Question 1.
Choose correct option
(A) Which one of the following will grow better in moist and shady region?
(a) Opuntia
(b) Orchid
(c) Mangrove
(d) Lotus
(B) A particular plant had a pair of leaves at each node arranged in one plane. What is the arrangement called?
(a) Alternate phyllotaxy
(b) Decussate phyllotaxy
(c) Superposed phyllotaxy
(b) Whorled phyllotaxy
Answer :
(c) Superposed phyllotaxy
[collapse]
(C) In a particular flower the insertion of floral whorls was in such a manner, so the ovary was below other three whorls, but its stigma was taller than other three whorls. What will you call such flower?
(a) Hypogynous
(b) Perigynous
(c) Inferior ovary
(d) Half superior - half inferior
Answer :
(c) Inferior ovary
[collapse]
(D) Beet and Arum both store food for perennation. Are the examples for two different types?
(a) Beet is a stem but Arum is a root
(b) Beet is a root but Arum is a stem
(c) Beet is a stem but Arum is a leaf
(d) Beet is a stem but Arum is an inflorescence
Answer :
(b) Beet is a root but Arum is a stem
[collapse]
Question 2.
Answer the following questions
(A) Two of the vegetables we consume are nothing but leaf bases. Which are they?
(B) Opuntia has spines but Carissa has thorns. What is the difference?
Answer :
- In Opuntia, stem is modified into leaf like photosynthetic organ known as phylloclade.
- Spines growing on phylloclade of Opuntia are leaves, modified to reduce the loss of water through
- transpiration.
- Thorns in Carissa are modified apical buds. They provide protection against browsing animals.
- Thus, spines in Opuntia and thorns in Carissa have different origin and function.
[collapse]
(C) Teacher described Hibiscus as solitary Cyme. What it means?
Answer :
- In Cymose inflorescence, growth of peduncle is finite and it terminates into flower.
- In Hibiscus, flower is borne singly at the tip of peduncle.
Hence, teacher described Hibiscus as solitary cyme.
[collapse]
Question 3.
Write notes on
(A) Fusiform root.
Answer :
Fusiform root is the modification of tap root for food storage
The fusiform root is swollen in the middle and tapering towards both ends forming spindle shaped structure e.g. Radish (Raphanus sativus)
[collapse]
(B) Racemose inflorescence
Answer :
Racemose :
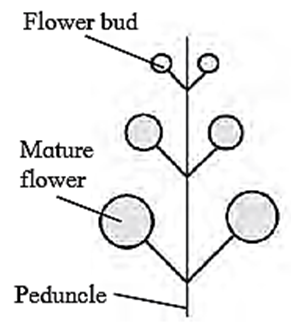
- Growth of peduncle is infinite or unlimited.
- Apical bud never terminates into flower,
- Flowers are arranged in acropetal succession (i.e, younger flower at the apex and older at the base).
- Opening of flowers is centripetal (younger flowers towards the centre and open later while older towards Periphery and open first).
- E.g. Gold mohur, Sunflower.
[collapse]
(C) Fasciculated tuberous roots
Answer :
Fasciculated tuberous root:
- Fasciculated tuberous roots are modification of adventitious roots for storage of food
- Fasciculated tuberous roots do not develop any definite shape like modified tap roots
- A cluster of roots arising from one point which becomes thick and fleshy due to storage of food is known as fasciculated tuberous root.
- These clusters are seen at the base of the stem.
- e.g. Dahlia, Asparagus, etc.
[collapse]
(D) Region of cell maturation
Answer :
Region of maturation/region of differentiation:
- It is the uppermost major part of the root.
- The cells of this region are quite impermeable to water due to thick wall. The cells show differentiation and form different types of tissues.
- This region helps in fixation of plant and conduction of absorbed substances.
- Development of lateral roots also takes place from this region.
[collapse]
(E) Rhizome
Answer :
- Rhizome is a modification of underground stem for storage of food.
- It is prostrate, dorsiventrally thickened and brownish in colour.
- It grows either horizontally or obliquely beneath the soil
- Rhizome shows nodes and internodes. It bears terminal and axillary buds at nodes.
- Terminal bud under favourable conditions produces aerial shoot which degenerates at the end of favourable condition.
- Growth of rhizome takes place with lateral buds, such growth is known as sympodial growth. e.g. Ginger (Zingiber officinale), Turmeric (Curcuma domesrica), Canna etc.
- In plants where rhizomes grow obliquely, temiinal bud brings about growth of rhizomes. This is known as monopodial growth. e.g. Nymphea, Nelumbo (Lotus), Preris (Fem) etc.
- Rhizomes perform functions like storage of food, vegetative propagation and perennation.
[collapse]
(F) Stolon
Answer :
Stolons :
- The slender lateral branch arising from the base of main axis is known as stolon.
- In some plants it is above ground (wild strawberry).
- Primarily stolon shows upward growth in the form of ordinary branch, but when it bends and touches the ground terminal bud grows into new shoot and develops adventitious roots.
- E.g. Wild Strawberry, Jasmine, Mentha, etc.
[collapse]
(G) Leaf venation
Answer :
Leaf venation: ‘
Arrangement of veins and veinlets in leaf lamina is known as venation.
- Veins are responsible for conduction of water and minerals as well as food.
- The structural framework of the lamina is developed by veins.
- There are two types of leaf venation: parallel venation which is found in monocot leaves and reticulate venation which is found in dicot leaves.
[collapse]
(H) Cymose inflorescence
Answer :
Cymose :

- Growth of peduncle is finite or limited.
- Apical bud always terminates into flower.
- Flowers are arranged in basipetal succession (i.e. older flowers at the apex and younger at the base).
- Opening of flower is centrifugal (older flowers at the centre and open first while younger towards periphery and open later)
- E.g. China rose, Jasmine
[collapse]
(I) Perianth
Answer :
Perianth (P):
- Many times, calyx and corolla remain undifferentiated. Such member is known as tepal.
- The whorl of tepals is known as Perianth.
- It protects other floral whorls.
- If all the tepals are free the condition is called as polyphyllous and if they are fused the condition is called as gamophyllous.
- Sepaloid perianth shows green tepals, while petaloid perianth shows brightly coloured tepals. e.g. Lily, Amaranthus, Celasia, etc.
- Petaloid tepal helps in pollination and sepaloid tepals can perform photosynthesis.
[collapse]
(J) Vexillary aestivation
Answer :
Vexillary: Corolla is butterfly shaped and consists of five petals. Outermost and largest is known as standard or vexillum, two lateral petals are wings and two smaller fused forming boat shaped structures keel. e.g. Pisum sativum
[collapse]
(K) Axile placentation
Answer :
Axile: Ovules are placed on the central axis of a multilocular ovary. e.g. China rose, Cotton, etc.
[collapse]
Question 4.
Identify the following figures and write down the types of leaves arrangement
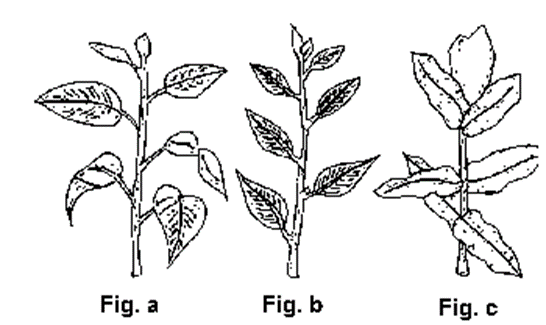
Answer :
The given figures represent phyllotaxy. It is the arrangement of leaves on the stem and branches in a specific manner.
Figure ‘a’ and ‘b’ represents, alternate phyllotaxy. In this type of phyllotaxy, single leaf arises from each node of a stem. e.g. Mango.
Figure ‘c’ represents opposite decussate phyllotaxy. In this type of phyllotaxy, a pair of leaf arise from each node and the consecutive pair at right angle to the previous one. e.g. Calotropis. . '
[collapse]
Question 5.
Students were on the excursion to a botanical garden. They noted following observation. Will you be able to help them in understanding those conditions?
(A) A wiry outgrowth was seen on a plant arising from in between the leaf and stem.
Answer :
A wiry outgrowth on a plant arising from in between the leaf and stem can be an axillary stem tendril.
- Tendrils are thin, wiry, photosynthetic, leafless coiled structures.
- They give additional support to developing plant.
- Tendrils have adhesive glands for fixation.
[collapse]
(B) There was a green plant with flat stem, but no leaves. The entire plant was covered by soft spines.
Answer :
Student must have observed phylloclade, which is a modification of stem.
Phylloclade:
- Modification of stem into leaf like photosynthetic organ is known as phylloclade.
- Being stem it possesses nodes and internodes.
- It is thick, fleshy and succulent, contains mucilage for retaining water e.g. Opuntia, Casuarina (‘Cylindrical shaped phylloclade) and Muehlenbeckia (ribbon like phylloclade).
[collapse]
(C) Many obliquely produced roots were given out from the lower nodes, apparently for extra support.
Answer :
Students must have observed adventitious roots in monocotyledonous plants like maize, sugarcane, wheat, etc.
- Adventitious roots develop from any part of a plant other than radicle.
- In such plants, adventitious roots arise from the lower node of a stem and provide extra support to the plant. These roots are also called as stilt roots.
[collapse]
(D) Many plants in the marshy region had upwardly growing roots. They could be better seen during low tide.
Answer :
Plants growing in marshy region (halophytes) produce upwardly growing roots called as pneumatophores or respiratory roots.
- The main root system of these plants does not get sufficient air for respiration as soil is waterlogged. Due to this, mineral absorption of plant also gets affected.
- To overcome this problem underground roots, develop special roots which are negatively geotropic, growing vertically upward.
- These roots are conical projections present around main trunk of plant.
- Respiratory roots show presence of lenticels which helps in gaseous exchange.
[collapse]
(E) A plant had leaves with long leaf apex, which was curling around a support.
Answer :
Students must have observed leaf tip tendril.
- In some weak stems, leaf apex modifies into thin, green, wiry, coiled structure called as leaf tendril
- Such leaf tendrils, help in climbing by curling around a support.
[collapse]
(F) A plant was found growing on other plant. Teacher said it is not a parasite. It exhibited two types of roots.
Answer :
Student must have observed an epiphytic plants like Dendrobium, Vanda growing on other plant.
The two types of roots exhibited by this plant must be clinging roots and epiphytic roots.
Clinging roots:
- Clinging roots are tiny roots develop along internodes, show disc at tips.
- It exudes sticky substance which enables plant to get attached to the substratum without damaging it.
Epiphytic roots:
- Epiphytic plants like Vanda, Dendrobium grow on branches of trees in dense rain forests and are unable to obtain moisture from soil.
- Such plants produce epiphytic roots which hang in the air;
- The roots are provided with a spongy membranous absorbent covering of the velamen tissue.
- The cells of velamen tissue are hygroscopic and have porous walls, thus they can absorb moisture from air.
- Epiphytic roots can be silvery white or green and are without root cap.
[collapse]
(G) While having lunch onion slices were served to them. Teacher asked which part of the plant are you eating ?
Answer :
- The edible part of an onion is fleshy leaves.
- Onion is a bulb, in which stem is highly reduced, discoid and possesses adventitious roots at the base.
- This stem bears a whorl of fleshy leaves which store food material.
- The scale leaves or fleshy leaves -are arranged in concentric manner over the stem. Some outer scale leaves become thin and dry. Thus, it is also called as tunicated or layered bulb.
[collapse]
(H) Students observed large leaves of coconut and small leaves of Mimosa. Teacher asked it what way they are similar?
Answer :
- Both large leaves of coconut and small leaves of Mimosa show pinnately compound leaves.
- In both plants, leaf lamina is divided into number of leaflets.
- Leaflets are present laterally on a commen axis called rachis, which are the midrib of the leaf
[collapse]
(I) Teacher showed them Marigold flower and said it is not one flower. What the teacher meant?
Answer :
- Marigold flower is an inflorescence in which flowers are produced in a definite manner on a peduncle.
- In Marigold, racemose type of inflorescence can be observed.
- In this, peduncle condenses to form a flat rounded structure called receptacle.
- Opening of flower centripetal i.e. younger flowers are towards the centre and open later, while older flowers towards the periphery and open first.
[collapse]
(J) Students cut open a Papaya fruit and found all the seeds attached to the sides. Teacher inquired about the possible placentation of Papaya ovary.
Answer :
- In Papaya, seeds are attached to the sides of a fruit. Thus, parietal placentation is possible in papaya ovary.
- In parietal placentation, ovules are placed on the inner wall of unilocular ovary of multicarpellary syncarpus gynoecium.
[collapse]
Question 6.
Match the following
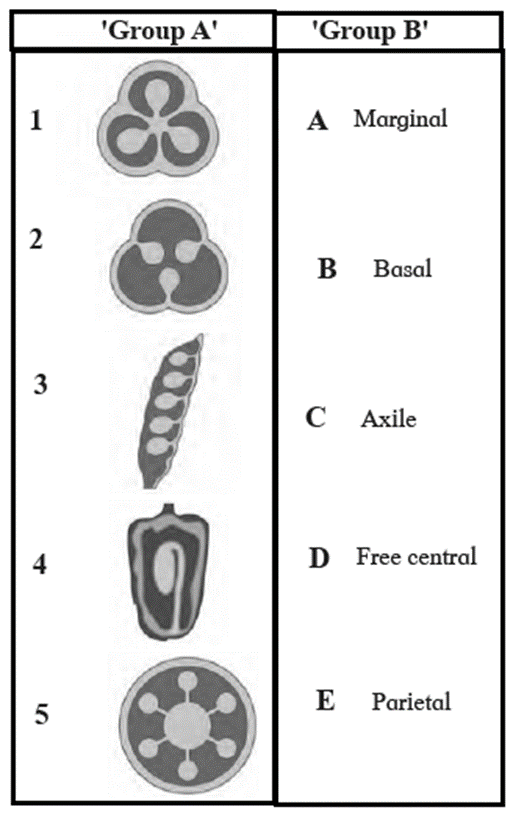
Answer :
(1-C), (2-E), (3-A), (4-B), (5-D)
[collapse]
Question 7.
Observe the following figures and label the different parts
Answer :
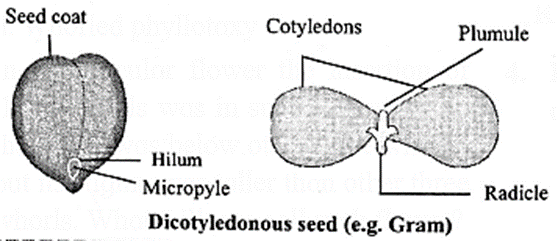
[collapse]
Question 8.
Differentiate with diagrammatic representation.
(A) Racemose and cymose infloresance
Answer :
| Racemose infloresance |
Cymose infloresance |
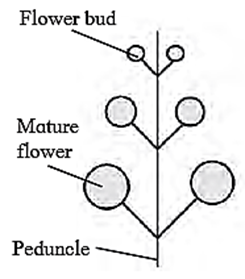 |
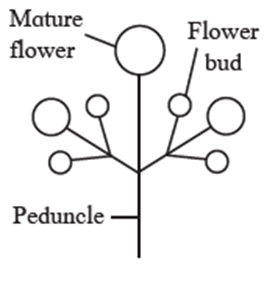 |
| Growth of peduncle is infinite or unlimited |
Growth of peduncle is finite or limited. |
| Apical bud never terminates into flower, |
Apical bud always terminates into flower. |
| Flowers are arranged in acropetal succession (i.e, younger flower at the apex and older at the base). |
Flowers are arranged in basipetal succession (i.e. older flowers at the apex and younger at the base). |
| Opening of flowers is centripetal (younger flowers towards the centre and open later while older towards Periphery and open first). |
Opening of flower is centrifugal (older flowers at the centre and open first while younger towards periphery and open later) |
| E.g. Gold mohur, Sunflower |
E.g. China rose, Jasmine |
[collapse]
(B) Reticulate and parallel venation
Answer :
(a) Reticulate venation :
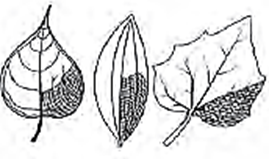
- In reticulate venation, veins and veinlets form a network.
- It is found in dicotyledonous plants
- E.g. Mango, Peepal, etc.
(b) Parallel venation :

- In parallel venation, veins run almost parallel to one another.
- It is found in monocotyledonous plants
- E.g. Banana, Grasses, etc.
[collapse]
(C) Tap root and Adventitious roots
Answer :
| Tap root |
Adventitious roots |
 |
 |
| It arises from radicle of an embryo during seed germination |
It arises from any pan other than radicle |
| It is differentiated into primary, secondary and teritary roots |
There is no such differentiation |
| The main root is very thick as compared to others. |
All roots are generally fibrous. |
| Tap root system is commonly seen in dicotyledonous plants. |
It is usually found in monocotvledons
|
| E.g. Pea, Bean, Sunflower etc. |
Maize, Wheat, Sugarcane, etc. |
[collapse]












We reply to valid query.