Enhancement in Food Production
Maharashtra Board-Class-12th-Biology-Chapter-11
Notes-Part-3
Topics to be Learn : Part-3
|
Microbes in human welfare :
Biotechnology: It is defined as applications of ‘Scientific and Engineering principles for the processing of materials by biological agents to provide goods and service to humans or for human welfare’.
Application of microbes :
- Variety of microorganisms like algae, fungi, bacteria, viruses, protozoans, nematodes, etc. and their products are used for welfare of humans in regard to food, health, industry, agriculture, medicine, biocontrol, etc.
- These organisms are used variously in food and feed technology, industry, waste utilization, energy, etc.
Microbes in food preparation : Many food preparations made at home involves the use of microorganisms.
Role of Microbes in Industrial Production :
Production on an industrial scale requires growing microbes in very large vessels, called fermenters.
The main function of a fermenter is to provide a controlled environment for growth of a microorganism, or a defined mixture of microorganisms, to obtain the desired product
- During fermentation, variety of products like alcoholic beverages, organic acids, vitamins, growth hormones, enzymes, antibiotics, etc. are produced.
- They are secondary metabolites produced during idio phase and are not required for their growth.
- A specific secondary metabolite is produced depending on the type of microorganism and the type of substrate.
- Statins produced by yeast Monascus purpureus are blood cholesterol lowering agents. They are competitive inhibitors of the enzyme that catalyzes synthesis of cholesterol.
Production of Alcoholic Beverages :
Production of organic acids: Microbes are used in the production of a number of organic acids.
Production of vitamins : Vitamins : Organic nitrogenous compounds capable of performing many life-sustaining functions inside our body. The microbes are involved in the industrial production of vitamins like thiamine (vitamin B1), riboflavin (vitamin B2), pyridoxine, folic acid, pantothenic acid, biotin, vitamin B12, ascorbic acid (Vitamin C), beta-carotene (provitamin A) and ergosterol (provitamin D). Examples of some vitamins produced by fermentation using different microbial sources are :
Production of Antibiotics :
Some common antibiotics and their microbial sources are as follows :
Antibiotic produced
Microbial sources
Chloromycetin
Streptomyces venezuelae
Erythromycin
Streptomyces erythreus
Penicillin
Penicillium chrysogenum
Streptomycin
Streptomyces griseus
Griseofulvin
Penicillium griseofulvum
Bacitracin
Bacillus licheniformis
Oxytetracycline / Terramycin
Streptomyces aurifaciens
Production of Enzymes :
Enzymes play a key role in metabolic reactions, these are essential for the survival of living beings.
Enzymes : Enzymes are biocatalyst proteins which accelerate biochemical processes.
- Many microbes synthesize and excrete large quantities of enzymes into the surrounding medium. Using this feature of these tiny organisms, many enzymes are produced commercially. These enzymes are Amylase, Cellulase, Protease, Lipase, Pectinase, Streptokinase etc.
Uses of enzymes in various industries :
Name of the enzyme and Microbial source
Gibberellin production:
Gibberellin is a group of growth hormones mainly produced by higher plants and fungi to promote growth by stem elongation.
Applications of gibberellins are as follows :
Microbes in Sewage Treatment :
Sewage is the waste matter carried off on drainage.
Composition of sewage :
- Composition of sewage varies depending upon its industrial source. e.g. textile, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, dairy, canning, brewing, meat packing, tannery, oil refineries and meat industries, etc.
- Sewage consists of human excreta, animal dung, household waste, slaughter house waste, dissolved organic matter, algae, nematodes, pathogenic bacteria, viruses and protozoa, discharged waste water from hospitals, industries (contains toxic dissolved organic and inorganic chemicals), tannery and pharmaceutical waste, etc.
- Sewage consists of about water (99.5% to 99.9%) and inorganic and organic matter (0.1 to 0.5%) in suspended and soluble form.
Microorganisms in Sewage:
- It contains bacteria from soil and pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria, viruses and protozoa) causing dysentery, cholera, typhoid, polio and infectious hepatitis and soil bacteria.
- Bacteria in sewage include coliforms, fecal Streptococci, anaerobic spore forming Bacilli and other types originating in the intestinal tract of humans.
Sewage treatment : Before waste water is made available for human use, it has to be treated properly, so as to remove organic matter, inorganic salts and pathogens as well. Sewage treatment process includes four basic steps : Effluents from these digesters are released in natural water bodies like rivers and streams after chlorination which kills pathogenic bacteria. Digested sludge is then disposed.
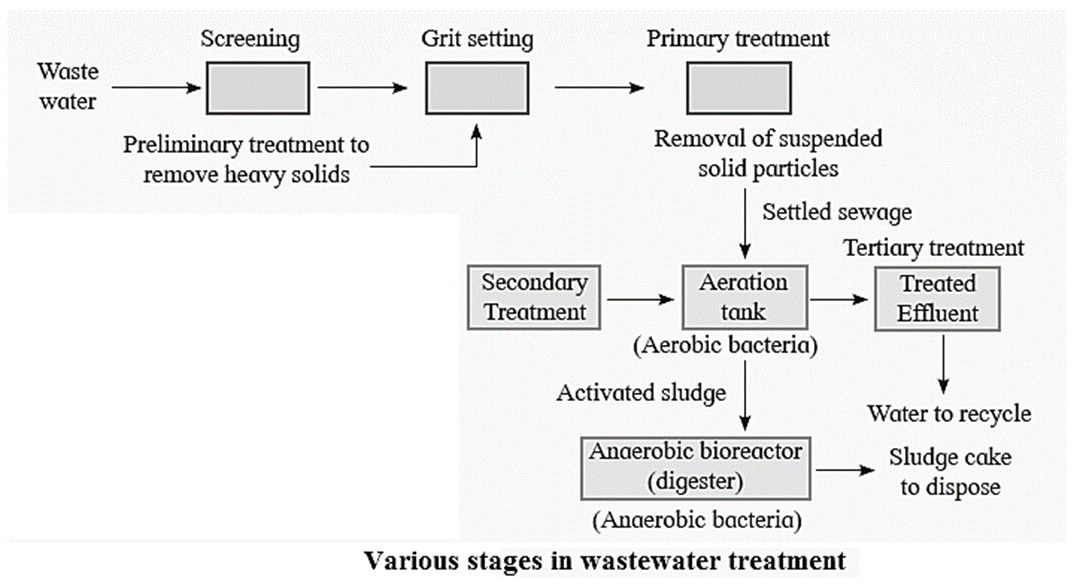
Microbes in Energy Generation :
- Biogas is used as a fuel for domestic as well as industrial purpose.
- It is a non-conventional and renewable source of energy and is obtained by microbial fermentation.
- Biogas is a mixture of methane CH4 (50-60%), CO2 (30-40%), H2S (0-3%) and other gases (CO, N2, H2) in traces.
- Biogas is highly inflamable and is used as a source of energy.
Substrates used for biogas production : Cattle dung (most commonly used substrate, a rich source of cellulose from plants), plant wastes, animal wastes, domestic wastes, agriculture waste, municipal wastes, forestry wastes, etc.
Biogas Production : Anaerobic digestion involves three processes : Hydrolysis or solublization, acidogenesis and methanogenesis. 12 mol CH3COOH —> 12CH4 + 12CO2 4 mol H.COOH —> CH4 + 3CO2 + 2H2O CO2 + 4H2 —> CH4 + 2H2O
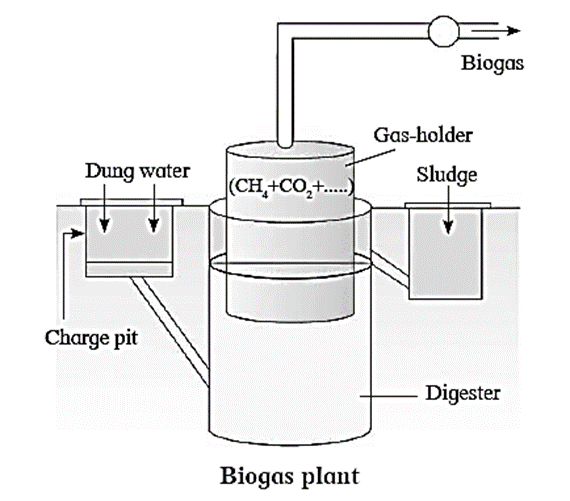
Benefits of biogas :
Role of Microbes as Biocontrol Agents:
The natural method of eliminating and controlling insects, pests and other diseasecausing agents, is by using their natural, biological enemies. This is called biocontrol or biological control.
Biocontrol agents : Microbes (bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoans) act as biocontrol agents in three ways : they cause the disease to the pest or compete or kill them.
Some examples of Microbial bio-control :
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) : It is used to get rid of butterfly, caterpillars.
- Trichoderma species : Effective bio-control agents against soil borne fungal plant pathogens.
Four groups of biocontrol agents are known. They are bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoans.
Microbial Pesticides and their host : The corelation is depicted as per the following table :
Pathogen
Host
Bacteria: Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), B. papilliae and B.lentimorbus
Caterpillars, cabbage worm, adult beetle,etc.
Fungi: Beavueria bassiana, Entomophthora. pallidaroseum, and Zoopthora radicans
Aphid crocci, A. unguiculata, mealy bugs, mites, white flies etc
Protozoans: Nosema lacustae
Grasshopper, caterpillars, crickets
Viruses: Nucleopolyhedrovirus (NPV) and Granulovirus (GV)
Caterpillars and Gypsy moth, ants, wasps and beetles.
Bioherbicides : They kill the weeds which compete with the main crop in the farm - land for water, space, minerals, light, air, etc. and also act as collateral hosts for several pathogens.
Pathogenic fungi as mycoherbicides :
- Phytophthora palmivora - controls milk weed in orchards.
- Alternaria crassa — controls water hyacinth.
- Fusarium spp. - control most of the weeds.
Bacterial pathogen as herbicides :
- Pseudgmonas spp. - attacks several weeds
- Xanthomonas spp. - attacks several weeds
- Agrobacterium spp. — attacks several weeds
Insects as herbicides :
- Tyrea moth — controls the weed Senecio jacobeac
- Cactoblastis cactorum — controls cacti weeds.
Role of Microbes as Biofertilizers:
Fertilizers are nutrients which are necessary for the growth of plants and thus for the productivity of cultivated plants. When they are applied to plants, in soil or in composting pits, soil fertility increases. Biofertilizers are cost effective and eco-friendly.
Classification of Biofertilizers :
- On the basis of nature or group of organisms, biofertilizers are classified as bacterial fertilizers and fungal fertilizers.
- On the basis of function, bacterial fertilizers are further grouped as nitrogen fixing, phosphate solubalizing and compost making biofertilizers.
- Cynobacterial biofertilizers, on the basis of function, are nitrogen fixing type.
- Fungal biofertilizers include mycorrhizal fungi. On the basis of function, they are classified as ectomycorrhizae and endomycorrhizae.
Bacterial biofertilizers : Nitrogen fixing bacterial biofertilizers: Phosphate solubilizing biofertilizers : Compost making biofertilizers : Cyanobacterial biofertilizers : Fungal biofertilizers : Mycorrhiza is a fungus which forms symbiotic association with the rhizomes and root of higher plants occurring in thick humid forests. Two types of mycorrhiza :
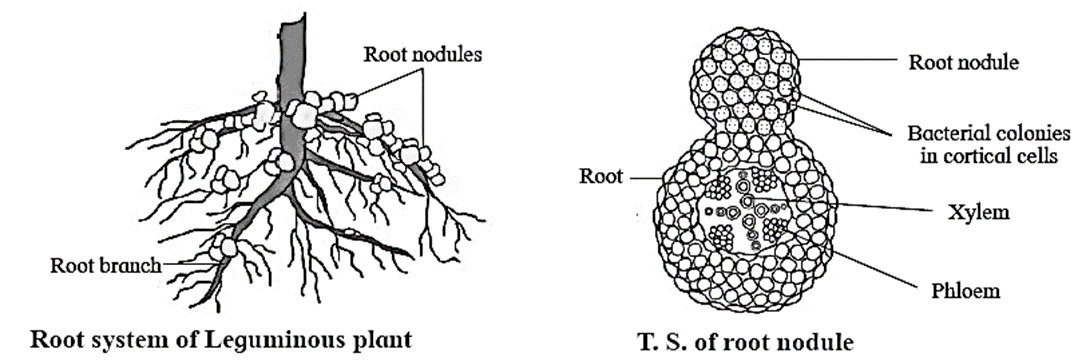
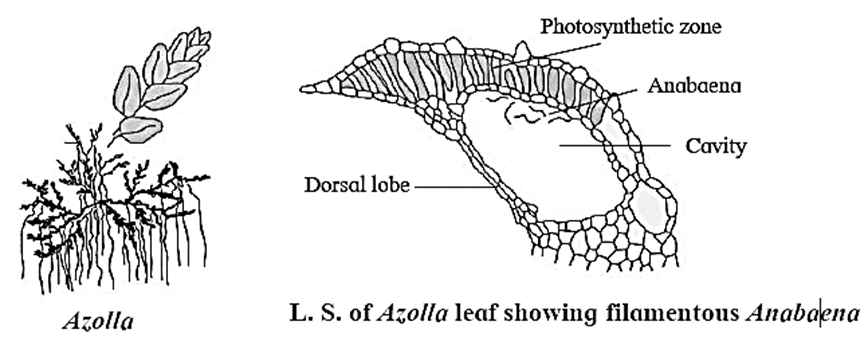
Benefits of Mycorrhiza :
Biofertilizer microorganisms :
- Rhizobia : Nitrogen fixing bacteria in root nodules of leguminous plants. e.g. R. leguminosarum is specific to pea and R. phaseoli is specific to beans.
- Azotobacter : Free living, nitrogen fixing bacterium associated with roots of grasses and certain plants.
- Azospirillum : Free living, aerobic nitrogen fixing bacterium associated with roots of corn, wheat and jowar.
- Anabaena : Filamentous nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria that forms symbiotic relationships with certain plants, such as the coralloid roots of Cycas and Anthoceros thallus. It has Heterocysts (Specialized colourless cells which are the sites for nitrogen fixation). It also fixes nitrogen in free living conditions.
- Azolla : A free-floating water fern. Anabaena present in the dorsal leaf lobe fixes nitrogen.
Benefits of Biofertilizers :
Notes, Solutions, Text Book-PDF
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-11-Enhancement in Food Production-Text Book
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-11-Enhancement in Food Production- Notes
Class 12th-Biology-Chapter-11-Enhancement in Food Production- Solution
PDF SET :
All Chapters Notes-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-130
All Chapters Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(15-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-128
All Chapters Notes+Solutions-Class-12-Biology-(30-PDF)-Maharashtra Board-Rs-240
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 12th-Biology – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-10-Human Health and Diseases– Online Notes
Next Chapter : Chapter-12-Biotechnology – Online Notes
We reply to valid query.