Elements of Group 1 and 2
Maharashtra State Board-Class-11-Science-Chemistry-Chapter -8
Solutions
Question 1. Explain the following
(A) Hydrogen shows similarity with alkali metals as well as halogens.
(i) Hydrogen shows similarity with alkali metals :
- Hydrogen has electronic configuration 1s1 which is similar to outer electronic configuration of alkali metals, ns1.
- Both, hydrogen and Alkali metals form univalent positive ions (+1) by loss of 1 electron.
- Both combine with halogen to form halides.
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCI
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl.
(ii) Hydrogen show similarity with halogens :
- Halogens have outer electronic configuration ns2np5 which resembles that of hydrogen 1s1. Both by gaining one electron aquire the electronic configuration of nearest inert gas, ns2 (Hydrogen) ns2np6 (Halogens).
- Both form univalent negative ion (-1).
- Both react with metals.
2Na(s)+ H2(g) \(\underrightarrow{Δ}\) 2NaH(s)
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaC1
(B) Standard reduction potential of alkali metals have high negative values.
- The general outer electronic configuration of alkali metals is ns1.
- They readily lose one valence shell electron to achieve stable noble gas configuration and hence, they are highly electropositive and are good reducing agents.
Hence, standard reduction potentials of alkali metals have high negative values.
(C) Alkaline earth metals have low values of electronegativity; which decrease down the group.
- Electronegativity represents an attractive force exerted by the nucleus on shared electrons.
- Electronegativity of alkaline earth metals decrease down the group. In a group as atomic number increases, atomic radius increases. Nuclear attraction decreases. The tendency to attract shared pair of electron decreases down the group and hence electronegativity decreases.
(D) Sodium dissolves in liquid ammonia to form a solution which shows electrical conductivity.
Sodium dissolves in liquid ammonia forming an ammoniated electron or solvated electron.
Na → Na+ + e−
Na+ + xNH3 → [Na(NH3)x]+ and
e− + yNH3 → [e(NH3)y] −
Thus, these ions conduct electric current. Hence the solution shows electrical conductivity.
(E) BeCl2 is covalent while MgCl2 is ionic.
- Beryllium is present in 2nd period. It has a very small atomic size and high ionization enthalpy. Hence it does not form ion but form covalent BeCl2.
- Magnesium is in 3rd period. Magnesium due to its lower ionization enthalpy and bigger atomic size loses its valence electrons easily forming Mg2+
Hence, BeCl2 is covalent while MgCl2 is ionic.
(F) Lithium floats an water while sodium floats and catches fire when put in water.
All the alkali metals react with water to form corresponding hydroxides with the evolution of hydrogen.
2Na + 2H2O → 2Na+ + 2OH− + H2 ↑.
Li, Na and K float on water due to release of bubbles of hydrogen gas. The reactions of sodium and potassium are highly exothermic and catch fire.
Question 2. Write balanced chemical equations for the following.
(A) CO2 is passed into concentrated solution of NaCl, which is saturated with NH3.

(B) A 50% solution of sulphuric acid is subjected to electrolyte oxidation and the product is hydrolysed.
2HSO4- \(\underrightarrow{Electrolysis}\) H2S2Og + 2e- (at anode).
Hydrolysis of the product, peroxydisulphuric acid is
HO-SO2-O-O-SO2-OH + 2H2O → 2H2SO4 + H2O2.
(C) Magnesium is heated in air.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
(D) Beryllium oxide is treated separately with aqueous HCl and aqueous NaOH solutions.
BeO + 2HCl(aq) → BeCl2 + H2O
BeO + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2BeO2 + H2O.
Question 3. Answer the following questions
(A) Describe the diagonal relationship between Li and Mg with the help of two illustrative properties.
Due to diagonal relationship lithium shows similarities with magnesium.
(i) Both lithium and magnesium form monoxide and nitride when heated in air.
4Li + O2 \(\underrightarrow{Δ}\) 2Li2O; 6Li + N2 \(\underrightarrow{Δ}\) 2Li,N.
2Mg + O2 \(\underrightarrow{Δ}\) 2MgO; 3Mg + N2 \(\underrightarrow{Δ}\) Mg3N2.
(ii) Lithium carbonate and magnesium carbonate decompose on heating to form their monoxides
Li2CO3 Li2O + CO2
MgCO3 MgO + CO2.
(iii) Both, LiCl and MgCl2 crystallise from aqueous solutions as their hydrates. LiCl.2H2O and MgCl2.8H2O.
(B) Describe the industrial production of dihydrogen from steam. Also write the chemical reaction involved.
Three stages are involved in this industrial process of preparation of hydrogen.
Stage I : Reaction of steam on coke or hydrocarbon in the presence of nickel catalyst, at high temperature (1270 K) yields a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
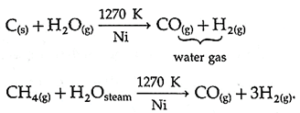
Stage II : Hydrogen is prepared from water gas by mixing it with steam and passing over iron chromate as catalyst (in a shift converter).
Carbon monoxide in the watergas is transformed into carbon dioxide liberating H2 gas. This is called water gas shift reaction.
Stage III : Carbon dioxide is removed by scrubbing with sodium arsenite solution.

(C) A water sample, which did not give lather with soap, was found to contain Ca(HCO3)2 and Mg(HCO3)2. Which chemical will make this water give lather with soap? Explain with the help of chemical reactions.
- Water sample containing Ca(HCO3)2 and Mg(HCO3)2 is hard water and does not give lather with soap.
- When sodium carbonate is added to this water, soluble sodium bicarbonate is formed and insoluble CaCO3 and MgCO3 precipitate out. Thus water becomes soft and gives lather with soap.
Ca(HCO3)2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) → CaCO3(s) + 2NaHCO3
Mg(HCO3)2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) → MgCO3 + 2NaHCO3
(D) Name the isotopes of hydrogen. Write their atomic composition schematically and explain which of these is radioactive ?
- Hydrogen has three isotopes i.e., hydrogen (), deuterium () and tritium () with mass numbers 1, 2 and 3
- They all contain one proton and one electron but different number of neutrons in the nucleus.
Atomic composition of isotopes of hydrogen:
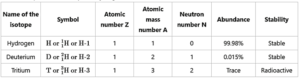
- Tritium is a radioactive nuclide with a half-life period of 12.4 years and emits low energy ß particles.
Question 4. Name the following
(A) Alkali metal with smallest atom.
Lithium Li
(B) The most abundant element in the universe.
Hydrogen.
(C) Radioactive alkali metal.
Radium
(D) Ions having high concentration in cell sap.
Potassium ion (K+).
(E) A compound having hydrogen, aluminium and lithium as its constituent elements.
Lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4)
Question 5. Choose the correct option.
(A) The unstable isotope of hydrogen is .....
(a) H-1
(b) H-2
(c) H-3
(d) H-4
(c) H-3
(B) Identify the odd one.
(a) Rb
(b) Ra
(c) Sr
(d) Be
(a) Rb
(C) Which of the following is Lewis acid ?
(a) BaCl2
(b) KCl
(c) BeCl2
(d) LiCl
(c) BeCl2
(D) What happens when crystalline Na2CO3 is heated ?
(a) releases CO2
(b) loses H2O
(c) decomposes into NaHCO3
(d) colour changes.
(b) loses H2O
PDF : Class-11-Chemistry-Chapter-8- Elements of Group 1 and 2- Notes
PDF : Class-11-Chemistry-Chapter-8- Elements of Group 1 and 2-Solution
All 16 Chapters Notes -11-Chemistry-(16 PDF) Rs.132
All 16 Chapters-Solutions-11-Chemistry- (16 PDF) Rs.128
All 16 Chapters-Notes+Solutions-11-Chemistry- (32 PDF) Rs.228
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 11th-Chemistry – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-7-Modern Periodic Table – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-9-Elements of Group 13, 14 and 15 – Online Solutions
We reply to valid query.