Basic Analytical Techniques
Class-11-Science-Chemistry-Chapter -3 Maharashtra State Board
Solutions
Question 1.
Choose the correct option
(A) Which of the following methods can be used to separate two compounds with different solubilities in the same solvent?
(a) Fractional crystallization
(b) Crystallization
(c) Distillation
(d) Solvent extraction
(a) Fractional crystallization
(B) Which of the following techniques is used for separation of glycerol from soap in soap industry ?
(a) Distillation under reduced pressure
(b) Fractional distillation
(c) Filtration
(d) Crystallization
(a) Distillation under reduced pressure
(C) Which technique is widely used in industry to separate components of mixture and also to purify them ?
(a) Steam distillation
(b) Chromatography
(c) Solvent extraction
(d) Filtration
(b) Chromatography
(D) A mixture of acetone and benzene can be seperated by the following method :
(a) Simple distillation
(b) Fractional distillation
(c) Distillation under reduced pressure
(a) Sublimation
(b) Fractional distillation
(E) Colourless components on chromatogram cannot be observed by the following :
(a) Using UV light
(b) Using iodine chamber
(c) Using the spraying reagent
(d) All of the above
(d) All of the above
Question 2.
Answer the following
(A) Which of the following techniques is used for purification of solid organic compounds?
(a) Crystallisation (b) Distillation
The technique of crystallization is used for the purification of solid organic compounds.
(B) What do you understand by the terms
(a) residue (b) filtrate.
Residue : The solid (insoluble part) that remains behind on the filter paper after filtration is called the residue. Filtrate : The liquid which passes through the filter paper and gets collected in the beaker is called the filtrate.
(C) Why is a condenser used in distillation process?
The condenser has a jacket with two outlets through which water is circulated. When the vapours of the liquid pass through the condenser, they get cooled and condense back into the liquid.
(D) Why is paper moistened before filtration?
A moistened filter paper sticks to the funnel preventing any solid from escaping from the sides of the funnel.
(E) What is the stationary phase in Paper Chromatography?
In paper chromatography, the water trapped in the fibres of the paper acts as the stationary phase.
(F) What will happen if the upper outlet of the condenser is connected to the tap instead of the lower outlet?
If when the upper outlet of the condenser is connected to the tap, the condenser will never be completely filled with water, due to which the vapours of the liquid passing through it will not be cooled efficiently. A completely filled condenser provides maximum cooling resulting in maximum recovery of the purified liquid.
(G) Give names of two materials used as stationary phase in chromatography.
The materials used as stationary phase in chromatography are alumina and silica gel.
(H) Which properties of solvents are useful for solvent extraction?
Properties of solvents for solvent extraction are :
(I) Why should spotting of mixture be done above the level of mobile phase ?
Spotting of mixture is done above the level of mobile phase to ensure that the solvent does not touch the spots before separation begins. If the solvent touches the spots in the beginning itself, it causes the spots to smear and become useless.
(J) Define :
(a) Stationary phase (b) Saturated solution.
(a) Stationary phase : The stationary phase is a solid or liquid supported on a solid which remains fixed in a place. The substances to be separated are selectively adsorbed or retained on the stationary phase. (b) Saturated solution : A saturated solution is a solution which cannot dissolve additional quantity of the solute.
(K) What is the difference between simple distillation and fractional distillation?
Simple distillation
Fractional distillation
Simple distillation can be used to separate a mixture of two miscible liquids with sufficiently large difference in their boiling points.
Fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture of two or more miscible liquids which do not differ much in their boiling points.
In Simple distillation process fractionating column not required.
Fractional distillation process requires a fractionating column fitted to the distillation flask.
Simple distillation is used to obtain distilled water.
Fractional distillation is used in the petroleum industry to separate different fractions of crude oil.
(L) Define
(a) Solvent extraction (b) Distillation.
(a) Solvent extraction : Solvent extraction is a method of separating compounds from a solution by shaking with an immiscible solvent on the basis of their solubility. (b) Distillation : Distillation is a process of heating a liquid to convert into vapour and then cooling the vapour to get back the liquid.
(M) List the properties of solvents which make them suitable for crystallization.
The solvent to be used for crystallization must have following properties :
(N) Name the different types of Chromatography and explain the principles underlying them.
Depending on the stationary phase chromatography is classified into two types : Adsorption chromatography is further classified into two types : Principle of adsorption chromatography : This type of chromatography is based on the principle of differential adsorption. Different solutes are adsorbed to different extent on the stationary phase depending upon their ability of adsorption. Principle of partition chromatography : In this type of chromatography, the separation of the components takes place by the continuous differential partitioning of the components between the stationary and mobile phase.
(O) Why do we see bands separating in column chromatography?
(P) How do you visualize colourless compounds after separation in TLC and Paper Chromatography?
Colourless compounds can be visualised by different ways :
(Q) Compare TLC and Paper Chromatography techniques.
are adsorbed to different extents on the stationary phase and are thus separated. mixture are separated depending upon their selective partitioning between the two phases. of plate as well as separation of components. preparation time as well as less time for separation of components.
TLC
Paper Chromatography
TLC is a type of Adsorption chromatography.
Paper chromatography is type of Partition chromatography.
The different components of the mixture
The different components of the
A thin layer of adsorbent silica gel or alumina spread over a glass plate is used for TLC. It is called chromplate.
A special type of paper called Whatman paper number 1 is used for paper chromatography. It is called chromatography paper.
The adsorbent silica gel or alumina acts as the stationary phase.
The water trapped in the fibres of the paper acts as the stationary phase.
The stationary phase is a solid, while the mobile phase is a liquid.
The stationary phase and mobile phase both are liquids.
TLC requires more time for preparation
Paper chromatography requires less
Question 3.
Label the diagram and explain the process in your words.
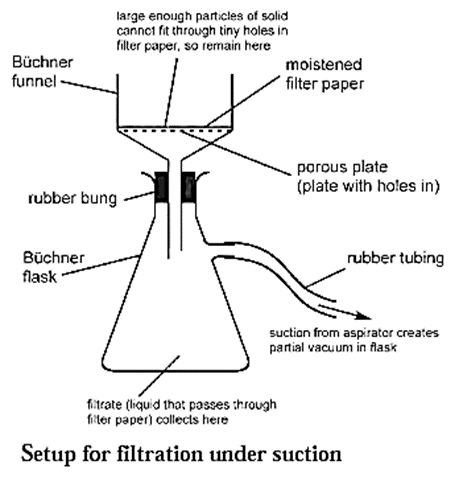
Filtration under suction : When filtration is carried out using a vacuum pump it is called filtration under suction. It is a faster and more efficient technique than simple filtration. Process for filtration under suction :
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 11th-Chemistry – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-2-Introduction to Analytical Chemistry – – Online Solution
Next Chapter : Chapter-4-Structure of Atoms – Online Solution
We reply to valid query.