Cell Divisions
Maharashtra Board-Class-11-Science-Biology-Chapter-7
Solution
Question 1.
Choose correct option
(A) The connecting link between Meiosis-I and Meiosis-II is ...............
a. interphase-I b. interphase-II
c. interkinesis d. anaphase-I
(c) interkinesis
(B) Synapsis is pairing of .............
a. any two chromosomes
b. non-homologous chromosomes
c. sister chromatids
d. homologous chromosomes
(d) homologous chromosomes
(C) Spindle apparatus is formed during which stage of mitosis?
a. Prophase. b. Metaphase.
c. Anaphase. d. Telophase.
(b) Metaphase.
(D) Chromosome number of a cell is almost doubled up during ...............
a. G1-phase b. S-phase
c. G2-phase d. G0-phase
(b) S-phase
(E) How many meiotic divisions are necessary for formation of 80 sperms?
a. 80 b. 40 c. 20 d. 10
(c) 20
(F) How many chromatides are present in anaphase-I of meiosis-I of a diploid cell having 20 chromosomes?
a. 4 b. 6 c. 20 d. 40
(d) 40
(G) In which of the following phase of mitosis chromosomes are arranged at equatorial plane?
a. Prophase b. Metaphase
c. Anaphase d. Telophase
(b) Metaphase
(H) Find incorrect statement -
a. Condensation of chromatin material occurs in prophase.
b. Daughter chromatids are formed in anaphase.
c. Daughter nuclei are formed at metaphase.
d. Nuclear membrane reappears in telophase.
(c) Daughter nuclei are formed at metaphase.
(I) Histone proteins are synthesized during ......
a. G1 phase b. S-phase
c. G2 phase d. Interphase
(b) S-phase
Question 2.
Answer the following questions
(A) While observing a slide, student observed many cells with nuclei. But some of the nuclei were bigger as compared to others but their nuclear membrane was not so clear. Teacher inferred it as one of the phase in the cell division. Which phase may be inferred by teacher?
Prophase
(B) Students prepared a slide of onion root tip. There were many cells seen under microscope. There was a cell with two groups of chromosomes at opposite ends of the cell. This cell is in which phase of mitosis?
Anaphase
(C) Students were shown some slides of cancerous cells. Teacher made a comment as if there would have been a control at one of its cell cycle phase, there wouldn’t have been a condition like this. Which phase the teacher was referring to?
The phase teacher was referring would be G1 phase. [Note: Cells actively control only three checkpoints in the cycle. These checkpoints (G1/S, G2/M, the Spindle checkpoint) allow the cell cycle to be delayed or halted when necessary. ]
(D) Some Mendelian hybridization experimental results were shown to the students. Teacher informed that there are two genes located on the same chromosome. He enquired if they will be ever separated from each other?
(E) Students were observing a film on Paramoecium. It underwent a process of reproduction. Teacher said it is due to cell division. But students objected and said that there was no disappearance of nuclear membrane and no spindle formation, how can it be cell division? Can you clarify?
(F) Is the meiosis responsible for evolution? Justify your answer.
(G) Why mitosis and meiosis-II are called as homotypic division?
(H) Write the significance of mitosis.
(I) Enlist the different stages of prophase-I.
Prophase -I: Leptotene : Zygotene : Pachytene: Diplotene : Diakinesis :
Question 3.
Draw labelled digrams and write explanation
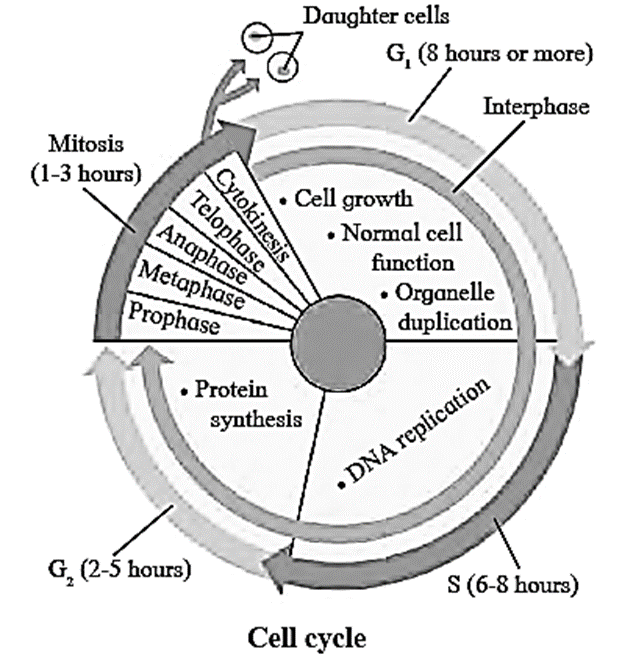
(A) With the help of suitable diagram, describe the cell cycle.
Cell cycle : Click here to View Figure-1
Interphase: It is the stage between two successive cell divisions. It is the longest phase of a cell cycle during which the cell is highly active and prepares itself for cell division. The interphase is subdivided into three sub-phases as G1-phase, S-phase and G2-phase. G1- phase (First gap period/First Gap Phase): S - phase (Synthesis phase): G2- phase (Second growth phase/Second Gap Phase):
(B) Distinguish between mitosis and meiosis.
Difference Between mitosis and meiosis : 2-In this nucleus divides only once. 3-In these two daughter cells are formed. 4-Daughter cells formed by mitotic division are diploid (2n). 5-Mitosis plays an important role in growth, repair, healing and development. 2-In this nucleus divides twice (Meiosis I and Meiosis II). 3-In these four daughter cells are formed. 4-Daughter cells formed by meiotic division are haploid 5-Meiosis 1s important for formation of haploid gametes and spores.
Mitosis
Meiosis
1-It occurs in somatic cells and stem cells.
1-It occurs in germ cells.
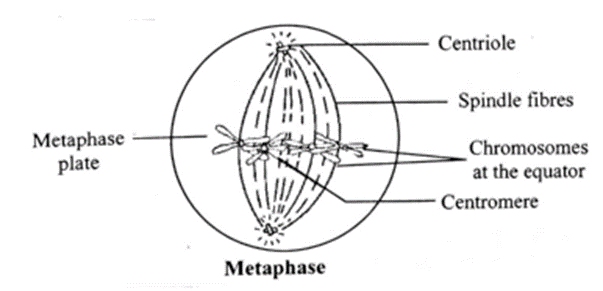
(C) Draw the diagram of metaphase.
Metaphase : Click here to View Figure-2
Question 4.
Match the following column-A with column-B
| Column-A
(phases) |
Column-B
(Their events) |
| a. Leptotene
b. Zygotene c. Pachytene d. Diplotene |
1. Crossing over
2. Desynapsis 3. Synapsis 4. Bouquet stage |
(phases) (Their events) b. Zygotene c. Pachytene d. Diplotene 3. Synapsis 1. Crossing over 2. Desynapsis
Column-A
Column-B
a. Leptotene
4. Bouquet stage
Question 5.
Is a given figure correct? why?

Question 6.
If an onion has 16 chromosomes in its leaf cell, how many chromosomes will be there in its root cell and pollen grain.
Question 7.
Identify the following phases of mitosis and label the 'A' and 'B' given in diagrams

A: Chromosomes arranged on metaphase plate. B: Chromatids moving to opposite poles
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 11th-Biology – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-6-Biomolecules – Online Solution
Next Chapter : Chapter-8-Plant Tissues and Anatomy – Online Solution
We reply to valid query.