Chapter-5-Origin and Evolution of Life
Maharashtra Board-Class-12th-Biology-Chapter-5
Notes-Part-1
Topics to be learn in Part-2 :
|
Hardy-Weinberg’s principle :
- Hardy and Weinberg were two scientists who proposed a concept of genetic equilibrium popularly known as Hardy-Weinberg principle or equilibrium.
- This principle states that gene, allele or genotype frequencies remain the same from generation to generation unless disturbed by factors like mutation, non-random mating, genetic drift, etc.
- For explaining the concept of equilibrium they assumed that there are two alleles located at a single locus (A and a).
- Their respective frequencies are p and q.
- The frequency of genotype AA is p, for 2Aa is 2pq and for aa is q.
- The equilibrium equation is p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
- It says that if sum total of gene frequencies is 1, then sum total of genotype frequencies is also equal to 1. When the equilibrium is disturbed then only evolution occurs.
Adaptive radiation :
- Adaptive radiation is the process of evolution which results in transformation of original species to many different varieties.
- The well-known example of adaptive radiation is Darwin’s Finches. When Charles
- Darwin went on his voyage to Galapagos, islands, he noticed finches which is a variety of small birds.
- According to Darwin’s observations, the American main land species of finches was the original one which must have migrated to the different islands of Galapagos.
- Since environmental conditions here were different, they adapted in various ways to the differing environmental conditions of these islands.
- Original bird had a beak suited for eating seeds, but the changed feeding pattern has changed the shape of beaks too. Some birds also show altered beaks for insectivorous mode. Thus, this demonstrated adaptive radiation.
- Adaptive radiation in Australian Marsupials is also Well studied. In Australia, there are many marsupial mammals who evolved from common ancestor.
- Adaptive radiation leads to divergent evolution.
Evidences of organic evolution :
The theory of organic evolution states that the present day complex organisms have originated from earlier simpler forms of life.
The process of evolution is supported by evidences provided by various branches of biology such as : Palaeontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular biology.
(i) Palaeontology : The study of ancient life with help of fossils is called palaeontology.
- The study of fossils provides the most convincing and direct evidence of evolution.
- Fossils are formed in sedimentary rocks, amber (yellowish fossils resin), ice, peat bogs etc.
- During fossilization, the primitive forms of organisms occupy the older, lower layers and the advanced forms occupy the upper, more recent layers of the earth.
Types of fossils : There are four main types of fossils : actual remains, moulds, casts and compressions.
Significance of Palaeontology :
- It is useful in reconstruction of phylogeny.
- It helps in studying various forms and structures of extinct animals.
- It provides record of missing link between two groups of organsims.
- It helps in the study of habits of extinct organisms.
A connecting link (missing link) : A connecting link is an intermediate or transitional state between two systematic groups of organisms.
(ii) Morphology (comparative anatomy) : Morphology deals with study of external structures while, anatomy deals with study of internal structures.
From comparative study of morphology and anatomy we can understand the evolutionary aspects in the form of homologous, analogous and vestigeal organs.
Homologous organs: Homologous organs are those organs which are structurally similar but functionally dissimilar. Examples: The structural similarities between the homologous organs indicate that they have a common ancestry. Different homologous organs indicate divergent evolution or adaptive radiation. Homologous organs help in tracing the phylogenetic relationships.
Analogous organs : Analogous organs are similar in function but dissimilar in structural details, They do not help to trace the relationship in the evolution but help to understand the convergent evolution. Structural modifications in the organs are due to similar habitat. Examples :
Vestigial organ : Examples of vestigial organs in human beings :
(iii)Embryological Evidences : Different vertebrates have similar development pattern.
(iv) Molecular Biological Evidences :
- Different organisms have basic similarities in their molecules constituents, and the cellular.
- All living organisms have the same basic structural and functional unit, i.e. cell.
- Cell organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, mitochondria, etc. are present in different types of organisms.
- Proteins and gene performing different functions have the same basic pattern which shows a common ancestry.
- Catabolic activities of liberating energy, synthesis of macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, etc. are similar in different organisms.
- ATP is the common energy currency of all the organisms.
- All the above facts are called molecular evidences in favour of evolution.
Speciation :
Speciation : The process of formation of a new species from the pre-existing species.
Species : A group of similar organisms that can interbreed and produce a fertile offspring in nature
Types of Speciation (i) Intraspecific Speciation : (a) Allopatric speciation : Allopatric speciation is the formation of a new species due to separation of a segment of population from the original population. (b) Synipatric speciation : Formation of species within single population without geographical isolation. (ii) Interspecific Speciation :
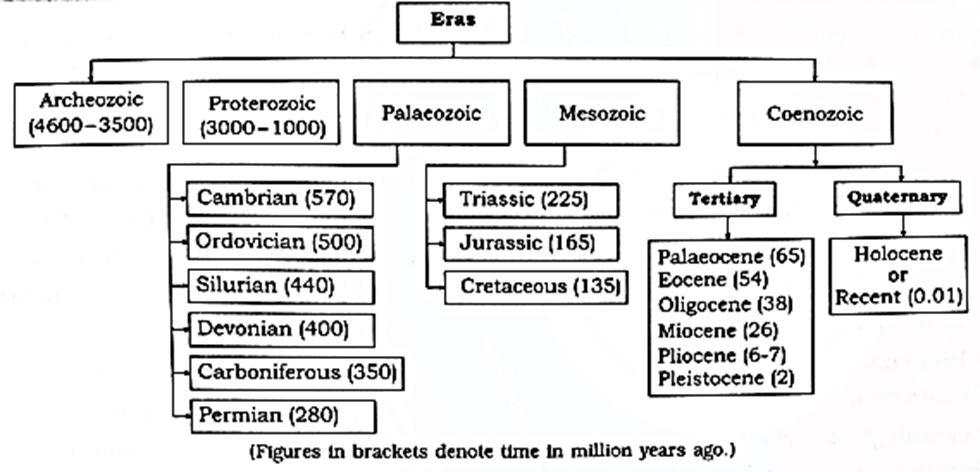
Geological time scale :
- Geological time scale is the arrangement of major divisions of geological time into eras, periods and epochs on the time scale.
- This division is based on the study of fossilized organisms obtained from the different strata of the earth.
- The characteristic significant events that occurred in the organization of organisms helped the geologists to understand the geological time scale.
- The major divisions of geological time are called eras.
- The eras are divided into periods and the periods into epochs.
- By studying fossils in the earth crust, the evolutionary changes in the organisms have been traced out.
Human Evolution :
Major changes in evolutionary development of man :
- Increase in size and complexity of brain and enhanced intelligence with increased cranial capacity.
- Bipedal locomotion, erect posture.
- Opposable thumb.
- Shortening of forelimbs and lengthening of hind limbs.
- Development of chin. Orthognathous face.
- Broadening of pelvic girdle, development of lumbar curvature.
- Articulated speech, art, development of tools, social and cultural development.
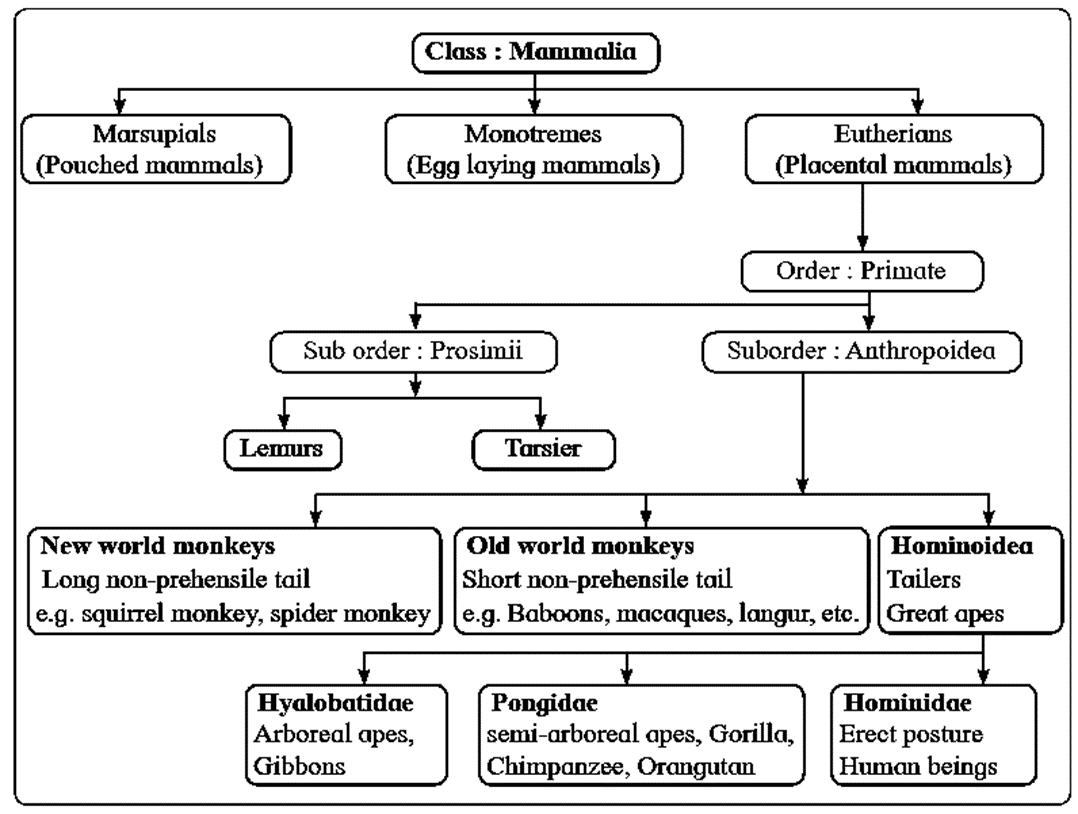
Classification of mammals :
Origin and evolution of human being :
Order Primates is divided into two sub-orders :
- Prosimii : Including lemurs, lorises and tarsiers
- Anthropoidea : Including New world monkeys—Ceboidea, Old world monkeys-Cercopithecoidea, Apes and Man - Hominoidea.
Hominoidea evolved in Miocene in three separate lines are shown as under :
- Hyalobatidae — Gibbons
- Pongidae — Gorilla, Chimpanzee and Orangutan
- Hominidae — Primates with human characteristics.
Palaeontological evidences of human evolution:
The available fossils are skulls, mandibles, teeth, bones like humerus, femur and stone implements.
Important stages in the origin of man :
- Ape like stage : Dryopithecus
- Men-like stage : Ramapithecus
- Connecting link between ape and man : Australopithecus.
- Handy man : Homo habilis
- Ape man : Homo erectus
- Advanced prehistoric man : Homo neanderthalensis (Neanderthal man)
- Modern man : Homo sapiens
Dryopithecus : Dryopithecus is also called proconsul.
Ramapithecus :
Australopithecus :
Homo habilis :
Homo erectus :
Neanderthal man :
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-5-Origin and Evolution of Life-Text Book
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-5-Origin and Evolution of Life- Notes
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-5-Origin and Evolution of Life- Solution
PDF SET :
All Chapters Notes-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-130
All Chapters Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-128
All Chapters Notes+Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(30-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-240
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Biology – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-4-Molecular Basis of Inheritance – Online Notes
Next Chapter : Chapter-6-Plant Water Relations – Online Notes
We reply to valid query.