls :

Sexual reproduction - Two major events : Meiosis : Production of gametes (n) Fusion of gametes (Fertilization) ->Diploid zygote -> Embryo -> New plant—(2n) sporophyte Diploid sporophyte is dominant plant body —> Meiosis -> Haploid spores-> gametophyte-> Reduced structure -> Wlthin flowe-> garnetes
Structure of anther - Mature anther : An immature stage of anther is represented
by group of parenchymatous tissue surrounded by single layered epidermis.
- Usually dithecous (Having two lobes) —> tetrasporangiate (Having four pollen sacs)
- Monothecous (Having single lobe) -> Bisporangiate (Having two pollen sacs)
- When young it is homogeneous.
- Parenchymatous with epidermis.
- Heterogeneity appears with formation of archesporial cell.
T. S. of anther (Transverse section of anther) : Internally it shows four chambers called microsporangia or pollen sacs. The anther consists of two main parts, viz., anther wall and microsporangium or pollen sac. The wall of the anther can be differentiated into four layers. viz., epidermis, endothecium, middle layers and tapetum.

Microsporogenesis : Process of formation of Microspores by meiosis from MMC (Microspore Mother Cell). Each microspore mother cell divides meiotically to form tetrad of haploid microspores (pollen grains).
- Pollen grain — Non-motile with single nucleus, Haploid
- Pollen wall, double layered - Sporoderm
Structure of microspore : Typical pollen grain is a non-motile, haploid, unicellular body with single nucleus. It is surrounded by a two layered wall called sporoderm. Exine (outer layer) : Intine (inner wall layer): The inner wall layer, intine consists of cellulose and pectin. Forms pollen Tube smooth.
Pollen Viability: It is a functional ability of pollen grain to form male gametophyte by its germination.
- Viable pollen grains germinate on stigmatic surface,
- Environmental factors mainly temperature and humidity influence its germination.
- Viability is low up to 30 minutes in plants like rice and wheat.
- Duration of viability is up to months in some plants of family Leguminosae, Rosaceae and Solanaceae.
Development of male gametophyte :. It is considerably reduced. Develops in flower. First mitotic division —> Two unequal cells ->(i) Vegetative cell (ii)Generative cell. Second mitotic division -> In generative cell ->equal cells. 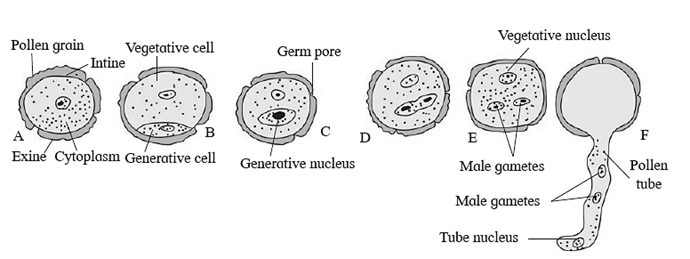
Structure of Anatropous ovule (Most common type) : The ovule which has a bent axis and downwardly directed micropyle is called anatropous ovule.
It is the most common type of ovule in angiosperms.
The matured anatropous ovule consists of two parts, viz., the stalk and the body.
Ovules are present in ovary.
- Uniovulate — Mango, Wheat, Rice.
- Multiovulate — Tomato, Lady's finger
Parts of ovule :

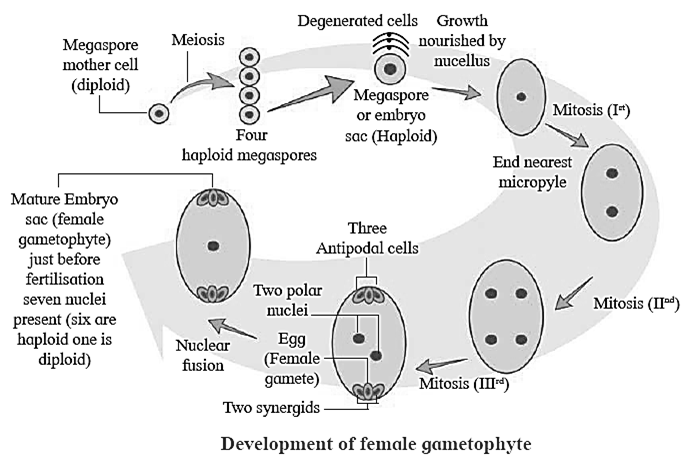
Megasporogenesis : The process by which the diploid megaspore mother cell of nucellus undergoes meiosis to form a tetrad of haploid megaspores is known as megasporogenesis.
Development of female gametophyte : Generally, the chalazal megaspore becomes the functional megaspore. The other three megaspores degenerate. In the meantime, one nucleus from each pole called polar nucleus moves towards the centre of the embryo sac and fuse to form a diploid nucleus called secondary nucleus. The female gametophyte consists of an egg apparatus, a secondary nucleus and three antipodal cells, A seven celled 8 nucleated structure.
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Biology – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Download : Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-1-Reproduction in Lower & Higher Plants–Text Book
Next Chapter :Chapter-2-Reproduction in Lower & Higher Animals – Online Notes
👍